Abstract
Objectives
The shape of the anterior region of the maxilla is critical when planning implant treatment. The purpose of the present study was to assess the typical morphology of the incisive canal and surrounding bone.
Methods
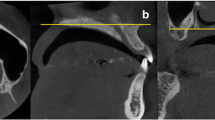
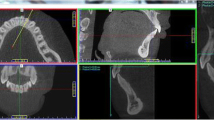
In total, 70 maxillae of Japanese dry skulls were used after being divided into dentate and edentulous groups. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of the maxilla were acquired by using standardized methods. Using the anterior nasal spine as a reference point, the change in position was measured and analyzed statistically. Also, three-dimensional (3-D) images of the incisive canal were classified into five subsets: cylinder, groove, penetration, bifurcation at the superior portion, and bifurcation at the inferior portion.
Results
The quantity of alveolar bone in the incisor region was greatly reduced from the alveolar ridge and labial surface. Moreover, the vertical position of the incisive foramen was significantly (P < 0.05) superior in the edentulous groups. Regarding the classification of maxillae by the 3-D shape of the incisive canal, many canals were cylindrical.
Conclusions
Horizontal bone reduction from the labial side and vertical bone reduction from the alveolar crest were conspicuous; thus, the angle of the anterior alveolar bone changed after the loss of teeth. The incisive canal diameter in the edentulous group was larger than in the dentate group. The nondestructive assessment of the incisive canals and surrounding bone with CBCT showed two typical shapes for the presence or absence of the incisors. These findings indicate the importance of image diagnosis before esthetic restoration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraut RA, Boyden DK. Location of incisive canal in relation to central incisor implants. Implant Dent. 1998;7:221–3.
Cavalcanti MGP, Yang J, Ruprecht A, Vannier MW. Accurate linear measurements in the anterior maxilla using orthoradially reformatted spiral computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1999;28:137–40.
İplikçioğlu H, Akça K, Çehreli CM. The use of computerized tomography for diagnosis and treatment planning in implant dentistry. J Oral Implantol. 2002;28:29–36.
DuBrul EL. Sicher and DuBrul’s oral anatomy. 8th ed. St. Louis: Ishiyaku EuroAmerica, Inc.; 1988. p. 27–8.
Williams PL, Bannister LH, Collins P, Dyson M, Dussek JE, Ferguson MWJ, editors. Gray’s anatomy. 38th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995. p. 602.
White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 5th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2004. p. 174–5, 400–1.
Langland OE, Langlais RP, Preece JW. Principles of dental imaging. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002. p. 336–7.
Filippi A, Pohl Y, Tekin U. Sensory disorders after separation of the nasopalatine nerve during removal of palatal displaced canines: prospective investigation. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;37:134–6.
Hosokawa T, Nishihara J, Miyoshi S, Fujishima Y, Miyake M, Nagahata S. A case of hematoma of the palate associated with extirpation of impacted supernumerary teeth in the anterior maxilla one week after. Pediatr Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;10:29–32.
Brånemark PI, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T. Tissue-integrated prostheses. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co., Inc.; 1987. p. 11.
Ekestubbe A, Thilander A, Gröndahl K, Gröndahl H-G. Absorbed doses from computed tomography for dental implant surgery: comparison with conventional tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1993;22:13–7.
Lecomber AR, Yoneyama Y, Lovelock DJ, Hosoi T, Adams AM. Comparison of patient dose from imaging protocols for dental implant planning using conventional radiography and computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2001;30:255–9.
Sato S, Arai Y, Shinoda K, Ito K. Clinical application of a new cone-beam computerized tomography system to assess multiple two-dimensional images for the preoperative treatment planning of maxillary implants: case reports. Quintessence Int. 2004;35:525–8.
Arai Y, Tammisalo E, Iwai K, Hashimoto K, Shinoda K. Development of a compact computed tomographic apparatus for dental use. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1999;28:245–8.
Hamada Y, Kondoh T, Noguchi K, Iino M, Isono H, Ishii H, et al. Application of limited cone beam computed tomography to clinical assessment of alveolar bone grafting: a preliminary report. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2005;42:128–37.
Suomalainen A, Vehmas T, Kortesniemi M, Robinson S, Peltola J. Accuracy of linear measurements using dental cone beam and conventional multislice computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37:10–7.
Guerrero ME, Jacobs R, Loubele M, Schutser F, Suetens P, van Steenberghe D. State-of-the-art on cone beam CT imaging for preoperative planning of implant placement. Clin Oral Invest. 2006;10:1–7.
Hashimoto K, Arai Y, Iwai K, Araki M, Kawashima S, Terakado M, et al. A comparison of a new limited cone beam computed tomography machine for dental use with a multidetector row helical CT machine. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;95:371–7.
Ludlow JB, Ivanovic M, Hill C. Comparative dosimetry of dental CBCT devices and 64-slice CT for oral and maxillofacial radiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106:106–14.
Cawood JI, Howell RA. A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988;17:232–6.
Atwood DA. Some clinical factors related to rate of resorption of residual ridge. J Prosthet Dent. 1962;13:441–50.
Song WC, Jo DI, Lee JY, Kim JN, Hur MS, Hu KS, et al. Microanatomy of the incisive canal using three-dimensional reconstruction of microCT images: an ex vivo study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108:583–90.
Funaki A. Mechanical effects of bone thickness surrounding implant and fixture installation angle on the strain in the bone around implant—experimental study in the model missing maxillary incisors. J Jpn Soc Oral Implant. 2000;13:544–58.
Peñarrocha M, Carrillo C, García B. The nasopalatine canal as an anatomic buttress for implant placement in the severely atrophic maxilla: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24:936–42.
Mardinger O, Namani-Sadan N, Chaushu G, Schwartz-Arad D. Morphologic changes of the nasopalatine canal related to dental implantation: a radiologic study in different degrees of absorbed maxillae. J Periodontol. 2008;79:1659–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asaumi, R., Kawai, T., Sato, I. et al. Three-dimensional observations of the incisive canal and the surrounding bone using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol 26, 20–28 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0039-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0039-4