Abstract
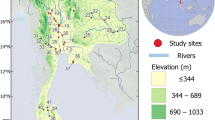
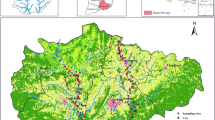
For decades, the river health of the Yellow River source region (YRSR) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau has been a focal issue owing to its unique geographic location and ecological functions. This study investigated the ecological status of the headwater streams, the main stem, and the tributaries of the Yellow River in the YRSR using the tolerance values of macroinvertebrates and those related to biotic indices. The macroinvertebrate assemblages of the headwater streams were characterized by lower biodiversity than the tributaries downstream, based on comparisons of taxonomical composition, functional feeding group composition, and the pollution-tolerant capacity of taxa. The headwater streams had a lower ratio (16%) of pollution-sensitive macroinvertebrate taxa than that of the tributaries downstream (30%). The biotic indices (family- and genus-level biotic indices) indicated that the ecological health of the headwater streams was comparably poorer than that of the downstream tributaries. The combined effect of vulnerable natural conditions and increasing human disturbance is likely the main cause of eco-environmental degradation in the Yellow River headwater streams.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Gao JF, Begum F, Rasool A, Ismail M, Cai YJ, Ali S, Ali S (2017) Health assessment using aqua-equality indicators of alpine streams (Khunjerab National Park), Gilgit, Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:4685–4698
Bressler DW, Stribling JB, Paul MJ, Hicks MB (2006) Stressor tolerance values for benthic macroinvertebrates in Mississippi. Hydrobiologia 573:155–172
Brierley GJ, Li XL, Cullum C, Gao J (2016) Introduction: landscape and ecosystem diversity in the Yellow River Source Zone. In: Brierley GJ, Li X, Cullum C, Gao J (eds) Landscape and ecosystem diversity, dynamics and management in the Yellow River Source Zone. Springer, New York, pp 1–34
Brix H (1997) Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci Technol 35:11–17
Carrie R, Dobson M, Barlow J (2017) Challenges using extrapolated family-level macroinvertebrate metrics in moderately disturbed tropical streams: a case-study from Belize. Hydrobiologia 794:257–271
Chang GG, Li L, Zhu XD, Wang ZY, Xiao JS, Li FX (2007) Influencing factors of water resources in the source region of the Yellow River. J Geogr Sci 17:131–140
Christensen PB, Sørensen J (1986) Temporal variation of denitrification activity in plant-covered, littoral sediment from lake Hampen, Denmark. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1174–1179
Duan XH, Wang ZY, Xu MZ (2010) Benthic macroinvertebrate and application in the assessment of stream ecology. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract)
Duan XH, Wang ZY, Xu MZ (2011) Effects of fluvial processes and human activities on stream macro-invertebrates. Int J Sediment Res 26:416–430
Duka S, Pepa B, Keci E, Paparisto A, Lazo P (2017) Biomonitoring of water quality of the Osumi, Devolli, and Shkumbini rivers through benthic macroinvertebrates and chemical parameters. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 52:471–478
Epler JH (2001) Identification manual for the larval Chironomidae (Diptera) of North and South Carolina: a guide to the taxonomy of the midges of the southeastern United States, including Florida. Special Publication SH2001-SP13. North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Raleigh, North Carolina
Feng JM, Wang T, Xie CW (2006) Eco-environmental degradation in the source region of the Yellow River, Northeast Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Environ Monit Assess 122:125–143
Ferreira WR, Hepp LU, Ligeiro R, Macedo DR, Hughes RM, Kaufmann PR, Callisto M (2017) Partitioning taxonomic diversity of aquatic insect assemblages and functional feeding groups in neotropical savanna headwater streams. Ecol Indic 72:365–373
Fierro P, Bertran C, Tapia J, Hauenstein E, Pena-Cortes F, Vergara C, Cerna C, Vargas-Chacoff L (2017) Effects of local land-use on riparian vegetation, water quality, and the functional organization of macroinvertebrate assemblages. Sci Total Environ 609:724–734
Fu L, Jiang Y, Ding J, Liu Q, Peng Q-Z, Kang M-Y (2016) Impacts of land use and environmental factors on macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups in the Dongjiang River basin, southeast China. J Freshw Ecol 31:21–35
Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ (2003) The nitrogen cascade. BioScience 53:341–356
Garcia E, Suarez PA, Alejandro D (2007) Community structure and phenology of chironomids (Insecta : Chironomidae) in a Patagonian Andean stream. Limnologica 37:109–117
Gödde M, Conrad R (1999) Immediate and adaptational temperature effects on nitric: oxide production and nitrous oxide release from nitrification and denitrification in two soils. Biol Fertil Soils 30:33–40
González OS, Almeida CA, Calderon M, Mallea MA, Gonzalez P (2014) Assessment of the water self-purification capacity on a river affected by organic pollution: application of chemometrics in spatial and temporal variations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10583–10593
Grimm NB (1988) Role of macroinvertebrates in nitrogen dynamics of a desert stream. Ecology 69:1884–1893
Grutters BMC, Gross EM, Bakker ES (2016) Insect herbivory on native and exotic aquatic plants: phosphorus and nitrogen drive insect growth and nutrient release. Hydrobiologia 778:209–220
He XB (2011) Studies on faunae of aquatic Oligochaeta (Annelida) in Tibet and four large rivers of China. Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hilsenhoff WL (1988) Rapid field assessment of organic pollution with a family-level biotic index. J N Am Benthol Soc 7:65–68
Kitchin PL (2005) Measuring the amount of statistical information in the EPT index. Environmetrics 16:51–59
de Klein JJM, Overbeek CC, Jorgensen CJ, Veraart AJ (2017) Effect of temperature on oxygen profiles and denitrification rates in freshwater sediments. Wetlands 37:975–983
Klemm DJ, Blocksom KA, Thoeny WT, Fulk FA, Herlihy AT, Kaufmann PR, Cormier SM (2002) Methods development and use of macroinvertebrates as indicators of ecological conditions for streams in the Mid-Atlantic Highlands Region. Environ Monit Assess 78:169–212
Lampitt RS, Wishner KF, Turley CM, Angel MV (1993) Marine snow studies in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: distribution, composition and role as a food source for migrating plankton. Mar Biol 116:689–702
Lepš J, Šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Martinez J, Dabert P, Barrington S, Burton C (2009) Livestock waste treatment systems for environmental quality, food safety, and sustainability. Bioresour Technol 100:5527–5536
Maxted JR, Barbour MT, Gerritsen J, Poretti V, Primrose N, Silvia A, Penrose D, Renfrow R (2000) Assessment framework for mid-Atlantic coastal plain streams using benthic macroinvertebrates. J N Am Benthol Soc 19:128–144
McGregor GR (2016) Climate variability and change in the Sanjiangyuan region. In Landscape and Ecosystem Diversity, Dynamics and Management in the Yellow River Source Zone. Springer, Cham, pp 35–57
Menezes S, Baird DJ, Soares AMVM (2010) Beyond taxonomy: a review of macroinvertebrate trait-based community descriptors as tools for freshwater biomonitoring. J Appl Ecol 47:711–719
Morse JC, Yang LF, Tian LX (1994) Aquatic insects of China useful for monitoring water quality. Hohai University Press, Nanjing
Oguma AY, Klerks PL (2017) Pollution-induced community tolerance in benthic macroinvertebrates of a mildly lead-contaminated lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19076–19085
Palmer CG, Maart B, Palmer AR, Okeeffe JH (1996) An assessment of macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups as water quality indicators in the Buffalo River, eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Hydrobiologia 318:153–164
Pan B, Wang Z, Xu M, Xing L (2012) Relation between stream habitat conditions and macroinvertebrate assemblages in three Chinese rivers. Quat Int 282:178–183
Poikane S, Johnson RK, Sandin L, Schartau AK, Solimini AG, Urbanič G, Arbačiauskas K, Aroviita J, Gabriels W, Miler O, Pusch MT, Timm H, Böhmer J (2016) Benthic macroinvertebrates in lake ecological assessment: a review of methods, intercalibration and practical recommendations. Sci Total Environ 543:123–134
Qin C, Zhou J, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Hughes RM, Wang B (2014) Quantitative tolerance values for common stream benthic macroinvertebrates in the Yangtze River Delta, Eastern China. Environ Monit Assess 186:5883–5895
Qin Y, Yang D, Gao B, Wang T, Chen J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Zheng G (2017) Impacts of climate warming on the frozen ground and eco-hydrology in the Yellow River source region, China. Sci Total Environ 605:830–841
Raburu PO, Masese FO, Tonderski KS (2017) Use of macroinvertebrate assemblages for assessing performance of stabilization ponds treating effluents from sugarcane and molasses processing. Environ Monit Assess 189(2):79
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman & Hall, London
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:379–423
Sola C, Burgos M, Plazuelo A, Toja J, Plans M, Prat N (2004) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and macroinvertebrate community changes in a Mediterranean stream affected by acid mine drainage and an accidental spill (Guadiamar River, SW Spain). Sci Total Environ 333:109–126
Svensson O, Bellamy AS, Van den Brink PJ, Tedengren M, Gunnarsson JS (2018) Assessing the ecological impact of banana farms on water quality using aquatic macroinvertebrate community composition. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13373–13381
Teira-Esmatges MR, Flotats X (2003) A method for livestock waste management planning in NE Spain. Waste Manag 23:917–932
The State Environmental Protection Administration (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Tomanova S, Usseglio-Polatera P (2007) Patterns of benthic community traits in neotropical streams: relationship to mesoscale spatial variability. Fundam Appl Limnol / Archiv für Hydrobiologie 170:243–255
Tomanova S, Goitia E, Helešic J (2006) Trophic levels and functional feeding groups of macroinvertebrates in neotropical streams. Hydrobiologia 556:251–264
Tyler HL, Moore MT, Locke MA (2012) Influence of three aquatic macrophytes on mitigation of nitrogen species from agricultural runoff. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:3227–3236
Wang JG (2003) Tolerance values of benthic macroinvertebrates and bioassessment of water quality in the Lushan nature reserve. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 9:279–284 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang X, Tan X (2017) Macroinvertebrate community in relation to water quality and riparian land use in a substropical mountain stream, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:14682–14689
Wang BX, Yang LF (2004) A study on tolerance values of benthic macroinvertebrate taxa in eastern China. Acta Ecol Sin 24:2768–2775 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GX, Guo XY, Cheng GD (2002) Dynamic variations of landscape pattern and the landscape ecological functions in the source area of the Yellow River. Acta Ecol Sin 22:1587–1598 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YL, Wang X, Li CH, Wu FF, Yang ZF (2015) Spatiotemporal analysis of temperature trends under climate change in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Theor Appl Climatol 119:123–133
Wiggins GB (2015) Larvae of the North American caddisfly genera (Trichoptera). University of Toronto Press, Canada
Xu M, Wang Z, Pan B, Zhao N (2012) Distribution and species composition of macroinvertebrates in the hyporheic zone of bed sediment. Int J Sediment Res 27:129–140
Xu M, Wang Z, Duan X, Pan B (2014) Effects of pollution on macroinvertebrates and water quality bio-assessment. Hydrobiologia 729:247–259
Zhang J, Li G, Liang S (2012) The response of river discharge to climate fluctuations in the source region of the Yellow River. Environ Earth Sci 66:1505–1512
Zhao N, Xu M, Li Z, Wang Z, Zhou H (2017) Macroinvertebrate distribution and aquatic ecology in the Ruoergai (Zoige) Wetland, the Yellow River source region. Front Earth Sci 11:554–564
Zhou HK, Zhou L, Liu W, Zhao XQ, Lai DZ (2003) Causes of grassland degradation and sustainable development of animal husbandry in Maduo County, Qinghai Province. Grassland China 25:63–67 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor Dr. Philippe Garrigues and the two anonymous reviewers for their review comments that significantly strengthened the paper.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the National Science Fund China (91547204, 51779120, 51622901), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0402407, 2016YFC0402406), Tsinghua University Project (2015THZ02-1), State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering Project (2016-KY-04), and the Yellow River Institute of Hydraulic Research (HKY-JBYW-2016-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Xu, M., Zhao, N. et al. River health assessment of the Yellow River source region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China, based on tolerance values of macroinvertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 10251–10262 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04110-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04110-0