Abstract
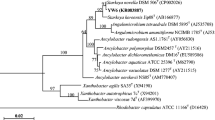
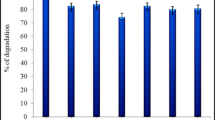
We report here the degradation of a pesticide, malathion, by Brevibacillus sp. strain KB2 and Bacillus cereus strain PU, isolated from soil samples collected from malathion contaminated field and an army firing range respectively. Both the strains were cultured in the presence of malathion under aerobic and energy-limiting conditions. Both strains grew well in the medium having malathion concentration up to 0.15%. Reverse phase HPLC–UV analysis indicated that Strain KB2 was able to degrade 72.20% of malaoxon (an analogue of malathion) and 36.22% of malathion, while strain PU degraded 87.40% of malaoxon and 49.31% of malathion, after 7 days of incubation. The metabolites mal-monocarboxylic acid and mal-dicarboxylic acid were identified by Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. The factors affecting biodegradation efficiency were investigated and effect of malathion concentration on degradation rate was also determined. The strain was analyzed for carboxylesterase activity and maximum activity 210 ± 2.5 U ml−1 and 270 U ± 2.7 ml−1 was observed for strains KB2 and PU, respectively. Cloning and sequencing of putative malathion degrading carboxylesterase gene was done using primers based PCR approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel YM (2005) Molecular characterization of malathion biodegrading enzymes extracted from Egyptian bacterial isolates. N Egypt J Microbiol 10:226–231
Abhilash PC, Singh N (2009) Pesticide use and application an Indian scenario. J Hazard Mater 165:1–12
Abo-Amer AE (2007) Involvement of chromosomally-encoded genes in malathion utilization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AA112. Acta Microbiologica Immunologica Hungarica 54:261–277
Ahmed M, Rocha JBT, Mazzanti CM, Morsch ALB, Cargnelutti D, Correa M, Loro V, Morsch VM, Schetinger MRC (2007) Malathion, carbofuran and paraquat inhibit Bungarus sindanus (krait) venom acetylcholinesterase and human serum butyrylcholinesterase in vitro. Ecotoxicology 16:363–369
Aneja KR (2003) Experiments in microbiology, plant pathology and biotechnology. New Age International Publishers, New Delhi
Bourquin AW (1977) Degaradation of malathion by salt marsh microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:356–362
Budischak SA, Belden LK, Hopkins WA (2009) Relative toxicity of malathion to trematode-infected and noninfected Rana palustris tadpoles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:123–128
Durkin PR (2008) Malathion, human health and ecological risk assessment. SERA TR-052-02-02c
El-Dib MA, El-Elaimy IA, Kotb A, Elowa SH (1996) Activation of in vivo metabolism of malathion in male Tilapia nilotica. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 57:667–674
Foster LJR, Bia H (2004) Microbial degradation of the organophosphate pesticide, Ethion. FEMS Microbiol Lett 240:49–53
Galloway T, Handy R (2003) Immunotoxicity of organophosphorous pesticides. Ecotoxicol 12:345–363
Goda SK, Elsayed EE, Khodair TA, El-Sayed Walaa, Mohamed ME (2010) Screening for and isolation and identification of malathion-degrading bacteria: cloning and sequencing a gene that potentially encodes the malathion-degrading enzyme, carboxylestrase in soil bacteria. Biodegradation doi:10.1007/s10532-010-9350-3
Gurushankara HP, Krishnamurthy SV, Vasudev V (2007) Effect of malathion on survival, growth, and food consumption of Indian cricket frog (Limnonectus limnocharis) tadpoles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:251–256
Hashmi I, Khan MA, Jong-Guk K (2002) Growth response of a selected bacterial population (Pseudomonas) exposed to malathion. Pak J Biol Sci 5:699–703
Hashmi I, Khan MA, Kim JG (2004) Malathion degradation by Pseudomonas using activated sludge treatment system (Biosimulator). Biotechnology 3:82–89
Hinz B (2002a) Analytical method VAM 208-01: determination of malaoxon (CAS No. 1634-78-2) in Malafin DP formulations. Study: VAM 208-01.Cheminova
Hinz B (2002b) Validation of analytical method VAM 208-01 for determination of malaoxon (CAS No. 1634-78-2) in Malafin DP formulation. Cheminova A/S
Indeerjeet K, Mathur RP, Tandon SN, Prem D (1997) Identification of metabolites of malathion in plant, water and soil by GC-MS. Biomed Chromatogr 11:352–355
Kamal Z, Fetyan NAH, Ibrahim MA, Sherif EN (2008) Biodegradation and detoxification of malathion by of Bacillus thuringiensis MOS-5. Austral J Basic Appl Sci 2(3):724–732
Kim YH, Ahng JY, Hyeonmoon S, Lee J (2005) Biodegradation and detoxification of organophosphate insecticide, malathion by Fusarium oxisporum F. sp pisi cutinase. Chemosphere 60:1349–1355
Kumar R, Nagpure NS, Kushwaha B, Srivastava SK, Lakra WS (2010) Investigation of the genotoxicity of malathion to freshwater teleost fish Channa punctatus (bloch) using the micronucleus test and comet assay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:123–130
Kumari B, Guha A, Pathak MG, Bora TC, Roy MK (1998) Experimental biofilm and its application in malathion degradation. Folia Microbiol 43:27–30
Lauwer AM, Heinen W, Gorris M, Leon G, Chris VD (1990) Early stages in biofilm development in methanogenic fluidized-bed reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:352–358
Lewis DL, Paris DF, Baughman GL (1975) Transformation of malathion by a fungus Aspergillus Oryzae isolated from a freshwater pond. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 13:596
Mohamed KZ, Ahmed MA, Fetyan NA, Elnagdy SM (2010) Isolation and molecular characterisation of malathion-degrading bacterial strains from waste water in Egypt. J Adv Res 1:145–149
Mostafa IY, Bahig MRE, Fakhr IMI, Adam Y (1972a) Metabolism of organophsphorus insecticides. XIV Malathion breakdown by soil fungi. Z Naturforsc 276:1115
Mostafa IY, Fakhr IMI, Bahig ME (1972b) Metabolism of organophsphorus insecticidesXIII degaradation of malathion by rhizobium sp. Arch Environ Microbiol 86:221
Pillans PIB, Steohenson A, Folb PI (1988) Cyclophosphamide effects on fetal mouse cephalic acetylcholinesterase. Arch Environ Toxicol 62:230–231
Rogers KR, Wang Y, Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Chen W (1999) Organophosphorus hydrolase-based assay for organophosphate pesticides. Biotechnol Prog 15:517–521
Rosenberg A, Alexander M (1979) Microbial cleavage of various organophosphorus insecticides. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:886–891
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. CSH Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Senanayake N, Karalliedde L (1987) Neurotoxic effects of organophosphorus insecticides. N Engl J Med 316:761–763
Shan X, Junxin L, Lin L, Chuanling Q (2009) Biodegradation of malathion by Acinetobacter johnsonii MA19 and optimization of cometabolism substrates. J Environ Sci 21:76–82
Shimazu M, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2001) Simultaneous degradation of organophosphorus pesticides and p-nitrophenol by a genetically engineered Moraxella sp. with surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:318–324
Singh AK, Seth PK (1989) Degradation of malathion by microorganisms isolated from industrial effluents. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 43:28–35
Singh B, Kaur J, Singh K (2011) 2,4,6-trinitrophenol degradation by Bacillus cereus isolated from a firing range. Biotechnol lett doi:10.1007/s10529-011-0726-1
Uygun U, O’ zkara R, O’zbey A, Koksel H (2007) Residue levels of malathion and fenitrothion and their metabolites in post harvest treated barley during storage and malting. Food Chem 100:1165–1169
Walker WW (1976) Chemical and microbiological degradation of malathion and parathion in an estuarine environment. J Environ Qual 5:210–216
Zweiner RJ, Ginsberg CK (1988) Organophosphate and Carbamate poisoning in infants and children. Pediatric 81:121–128
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Dr. Ashwini kumar, Department of Chemistry, Punjabi university, Patiala, India, for his valuable help and technical support during HPLC analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, B., Kaur, J. & Singh, K. Biodegradation of malathion by Brevibacillus sp. strain KB2 and Bacillus cereus strain PU. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 1133–1141 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0916-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0916-y