Abstract
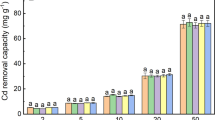
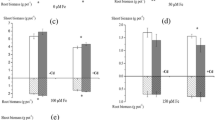
A hydroponic culture experiment was performed to investigate the effects of endophytic Bacillus megaterium H3 on the plant biomass, Cd accumulation and tolerance of hybrid pennisetum, and the mechanisms involved in the different levels of Cd-contaminated aquatic environments. Strain H3 significantly increased the plant growth (ranging from 13 to 71 %) and total Cd uptake (ranging from 41 to 160 %) but decreased Cd translocation factors of hybrid pennisetum treated with 0–20 μM Cd compared with the controls. Furthermore, most of Cd (71–77 %) was accumulated in the roots of the bacterial-inoculated hybrid pennisetum. Notably, strain H3 could significantly increase the production of oxalic and propanedioic acids (ranging from 18 to 188 %) but decrease the production of phytochelatins of hybrid pennisetum compared to the controls under different levels of Cd stress. The live bacterial-induced increase in organic acid production and decrease in phytochelatins production by hybrid pennisetum might be responsible for the increased plant growth, root Cd accumulation, and Cd toxicity alleviation of the plant under different levels of Cd stress. The results highlight that hybrid pennisetum plus endophytic B. megaterium H3 may be utilized for biomass production and Cd phytostabilization of the plant in the different levels of Cd-contaminated aquatic environments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahner BA, Kong S, Morel FMM (1995) Phytochelatin production in marine algae. 1. An interspecies comparison. Limnol Oceanogr 40:649–657
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2005) Cadmium-induced toxicity reversal by zinc in Ceratophyllum demersum L. (a free floating aquatic macrophyte) together with exogenous supplements of amino- and organic acids. Chemosphere 61:1720–1733
Arshad M, Saleem M, Hussain S (2007) Perspectives of bacterial ACC deaminase in phytoremediation. Trends Biotechnol 25:356–362
Asensio V, Covelo EF, Kandeler E (2013) Soil management of copper mine tailing soils-sludge amendment and tree vegetation could improve biological soil quality. Sci Total Environ 456-457:82–90
Babu AG, Kim JD, Oh BT (2013) Enhancement of heavy metal phytoremediation by Alnus firma with endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis GDB-1. J Hazard Mater 250–251:477–483
Babu AG, Shea PJ, Sudhakar D, Jung IB, Oh BT (2015) Potential use of Pseudomonas koreensis AGB-1 in association with Miscanthus sinensis to remediate heavy metal(loid)-contaminated mining site soil. J Environ Manag 151:160–166
Balsamo RA, Kelly WJ, Satrio JA, Ruiz-Felix MN, Fetterman M, Wynn R, Hagel K (2015) Utilization of grasses for potential biofuel production and phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediat 17:448–455
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Chen W, Luo L, He LY, Wang Q, Sheng XF (2016) Distinct mineral weathering behaviors of the novel mineral-weathering strains Rhizobium yantingense H66 and Rhizobium etli CFN42. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:4090–4099
Chen ZJ, Sheng XF, He LY, Huang Z, Zhang WH (2013) Effects of root inoculation with bacteria on the growth, Cd uptake and bacterial communities associated with rape grown in Cd-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 244-245:709–717
Defreitas JR, Germida JJ (1992) Growth promotion of winter wheat by fluorescent Pseudomonas under field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1137–1146
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2005) Analysis of rhizobacterial communities in perennial Graminaceae from polluted water meadow soil, and screening of metal-resistant, potentially plant growth-promoting bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:153–162
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2008) Improvement of Brassica napus growth under cadmium stress by cadmium-resistant rhizobacteria. Soil Biol Biochem 40:74–84
Devos CHR, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R, Schat H (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98:853–858
Dresler S, Hanaka A, Bednarek W, Maksymiec W (2014) Accumulation of low molecular-weight organic acids in roots and leaf segments of Zea mays plants treated with cadmium and copper. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1565–1575
Duan GL, Hu Y, Liu WJ, Kneer R, Zhao FJ, Zhu YG (2011) Evidence for a role of phytochelatins in regulating arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Environ Exp Bot 71:416–421
Fernández R, Fernández-Fuego D, Bertrand A, González A (2014) Strategies for Cd accumulation in Dittrichia viscosa (L.) Greuter: role of the cell wall, non-protein thiols and organic acids. Plant Physiol Biochem 78:63–70
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374
Glick BR, Karaturovic DM, Newell PC (1995) A novel procedure for rapid isolation of plant growth promoting pseudomonads. Can J Microbiol 41:533–536
Grandlic CJ, Palmer MW, Raina M, Maier RM (2009) Optimization of plant growth-promoting bacteria-assisted phytostabilization of mine tailings. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1734–1740
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Vooijs R, Bookum WT, Schat H, Meharg AA (2001) Phytochelatins are involved in differential arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus. Plant Physiol 126:299–306
Hassan Z, Aarts MGM (2011) Opportunities and feasibilities for biotechnological improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni tolerance and accumulation in plants. Environ Exp Bot 72:53–63
Hawrylak-Nowak B, Dresler S, Matraszek R (2015) Exogenous malic and acetic acids reduce cadmium phytotoxicity and enhance cadmium accumulation in roots of sunflower plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 94:225–234
Konishi T, Matsumoto S, Tsuruwaka Y, Shiraki K, Hirata K, Tamaru Y, Masahiro TM (2006) Enhancing the tolerance of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to heavy metal toxicity by the expression of plant phytochelatin synthase. J Biotechnol 122:316–325
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Sa T (2007) Metal tolerating methylotrophic bacteria reduces nickel and cadmium toxicity and promotes plant growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Chemosphere 69:220–228
Marques APGC, Moreira H, Franco AR, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2013) Inoculating Helianthus annuus (sunflower) grown in zinc and cadmium contaminated soils with plant growth promoting bacteria—effects on phytoremediation strategies. Chemosphere 92:74–83
Mastretta C, Taghavi S, van der Lelie D, Mengoni A, Galardi F, Gonnelli C, Barac T, Boulet J, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J (2009) Endophytic bacteria from seeds of Nicotiana tabacum can reduce cadmium phytotoxicity. Int J Phytoremediat 11:251–267
Mleczek M, Rutkowski P, Rissmann I, Kaczmarek Z, Golinski P, Szentner K, Strazynska K, Stachowiak A (2010) Biomass productivity and phytoremediation potential of Salix alba and Salix viminalis. Biomass Bioenerg 34:1410–1418
Mohamed AA, Castagna A, Ranieri A, di Toppi LS (2012) Cadmium tolerance in Brassica juncea roots and shoots is affected by antioxidant status and phytochelatin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 57:15–22
Nassar AH, El-Tarabily KA, Sivasithamparam K (2003) Growth promotion of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by a polyamine producing isolate of Streptomyces griseoluteus. Plant Growth Regul 40:97–106
Pérez-Esteban J, Escolástico C, Moliner A, Masaguer A, Ruiz-Fernández J (2014) Phytostabilization of metals in mine soils using Brassica juncea in combination with organic amendments. Plant Soil 377:97–109
Puente ME, Li CY, Bashan Y (2009) Endophytic bacteria in cacti seeds can improve the development of cactus seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 66:402–408
Rathnayake IVN, Megharaj M, Krishnamurti GSR, Bolan NS, Naidu R (2013) Heavy metal toxicity to bacteria—are the existing growth media accurate enough to determine heavy metal toxicity? Chemosphere 90:1195–1200
Rizzi L, Petruzzelli G, Poggio G, Vigna GG (2004) Soil physical changes and plant availability of Zn and Pb in a treatability test of phytostabilization. Chemosphere 57:1039–1046
Santibáñez C, Verdugo C, Ginocchio R (2008) Phytostabilization of copper mine tailings with biosolids: implications for metal uptake and productivity of Lolium perenne. Sci Total Environ 395:1–10
Sheng XF, Sun LN, Huang Z, He LY, Zhang WH, Chen ZJ (2012) Promotion of growth and Cu accumulation of bio-energy crop (Zea mays) by bacteria: implications for energy plant biomass production and phytoremediation. J Environ Manag 103:58–64
Sheng XF, Xia JJ, Jiang CY, He LY, Qian M (2008) Characterization of heavy metal-resistant endophytic bacteria from rape (Brassica napus) roots and their potential in promoting the growth and lead accumulation of rape. Environ Pollut 156:1164–1170
Speiser D, Abrahamson SL, Banuelos G, Ow D (1992) Indian mustard produces a PC-Cd-sulfide complex. Plant Physiol 99:817–821
Sturz AV, Christie BR, Nowak J (2000) Bacterial endophytes: potential role in developing sustainable systems of crop production. Cri Rev Plant Sci 19:1–30
Sun LN, Zhang YF, He LY, Chen ZJ, Wang QY, Qian M, Sheng XF (2010) Genetic diversity and characterization of heavy metal-resistant-endophytic bacteria from two copper-tolerant plant species on copper mine wasteland. Bioresour Technol 101:501–509
Sun RL, Zhou QX, Sun FH, Jin CX (2007) Antioxidative defense and proline/phytochelatin accumulation in a newly discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator, Solanum nigrum L. Environ Exp Bot 60:468–476
Zhang YF, He LY, Chen ZJ, Zhang WH, Wang QY, Qian M, Sheng XF (2011) Characterization of lead-resistant and ACC deaminase-producing endophytic bacteria and their potential in promoting lead accumulation of rape. J Hazard Mater 186:1720–1725
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (41471273) and Social Development Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2013710, BE2016744).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Han, H., He, L.Y. et al. Inoculation with endophytic Bacillus megaterium H3 increases Cd phytostabilization and alleviates Cd toxicity to hybrid pennisetum in Cd-contaminated aquatic environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 1416–1423 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7930-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7930-4