Abstract
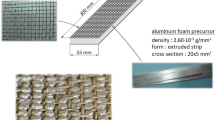
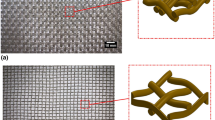
New fabrication technologies now allow for hybrid sandwich structures, known as X-core, to be manufactured. The X-core panels consist of a pin reinforced polymer foam core with carbon fiber face sheets. Carbon fiber or metallic (Titanium/Steel) pins are inserted into the foam core in the out-of-plane direction and extend from face sheet to face sheet. The through thickness three-point simply supported bending behavior of these panels is used to evaluate the collapse characteristics of the panels. Explicit experimental observations are used to calibrate analytical energy balance models describing the panel collapse as a function of geometry and properties. The mechanical response of X-core sandwich panels is compared to current sandwich materials for material selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibson L, Ashby M (1988) Cellular Solids, Cambridge University Press.
Lingaiah K, Suryanarayana B (1991) Strength and stiffness of sandwich beams in bending. Exp Mech 31(1):1–7.
Zenkert D (1995) An Introduction to Sandwich Construction, Engineering Materials Advisory Service.
Chen C, Harte AM, Fleck N (2001) The plastic collapse of sandwich beams with a metallic foam core. Int J Mech Sci 43(6):1483–1506.
McCormack T, Miller R, Kesler O, Gibson L (2001) Failure of sandwich seams with metallic foam cores. Int J Solids Struct 38(28–29):4901–4920.
Steeves CA, Fleck NA (2004) Collapse mechanisms of sandwich beams with composite faces and a foam core, loaded in three-point bending. Part I: analytical models and minimum weight design. Int J Mech Sci 46(4):561–583.
Steeves CA, Fleck NA (2004) Collapse mechanisms of sandwich beams with composite faces and a foam core, loaded in three-point bending. Part II: experimental investigation and numerical modeling. Int J Mech Sci 46(4):585–608.
Deshpande VS, Ashby MF, Fleck NA (2001) Foam topology bending versus stretching dominated structures. Acta Mater 49.
Theotkoglou E (1996) Analytic determination of the ultimate strength of sandwich beams. Appl Compos Mater 3:345–353.
Triantafillou T, Gibson L (1987) Minimum weight design of foam core sandwich panels for a given strength. Mater Sci Eng 95:55–62.
Ashby M, Evans A, Fleck N, Gibson L, Hutchinson J, Wadley H (2000) Metal foam: a design guide. Butterworth Heinemann.
Cartié D, Fleck NA (2003) The effect of pin reinforcement upon the through-thickness compressive strength of foam-cored sandwich panels. Compos Sci Technol 63(16):2401–2409.
Paik KJ, Theyamballi AK, Kim GS (1999) The strength characteristics of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels. Thin-Walled Struct 35(3):205–231.
Tagarielli VL (2005) The Static and Dynamic Response of Sandwich Beams to Transverse Loading. Doctoral thesis, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rice, M.C., Fleischer, C.A. & Zupan, M. Study on the Collapse of Pin-Reinforced Foam Sandwich Panel Cores. Exp Mech 46, 197–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-006-7103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-006-7103-3