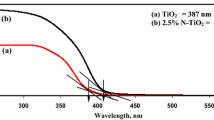
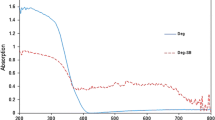
Abstract
Photocatalytic degradation of hydrolyzed reactive orange 16 (RO16) using titanium dioxide (TiO2) was analyzed in our study. The effects of various parameters, such as photocatalyst amount, RO16 concentration, light intensity, and temperature on photocatalytic degradation were investigated. Decolorization of hydrolyzed RO16 resulted in an decreasing of toxicity (EC50 = 76.54 ± 2.16). It was found that the decolorization efficiency was 87% after 20-min reaction and 100% after 80-min reaction. The total mineralization was 70% after 20 min and nearly 100% after 120 min, respectively. The results indicate that color degradation was faster than the decrease of total organic carbon. The photocatalytic degradation process was well described by first-order reaction. The final mineralization product was acetamide and the intermediate products were identified by gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterjee, D., Patnam, V. R., Sikdar, A., Joshi, P., Misra, R., & Rao, N. N. (2008). Kinetics of the decoloration of reactive dyes over visible light-irradiated semiconductor photocatalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156, 435–441. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.038.
Chen, D., & Ray, A. K. (1998). Photodegradation kinetics of 4-nitrophenol in TiO2 suspension. Water Research, 32, 3223–3234. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00118-3.
Chen, C. C., Fan, H. J., Jang, C. Y., Jan, J. L., Lin, H. D., & Lu, C. S. (2006). Photooxidative N-de-methylation of crystal violet dye in aqueous nano-TiO2 dispersions under visible light irradiation. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 184, 147–154. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.04.008.
Erdemoglu, S., Aksu, S. K., Sayilkan, F., Izgi, B., Asilturk, M., Sayilkan, H., et al. (2008). Photocatalytic degradation of Congo Red by hydrothermally synthesized nanocrystalline TiO2 and identification of degradation products by LC-MS. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155, 469–476. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.087.
Farah, J. Y., EI-Gendy, N. S., & Farahat, L. A. (2007). Biosorption of Astrazone Blue basic dye from an aqueous solution using dried biomass of Baker’s yeast. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 402–408. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.053.
Fernandez-Alba, A. R., Hernando, D., Aguera, J., Caceres, J., & Malato, S. (2002). Toxicity assays: A way for evaluating AOPs efficiency. Water Research, 36, 4255–4262. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00165-3.
González, A. S., & Martínez, S. S. (2008). Study of the sonophotocatalytic degradation of basic blue 9 industrial textile dye over slurry titanium dioxide and influencing factors. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15, 1038–1042. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.03.008.
Gottlieb, A., Shaw, C., Smith, A., Wheatley, A., & Forsythe, S. (2003). The toxicity of textile reactive azo dyes after hydrolysis and decolourisation. Journal of Biotechnology, 101, 49–56. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00302-4.
Habibi, M. H., & Talebian, N. (2007). Photocatalytic degradation of an azo dye X6G in water: A comparative study using nanostructured indium tin oxide and titanium oxide thin films. Dyes and Pigments, 73, 186–194. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.11.006.
He, Z., Song, S., Zhou, H., Ying, H., & Chen, J. (2007). C.I. Reactive black 5 decolorization by combined sonolysis and ozonation. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 14, 298–304. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.09.002.
Ioannis, K. K., & Triantafyllos, A. A. (2004). TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 49, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010.
Kansal, S. K., Singh, M., & Sud, D. (2007). Studies on photodegradation of two commercial dyes in aqueous phase using different photocatalysts. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 581–590. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.035.
Khodja, A. A., Sehili, T., Pihichowski, J. F., & Boule, P. (2001). Photocatalytic degradation of 2-phenylphenol on TiO2 and ZnO in aqueous suspensions. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 141, 231–239. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00423-3.
Konstantinou, I. K., & Albanis, T. A. (2004). TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: Kinetic and mechanistic investigations. A review. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 49, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010.
Kositzi, M., Poulios, I., Samara, K., Tsatsaroni, E., & Darakas, E. (2007). Photocatalytic oxidation of Cibacron Yellow LS-R. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 680–685. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.071.
Kritikos, D. E., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Psillakis, E., & Mantzavinos, D. (2007). Photocatalytic degradation of reactive black 5 in aqueous solutions: Effect of operating conditions and coupling with ultrasound irradiation. Water Research, 41, 2236–2246.
Ku, Y., Lee, Y. C., & Wang, W. Y. (2006). Photocatalytic decomposition of 2-chlorophenol in aqueous solution by UV/TiO2 process with applied external bias voltage. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 138, 350–356.
Kusvuran, E., Samil, A., Atanur, O. M., & Erbatur, O. (2005). Photocatalytic degradation of di- and tri-substituted phenolic compounds in aqueous solution by TiO2/UV. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 58, 211–216. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.11.023.
Lars, B. R., & Mallika, I. (1997). Photocatalytic decolourization of reactive azo dye: A comparison between TiO2 and us photocatalysis. Chemosphere, 35, 585–596. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00122-7.
Lee, J. W., Choi, S. P., Thiruvenkatachari, R., Shim, W. G., & Moon, H. (2006). Evaluation of the performance of adsorption and coagulation processes for the maximum removal of reactive dyes. Dyes and Pigments, 69, 196–203. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2005.03.008.
Mariana, N., Siminiceanu, I., Yediler, A., & Kettrup, A. (2002). Kinetics of decolorization and mineralization of reactive azo dyes in aqueous solution by UV/H2O2 oxidation. Dyes and Pigments, 53, 93–99. doi:10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00012-8.
Pekakis, P., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., & Mantzavinos, D. (2006). Treatment of textile dyehouse wastewater by photocatalysis. Water Research, 40, 1276–1286. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.01.019.
Poulios, I., & Tsachpinis, I. (1999). Photodegradation of the textile dye Reactive Black 5 in the presence of semiconducting oxides. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 74, 349–357. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199904)74:4<349::AID-JCTB5>3.0.CO;2-7.
Sharma, S., Pathak, S., & Sharma, K. P. (2003). Toxicity of the azo dye methyl red to the organisms in microsystems, with special reference to the guppy (Poecillia reticulate Peters). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70, 753–760. doi:10.1007/s00128-003-0047-8.
Shu, H. Y., Chang, M. C., & Fan, H. J. (2004). Decolorization of azo dye acid violet 1 by the UV/H2O2 process and optimization of operating parameters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B113, 201–208. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.06.007.
So, C. M., Cheng, M. Y., Yu, J. C., & Wong, P. K. (2002). Degradation of azo dye Procion Red MX-5B by photocatalytic oxidation. Chemosphere, 46, 905–912. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00153-9.
Walker, G. M., Hansen, L., Hanna, J. A., & Allen, S. J. (2003). Kinetics of reactive dye adsorption onto dolomitic sorbents. Water Research, 37, 2081–2089. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00540-7.
Wenhua, L., Hong, L., Suo’an, C., Jianqing, Z., & Chunan, C. (2000). Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of aniline in water over TiO2 supported on porous nickel. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 131, 125–132. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(99)00232-4.
Zee, F. P. V. D., & Villaverde, S. (2005). Combined anaerobic-aerobic treatment of azo dyes—A short review of bioreactor studies. Water Research, 39, 1425–1440. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.03.007.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Grant from the National Science Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CY. Photocatalytic Degradation of Azo Dye Reactive Orange 16 by TiO2 . Water Air Soil Pollut 202, 335–342 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9980-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9980-4