Abstract
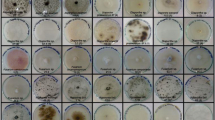
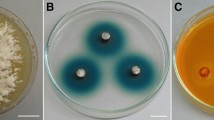
The production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by eleven basidiomycetes species isolated from two ecosystems of Georgia was investigated for the first time under submerged (SF) and solid-state fermentation (SSF) of lignocellulosic by-products. Notable intergeneric and intrageneric differences were revealed with regard to the extent of hydrolase and oxidase activity. Several fungi produced laccase along with hydrolases in parallel with growth during the trophophase, showing that the synthesis of this enzyme is not connected with secondary metabolism. The lignocellulosic substrate type had the greatest impact on enzyme secretion. Some of the substrates significantly stimulated lignocellulolytic enzyme synthesis without supplementation of the culture medium with specific inducers. Exceptionally high carboxymethyl cellulase (CMCase, 122 U ml−1) and xylanase (195 U ml−1) activities were revealed in SF of mandarin peelings by Pseudotremella gibbosa IBB 22 and of residue after ethanol production (REP) by Fomes fomentarius IBB 38, respectively. The SSF of REP by T. pubescens IBB 11 ensured the highest level of laccase activity (24,690 U l−1), whereas the SSF of wheat bran and SF of mandarin peels provided the highest manganese peroxidase activity (570–620 U l−1) of Trichaptum biforme IBB 117. Moreover, the variation of lignocellulosic growth substrate provides an opportunity to obtain enzyme preparations containing different ratios of individual enzymes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardon O, Kerem Z, Hadar Y (1996) Enhancement of laccase activity in liquid cultures of the ligninolytic fungus Pleurotus ostreatus by cotton stalk extract. J Biotechnol 51:201–207. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(96)01597-0
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270. doi:10.1016/0168-1656(92)90074-J
Baldrian P, Gabriel J (2003) Lignocellulose degradation by Pleurotus ostreatus in the presence of cadmium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220:235–240. doi:10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00102-2
Crestini C, D’Annibale A, Giovannozzi-Sermanni G (1996) Aqueous plant extracts as stimulators of laccase production in liquid cultures of Lentinus edodes. Biotechnol Tech 10:243–248. doi:10.1007/BF00184022
D’Souza TM, Merritt CS, Reddy CA (1999) Lignin-modifying enzymes of the white rot basidiomycetes Ganoderma lucidum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5307–5313
Elisashvili V, Kachlishvili E, Bakradze M (2002) Dependence of activities of polysaccharide hydrolases and oxidases from Cerrena unicolor on the source of carbon and aromatic compounds in culture medium. Appl Biochem Microbiol 38:210–213. doi:10.1023/A:1015407005093
Elisashvili V, Penninckx M, Kachlishvili E, Asatiani M, Kvesitadze G (2006) Use of Pleurotus dryinus for lignocellulolytic enzymes production in submerged fermentation of mandarin peels and tree leaves. Enzyme Microb Technol 38:998–1004. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.08.033
Elisashvili V, Penninckx M, Kachlishvili E, Tsiklauri N, Metreveli E, Khardziani T et al (2008) Lentinus edodes and Pleurotus species lignocellulolytic enzymes activity in submerged and solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic wastes of different composition. Bioresour Technol 99:457–462. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.011
Fenice M, Giovannozzi Sermanni G, Federici F, D’Annibale A (2003) Submerged and solid-state production of laccase and Mn-peroxidase by Panus tigrinus on olive mill wastewater-based media. J Biotechnol 100:77–85. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00241-9
Galhaup C, Wagner H, Hinterstoisser B, Haltrich D (2002) Increased production of laccase by the wood-degrading basidiomycete Trametes pubescens. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:529–536. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00522-1
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268. doi:10.1351/pac198759020257
Glenn JK, Gold MH (1985) Purification and characterization of an extracellular Mn(II)-dependant peroxidase from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys 242:329–341. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(85)90217-6
Kachlishvili E, Penninckx MJ, Tsiklauri N, Elisashvili V (2006) Effect of nitrogen source on lignocellulolytic enzyme production by white-rot basidiomycetes under solid-state cultivation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:391–397. doi:10.1007/s11274-005-9046-8
Kamm B, Kamm M (2004) Principles of biorefineries. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:137–145. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1537-7
Kapich AN, Prior BA, Botha A, Galkin S, Lundell T, Hatakka A (2004) Effect of lignocellulose-containing substrate on production of ligninolytic peroxidases in submerged cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium ME-446. Enzyme Microb Technol 34:187–195. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2003.10.004
Levin L, Herrmann C, Papinutti V (2008) Optimization of lignocellulolytic enzyme production by the white-rot fungus Trametes trogii in solid-state fermentation using response surface methodology. Biochem Eng J 39:207–214. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.09.004
Lorenzo M, Moldes D, Rodriguez Couto S, Sanroman A (2002) Improvement in laccase production by employing different lignocellulosic wastes in submerged cultures of Trametes versicolor. Bioresour Technol 82:109–113. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00176-6
Machuca A, Ferraz A (2001) Hydrolytic and oxidative enzymes produced by white- and brown-rot fungi during Eucalyptus grandis decay in solid medium. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:386–391. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00417-3
Mikiashvili N, Elisashvili V, Wasser S, Nevo E (2005) Carbon and nitrogen sources influence the ligninolytic enzyme activity of Trametes versicolor. Biotechnol Lett 27:955–959. doi:10.1007/s10529-005-7662-x
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030
Moldes D, Lorenzo M, Sanromán MA (2004) Different proportion of laccase isoenzymes produced by submerged cultures of Trametes versicolor grown on lignocellulosic wastes. Biotechnol Lett 26:327–330. doi:10.1023/B:BILE.0000015452.40213.bf
Nazareth SW, Sampy JD (2003) Production and characterisation of lignocellulases of Panus tigrinus and their application. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 52:207–214. doi:10.1016/S0964-8305(03)00051-9
Osma JF, Saravia V, Herrera JLT, Couto SR (2007) Mandarin peelings: the best carbon source to produce laccase by static cultures of Trametes pubescens. Chemosphere 67:1677–1680. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.11.051
Pandey A, Selvakumar P, Soccol CR, Nigam P (1999) Solid-state fermentation for the production of industrial enzymes. Curr Sci 77:149–162
Papinutti VL, Forchiassin F (2007) Lignocellulolytic enzymes from Fomes fomentarius growing in solid-state fermentation. J Food Eng 81:54–59. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.006
Reddy GV, Babu PR, Komaraiah P, Roy KRRM, Kothari IL (2003) Utilization of banana waste for the production of lignolytic and cellulolytic enzymes by solid substrate fermentation using two Pleurotus species (P. ostreatus and P. sajor-caju). Process Biochem 38:1457–1462. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00025-6
Rosales E, Rodriguez Couto S, Sanromán A (2002) New uses of food wastes: application to laccase production by Trametes hirsuta. Biotechnol Lett 24:701–704. doi:10.1023/A:1015234100459
Rosales E, Rodriguez Couto S, Sanromán MA (2005) Reutilisation of food processing wastes for production of relevant metabolites: application to laccase production by Trametes hirsuta. J Food Eng 66:419–423. doi:10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.04.010
Rosales E, Rodriguez Couto S, Sanromàn MA (2007) Increased laccase production by Trametes hirsuta grown on ground orange peelings. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1286–1290. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.09.015
Silva EM, Machuca A, Milagres AMF (2005) Effects of cereal brans on Lentinula edodes growth and enzyme activities during cultivation on forestry wastes. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:283–288. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01669.x
Songulashvili G, Elisashvili V, Wasser S, Nevo E, Hadar Y (2006) Laccase and manganese peroxidases activities of Phellinus robustus and Ganoderma adspersum grown on food industry wastes in submerged fermentation. Biotechnol Lett 28:1425–1429. doi:10.1007/s10529-006-9109-4
Songulashvili G, Elisashvili V, Wasser SP, Nevo E, Hadar Y (2007) Basidiomycetes laccase and manganese peroxidase activity in submerged fermentation of food industry wastes. Enzyme Microb Technol 41:57–61. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.11.024
Souza DF, Tychanowicz GK, Souza CGM, Peralta RM (2006) Co-production of ligninolytic enzymes by Pleurotus pulmonarius on wheat bran solid state cultures. J Basic Microbiol 46:126–134. doi:10.1002/jobm.200510014
Strong PJ, Burgess JE (2008) Fungal and enzymatic remediation of a wine less and five wine-related distillery wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 99:6134–6142. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.041
Sun X, Zhang R, Zhang Y (2004) Production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by Trametes gallica and detection of polysaccharide hydrolase and laccase activities in polyacrylamide gels. J Basic Microbiol 44:220–231. doi:10.1002/jobm.200310376
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the supports received from the Science & Technology Centre in Ukraine under project number STCU 3740 and from the Georgian National Science Foundation under project number GNSF/ST06-092. We are particularly grateful to Dr. I. Zmitrovich (Komarov Botanical Institute, Saint Petersburg) for the taxonomic determination of isolated basidiomycetes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elisashvili, V., Kachlishvili, E., Tsiklauri, N. et al. Lignocellulose-degrading enzyme production by white-rot Basidiomycetes isolated from the forests of Georgia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 331–339 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9897-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9897-x