Abstract
Background, aim and scope
This study is the first to investigate PBDE body burden with regard to the concurrent analyses of multiple human matrices, namely milk, placenta, and hair, collected from a group of childbearing-aged women at an electronic waste (e-waste) recycling site to determine the partitioning of PBDEs in these different human matrices and the possible health risks imposed to infants at the e-waste recycling site.
Methods and methods
Five sets of milk, placenta, and hair samples were collected from an e-waste site (Taizhou, Zhejiang Province) and a reference site (Lin’an city, Zhejiang Province; 245 km away from Taizhou) in China. The concentrations of total PBDEs in different human tissues were analyzed according to US EPA standard methods.
Results
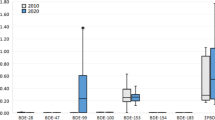
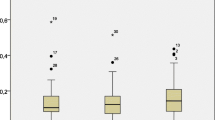
PBDE body burdens of women from the e-waste site (milk 117 ± 191, 8.89–457 ng/g fat, placenta 19.5 ± 29.9, 1.28–72.1 ng/g fat, hair 110 ± 210, 8.47–486 ng/g dry wt.) showed significantly higher levels than those from the reference site (milk 2.06 ± 0.94, 1.0–3.56 ng/g fat, placenta 1.02 ± 0.36, 0.59–1.42 ng/g fat, hair 3.57 ± 2.03, 1.56–5.61 ng/g dry wt.) and were higher than those reported in other studies, due to e-waste recycling operations, especially open burning. On a dry-weight basis, the following trend was found for PBDE among the samples from Taizhou: hair≫milk>placenta. Among the donors, the body burden of an e-waste worker ranked second. Higher brominated BDEs (hepta-BDEs) contributed a significantly greater proportion to total PBDEs in hair of the Taizhou women (20%) than that in milk (2.9%) and in placenta (2.6%). The estimated intake of PBDEs of 6-month-old breastfed infants living at the e-waste site was 572 ± 839 ng/kg body wt/day, which was 57 times higher than that of infants from the reference site (10.1 ± 4.60 ng/kg body wt/day). Moreover, the maximum calculated value (2,240 ng/kg body wt/day) exceeded the chronic oral reference dose for penta-BDE (2,000 ng/kg/day) of US EPA.
Discussion
BDE-47 was the dominant congener accounting for 20–30% in all the individual samples, while higher-brominated congeners, for example, BDE-183 and BDE-190, contributed between 2% and 20%. The presence of hepta-BDE congeners (BDE-181, BDE-190) in hair of the women in Taizhou suggest that thermal degradation of Deca-BDE from the open burning of e-waste may have been their source because these congeners are not found in either Penta-BDE or Octa-BDE technical products. Of the three types of samples analyzed, it was also suspected that hair may be more favorable to higher-brominated compounds which might explain why the hair samples contained the highest total PBDE concentrations and the highest proportion of higher-brominated BDEs (hepta-BDEs).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence that primitive e-waste recycling in China leads to high PBDE body burdens in local residents and can potentially threaten the health of infants.
Recommendations and perspectives
Control measures should be imposed to minimize the level of pollutants resulting from e-waste processing operations to the environment and to humans. In-depth investigations on epidemiological studies of health impacts caused by e-waste recycling operations should be conducted. It is recommended that further measurements of PBDE levels in local food (e.g., fish, shellfish, dairy products, meat, fruits, and vegetables), dust, air, water, and human specimens be collected from a larger sample size at the e-waste processing site for the determination of human exposure pathways to PBDEs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi X, Qu W, Sheng G, Zhang W, Mai B, Chen D (2006) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in South China maternal and fetal blood and breast milk. Environ Pollut 144:1024–1030
Bromine Science and Environmental Forum (2003) Total Market Demand. http://www.bsef.com
Chan JKY (2008) Dietary exposure, human body loadings, and health risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants at two major electronic waste recycling sites in China. PhD Thesis, Hong Kong Baptist University.
Chan JKY, Xing GH, Xu Y, Liang Y, Chen LX, Wu SC, Leung CKM, Wong MH (2007) Body loadings and health risk assessment of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans at an intensive electronic waste recycling site in China. Environ Sci Technol 41:7668–7674
Chao HR, Wang SL, Lee WJ, Wang YF, Päpke O (2007) Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in breast milk from central Taiwan and their relation to infant birth outcome and maternal menstruation effects. Environ Int 33:239–245
Chen D, Mai B, Song J, Sun Q, Luo Y, Luo X, Zeng EY, Hale RC (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in birds of prey from Northern China. Environ Sci Technol 41:1828–1833
Chen L, Mai B, Xu Z, Peng X, Han J, Ran Y, Sheng G, Fu J (2008) In- and outdoor sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their human inhalation exposure in Guangzhou, China. Atmos Environ 42:78–86
Costa LG, Giordano G (2007) Developmental neurotoxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants. Neurotoxicology 28:1047–1067
Covaci A, Tutudaki M, Tsatsakis AM, Schepens P (2002) Hair analysis: another approach for the assessment of human exposure to selected persistent organochlorine pollutants. Chemosphere 46:413–418
Darnerud PO, Eriksen GS, Johannesson T, Larsen PB, Viluksela M (2001) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers: occurrence, dietary exposure, and toxicology. Environ Health Perspect 109:49–68
Deng WJ, Zheng JS, Bi XH, Fu JM, Wong MH (2007) Distribution of PBDEs in air particles from an electronic waste recycling site compared with Guangzhou and Hong Kong, South China. Environ Int 33:1063–1069
de Wit CA (2002) An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 46:583–624
Eslami B, Koizumi A, Ohta S, Inoue K, Aozasa O, Harada K, Yoshinaga T, Date C, Fujii S, Fujimine Y, Hachiya N, Hirosawa I, Koda S, Kusaka Y, Murata K, Nakatsuka H, Omae K, Saito N, Shimbo S, Takenaka K, Takeshita T, Todoriki H, Wada Y, Watanabe T, Ikeda M (2006) Large-scale evaluation of the current level of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in breast milk from 13 regions of Japan. Chemosphere 63:554–561
Esteban M, Castaño A (2009) non-invasive matrices in human biomonitoring: A review. Envriron Int 35:438–449
Fängström B, Strid A, Grandjean P, Weihe P, Bergman Å (2005) A retrospective study of PBDEs and PCBs in human milk from the Faroe Islands. Environ Health: Global Access Sci Source 4:12–20
Gomara B, Herrero L, Ramos JJ, Mateo JR, Fernandez MA, Garcia JF, Gonzalez MJ (2007) Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human umbilical cord serum, paternal serum, maternal serum, placentas, and breast milk from Madrid population, Spain. Environ Sci Technol 41:6961–6968
Guan YF, Wang JZ, Ni HG, Luo XJ, Mai BX, Zeng EY (2007) Riverine inputs of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Pearl River Delta (China) to the coastal ocean. Environ Sci Technol 41:6007–6013
Guvenius DM, Aronsson A, Ekman-Ordeberg G, Bergman Å, Norén K (2003) Human prenatal and postnatal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls, polychlorobiphenylols, and pentachlorophenol. Environ Health Perspect 111:1235–1241
Hooper K, Petreas MX, She JW, Visita P, Winkler J, McKinney M, Mok M, Sy F, Garcha J, Gill M, Stephens RD, Seminova G, Sharmanov T, Chuvakova T (1997) Analysis of breast milk to assess exposure to chlorinated contaminants in Kazakhstan: PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in southern Kazakstan. Environ Health Perspect 105:1250–1254
Ingelido AM, Ballard T, Dellatte E, Domenico AD, Ferri F, Fulgenzi AR, Herrmann T, Iacovella N, Miniero R, Päpke O, Porpora MG, Felip ED (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in milk from Italian women living in Rome and Venice. Chemosphere 67:301–306
Jakobsson K, Thuresson K, Rylander L, Sjödin A, Hagmar L, Bergman Å (2002) Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and tetrabromobisphenol A among computer technicians. Chemosphere 46:709–716
Jaraczewska K, Lulek J, Covaci A, Voorspoels S, Kaluba-Skotarczak A, Drews K, Schepens P (2006) Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human umbilical cord serum, maternal serum and milk from Wielkopolska region, Poland. Sci Total Environ 372:20–31
Jin J, Wang Y, Yang CQ, Ju JC, Liu WZ, Cui J, Tang XY (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the serum and breast milk of the resident population from production area, China. Environ Int 35:1048–1052
Johnson-Restrepo B, Addink R, Wong C, Arcaro K, Kannan K (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and organochlorine pesticides in human breast milk from Massachusetts, USA. J Environ Monit 9:1205–1212
Jones-Otazo HA, Clarke JP, Diamond ML, Archbold JA, Ferguson G, Harner T, Richardson GM, Ryan JJ, Wilford B (2005) Is house dust the missing exposure pathway for PBDEs? An analysis of the urban fate and human exposure to PBDEs. Environ Sci Technol 39:5121–5130
Kalantzi OI, Martin FL, Thomas GO, Alcock RE, Tang HR, Drury SC, Carmichael PL, Nicholson JK, Jones KC (2004) Different levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and chlorinated compounds in breast milk from two UK regions. Environ Health Persp 112:1085–1091
Kazda R, Hajšlová J, Poustka J, Čajka T (2004) Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human milk samples in the Czech Republic: Comparative study of negative chemical ionisation mass spectrometry and time-of-flight high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 520:237–243
Leung AOW, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS, Wong MH (2007) Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soil and combusted residue at Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in Southeast China. Environ Sci Technol 41:2730–2737
Liem AKD, Ahlborg UG, Back H, Haschke F, Nygren M, Younes M, Ynanheikke E (1996) Levels of PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs in Human Milk: Second Round of WHO-Coordinated Exposure Study. WHO European Centre for Environment and Health, Copenhagen, Environmental Health in Europe No. 3
Luo Q, Cai ZW, Wong MH (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish and sediment from river polluted by electronic waste. Sci Total Environ 383:115–127
Ma J, Kannan K, Cheng JP, Horii Y, Wu Q, Wang WH (2008) Concentrations, profiles, and estimated human exposures for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from electronic waste recycling facilities and a chemical industrial complex in eastern China. Environ Sci Technol 42:8252–8259
Mai B, Chen S, Luo X, Chen L, Yang Q, Sheng G, Peng P, Fu J, Zeng EY (2005) Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ Sci Technol 39:3521–3527
Main KM, Kiviranta H, Virtanen HE, Sundqvist E, Tuomisto JT, Tuomisto J, Vartiainen T, Skakkaek NE, Toppari J (2007) Flame retardants in placenta and breast milk and cryptorchidism in newborn boys. Environ Health Perspect 115:1519–1526
Meng XZ, Zeng EY, Yu LP, Guo Y, Mai BX (2007) Assessment of human exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers in China via fish consumption and inhalation. Environ Sci Technol 41:4882–4887
Nakao T, Aozasa O, Ohta S, Miyata H (2005) Survey of human exposure to PCDDs, PCDFs, and coplanar PCBs using hair as an indicator. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 17:124–130
Polder A, Gabrielsen GW, Odland JØ, Savinova TN, Tkachev A, Løken KB, Skaare JU (2008) Spatial and temporal changes of chlorinated pesticides, PCBs, dioxins (PCDDs/PCDFs) and brominated flame retardants in human breast milk from Northern Russia. Sci Total Environ 391:41–54
Qu W, Bi X, Sheng G, Lu S, Fu J, Yuan J, Li L (2007) Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers among workers at an electronic waste dismantling region in Guangdong, China. Environ Int 33:1029–1034
Ramu K, Kajiwara N, Lam PKS, Jefferson TA, Zhou K, Tanabe S (2006) Temporal variation and biomagnification of organohalogen compounds in finless porpoises (Neophocaena phocaenoides) from the South China Sea. Environ Pollut 144:516–523
Schecter A, Papke O, Tung KC, Staskal D, Birnbaum L (2004) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers contamination of United States food. Environ Sci Technol 38:5306–5311
Schramm KW, Keuttnear T, Weber S, Lützke K (1992) Dioxin hair analysis as monitoring pool. Chemosphere 24:351–358
She J, Holden A, Sharp M, Tanner M, Williams-Derry C, Hooper K (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in breast milk from the Pacific Northwest. Chemosphere 67:307–317
Sjödin A, Carlsson H, Thuresson K, Sjödin S, Bergman Å, Östman C (2001) Flame retardants in indoor air at an electronics recycling plant and at other work environments. Environ Sci Technol 35:448–454
Sjödin A, Donald G, Patterson DG, Bergman A (2003) A review on human exposure to brominated flame retardants-particularly polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ Int 29:829–839
Sjödin A, Hagmar L, Klasson-Wehler E, Kronholm-Diab K, Jakobsson E, Bergman Å (1999) Flame retardant exposure: polybrominated diphenyl ethers in blood from Swedish workers. Environ Health Perspect 107:643–648
Smolders R, Schramm K-W, Nickmilder M, Schoeters G (2009) Applicability of non-invasively collected matrices for human biomonitoring. Environ Health 8:8–17
Strandam T, Koistinen J, Vartiainen T (2000) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in placenta and human milk. Organohalogen Compds 47:61–65
Sudaryanto A, Kajiwara N, Takahashi S, Muawanah, Tanabe S (2008) Geographical distribution and accumulation features of PBDEs in human breast milk from Indonesia. Environ Pollut 151:130–138
Taizhou Economic Committee, China (2007) http://www.tzsjw.gov.cn/index.php (in Chinese)
The World Bank (2005). Environmental Impact assessment of Zhejiang Province for PCB management and disposal demonstration project. http://www-wds.worldbank.org
Tanabe S (2008) Temporal trends of brominated flame retardants in coastal waters of Japan and South China: retrospective monitoring study using archived samples from es-Bank, Ehime University, Japan. Mar Pollut Bull 57:267–274
Thomsen C, Lundanes E, Becher G (2001) Brominated flame retardants in plasma samples from three different occupational groups in Norway. J Environ Monit 3:366–370
Toms LML, Harden FA, Symons RK, Burniston D, Fürst P, Müller JF (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in human milk from Australia. Chemosphere 68:797–803
Tsydenova OV, Sudaryanto A, Kajiwara N, Kunisue T, Batoev VB, Tanabe S (2007) Organohalogen compounds in human breast milk from Republic of Buryatia, Russia. Environ Pollut 146:225–232
UNEP (2005) E-waste, the hidden side of IT equipment’s manufacturing and use. http://www.grid.unep.ch/product/publication/download/ew_ewaste.en.pdf
UNEP (2009) Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Press Release: Governments unite to step-up reduction on global DDT reliance and add nine new chemicals under international treaty.
USEPA (2009) DecaBDE phase-out initiative. http://www.epa.gov/oppt/existingchemicals/pubs/actionplans/deccadbe.html (17 December 2009) http://www.unep.org/Documents.Multilingual/Default.asp?DocumentID=585&ArticleID=6158&l=en&t=long
US EPA (1996a) Method 3540C: Soxhlet Extraction. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US EPA (1996b) Method 3630C: Silica gel cleanup—Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods, SW-846. US EPA, Washington, DC
US EPA (1996c) Method 3620B: Florisil Cleanup—Solid Waste Analysis SW-846. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
US EPA (2003) US EPA Draft Method 1614: Brominated diphenyl ethers in water, soil, sediment, and tissue by HRGC/HRMS. USEPA, Washington, DC
Wong MH, Wu SC, Deng WJ, Yu XZ, Luo Q, Leung AOW, Wong CSC, Luksemburg WJ, Wong AS (2007) Export of toxic chemicals – A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ Pollut 149:131–140
Xian Q, Ramu K, Isobe T, Sudaryanto A, Liu X, Gao Z, Takahashi S, Yu H, Tanabe S (2008) Levels and body distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in freshwater fishes from the Yangtze River, China. Chemosphere 71:268–276
Xinhua Online. (2007) Seventy percent of worldwide electronic-waste goes to China. Dated January 1, http://news3.xinhuanet.com/tech/2007-01/09/content_5581834.htm (in Chinese)
Yu XZ, Gao Y, Wu SC, Zhang HB, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2006) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils at Guiyu area of China, affected by recycling of electronic waste using primitive technologies. Chemosphere 65:1500–1509
Zhao GF, Wang ZJ, Dong MH, Rao KF, Luo JP, Wang DH, Zha JM, Huang SB, Xu YP, Ma M (2008) PBBs, PBDEs, and PCBs levels in hair of residents around e-waste disassembly sites in Zhejiang Province, China, and their potential sources. Sci Tot Environ 397:46–57
Zou MY, Ran Y, Gong J, Mai BX, Zeng EY (2007) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in watershed soils of the Pearl River Delta, China: occurrence, inventory, and fate. Environ Sci Technol 41:8262–8267
Acknowledgements
We thank the mothers who contributed to the study and donated milk, placenta, and hair samples. This research was supported by The Research Grants Council of the University Grants Committee of Hong Kong (Central Allocation Group Research Project HKBU 1/03C), Match Fund from Hong Kong Baptist University, and a private donation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Anna OW Leung and Janet KY Chan contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leung, A.O.W., Chan, J.K.Y., Xing, G.H. et al. Body burdens of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in childbearing-aged women at an intensive electronic-waste recycling site in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17, 1300–1313 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0310-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0310-6