Abstract
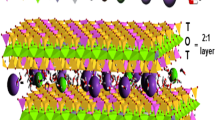
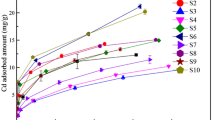
Removal of emerging pollutants, such as pharmaceuticals, from wastewater is a challenge. Adsorption is a simple and efficient process that can be applied. Clays, which are natural and low-cost materials, have been investigated as adsorbent. In this work, raw vermiculite and its three modified forms (expanded, base, and acid/base treated) were tested for removal of a widely used antidepressant, venlafaxine. Adsorption kinetics followed Elovich’s model for raw vermiculite while the pseudo-2nd order model was a better fit in the case of other materials. Equilibrium followed Langmuir’s model for the raw and the acid/base-treated vermiculite, while Redlich-Peterson’s model fitted better the expanded and the base-treated materials. The adsorption capacity of vermiculite was significantly influenced by the changes in the physical and chemical properties of the materials caused by the treatments. The base-treated, raw, and expanded vermiculites showed lower maximum adsorption capacities (i.e., 6.3 ± 0.5, 5.8 ± 0.7, 3.9 ± 0.2 mg g−1, respectively) than the acid/base-treated material (33 ± 4 mg g−1). The acid/base-treated vermiculite exhibited good properties as a potential adsorbent for tertiary treatment of wastewater in treatment plants, in particular for cationic species as venlafaxine due to facilitation of diffusion of the species to the interlayer gallery upon such treatment.

ᅟ



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barshad I (1950) The effect of interlayer cations on the expansion of the mica type of crystal lattice. Am Mineral 35
Brigatti MF, Galan E, Theng BKG (2006) Structures and mineralogy of clay minerals. In: Bergaya F, Theng BKG, Lagal G (eds) Handbook of clay science. Elsevier Ltd
Bueno MJM, Gomez MJ, Herrera S, Hernando MD, Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR (2012) Occurrence and persistence of organic emerging contaminants and priority pollutants in five sewage treatment plants of Spain: two years pilot survey monitoring. Environ Pollut 164:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.01.038
Chang P-H, Li Z, Jiang W-T, Jean J-S (2009) Adsorption and intercalation of tetracycline by swelling clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 46:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.07.002
Chang P-H, Li Z, Jean J-S, Jiang W-T, Wang C-J, Lin K-H (2012) Adsorption of tetracycline on 2:1 layered non-swelling clay mineral illite. Appl Clay Sci 67:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.11.004
Collins DR, Fitch AN, Catlow CRA (1992) Dehydration of vermiculites and montmorillonites: a time-resolved powder neutron diffraction study. J Mater Chem 2:865–873. https://doi.org/10.1039/JM9920200865
Daughton GC (2013) Pharmaceuticals in the environment: sources and their management. In: Petrovic M, Perez S, Barcelo D (eds) Analysis, removal, effects and risk of pharmaceuticals in the water cycle, 2nd edition, vol 62. Elsevier
de Jongh CM, Kooij PJ, de Voogt P, ter Laak TL (2012) Screening and human health risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in Dutch surface waters and drinking water. Sci Total Environ 427-428:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.010
Dordio AV, Miranda S, Prates Ramalho JP, Carvalho AJP (2017) Mechanisms of removal of three widespread pharmaceuticals by two clay materials. J Hazard Mater 323:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.091
Eichhorn P (2013) General introduction on pharmaceuticals. In: Petrovic M, Perez S, Barcelo D (eds) Analysis, removal, effects and risk of pharmaceuticals in the water cycle, 2nd edition, vol 62. Elsevier
Fernandes C, Catrinescu C, Castilho P, Russo PA, Carrott MR, Breen C (2007) Catalytic conversion of limonene over acid activated Serra de Dentro (SD) bentonite. Appl Catal A Gen 318:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2006.10.048
Ferrage E, Lanson B, Malikova N, Plançon A, Sakharov BA, Drits VA (2005) New insights on the distribution of interlayer water in bi-hydrated smectite from X-ray diffraction profile modeling of 00l reflections. Chem Mater 17:3499–3512. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm047995v
Ferrer I, Thurman EM (2013) Analysis of pharmaceuticals in drinking water, groundwater, surface water, and wastewater. In: Petrovic M, Perez S, Barcelo D (eds) Analysis, removal, effects and risk of pharmaceuticals in the water cycle, 2nd edition, vol 62. Elsevier
Földvári M (2011) Handbook of thermogravimetric system of minerals and its use in geological practice. Geological Institute of Hungary (=Magyar Állami Földtani Intézet)
Freundlich HMF (1906) Über die adsorption in läsungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470
Gupta VK, Ali I (2012) Environmental water: advances in treatment, remediation and recycling. Elsevier
Haul R (1982) S. J. Gregg, K. S. W. Sing: Adsorption, surface area and porosity. 2. Auflage, Academic Press, London 1982. 303 Seiten, Preis: $ 49.50. Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem 86:957–957. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbpc.19820861019
Ho YS (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000013305.99473.cf
Huo X, Wu L, Liao L, Xia Z, Wang L (2012) The effect of interlayer cations on the expansion of vermiculite. Powder Technol 224:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.02.059
Jiang W-T, Chang P-H, Wang Y-S, Tsai Y, Jean J-S, Li Z, Krukowski K (2013) Removal of ciprofloxacin from water by birnessite. J Hazard Mater 250:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.02.015
Jozefaciuk G, Muranyi A, Alekseeva T (2002) Effect of extreme acid and alkali treatment on soil variable charge. Geoderma 109:225–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00177-5
Kalinowski BE, Schweda P (2007) Rates and nonstoichiometry of vermiculite dissolution at 22°C. Geoderma 142:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.08.011
Kaviratna H, Pinnavaia TJ (1994) Acid hydrolysis of octahedral Mg2+ sites in 2:1 layered silicates: an assessment of edge attack and gallery access mechanisms. Clay Clay Miner 42:717–723
Kümmerer K (2008) Pharmaceuticals in the environment. Springer
Kunze GW (1965) Pretreatment for mineralogical analysis. In: Black CA (ed) Soil analysis. Part I. American Society of Agronomy, Wisconsin, pp 568–577
Kuzmanovic M, Banjac Z, Ginebreda A, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2013) Prioritization: selection of environmentally occurring pharmaceuticals to be monitored. In: Petrovic M, Perez S, Barcelo D (eds) Analysis, removal, effects and risk of pharmaceuticals in the water cycle, 2nd edition, vol 62. Elsevier,
Lagergren S (1898) About theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kongl Vetenskaps Academiens Handlingar 24:1–39
Lajeunesse A, Smyth SA, Barclay K, Sauvé S, Gagnon C (2012) Distribution of antidepressant residues in wastewater and biosolids following different treatment processes by municipal wastewater treatment plants in Canada. Water Res 46:5600–5612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.07.042
Lambropoulou D, Evgenidou E, Saliverou V, Kosma C, Konstantinou I (2017) Degradation of venlafaxine using TiO2/UV process: kinetic studies, RSM optimization, identification of transformation products and toxicity evaluation. J Hazard Mater 323:513–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.074
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li Z, Chang P-H, Jean J-S, Jiang W-T, Wang C-J (2010a) Interaction between tetracycline and smectite in aqueous solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 341:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.09.054
Li Z, Schulz L, Ackley C, Fenske N (2010b) Adsorption of tetracycline on kaolinite with pH-dependent surface charges. J Colloid Interface Sci 351:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.07.034
Li Z, Chang P-H, Jiang W-T, Jean J-S, Hong H, Liao L (2011) Removal of diphenhydramine from water by swelling clay minerals. J Colloid Interface Sci 360:227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.04.030
Li Z, Fitzgerald NM, Jiang W-T, Lv G (2016) Palygorskite for the uptake and removal of pharmaceuticals for wastewater treatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 101:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.09.008
Low MJD (1960) Kinetics of chemisorption of gases on solids. Chem Rev 60:267–312. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr60205a003
Marcos C, Argüelles A, Ruíz-Conde A, Sánchez-Soto PJ, Blanco JA (2003) Study of the dehydration process of vermiculites by applying a vacuum pressure: formation of interstratified phases. Mineral Mag 67:1253–1268. https://doi.org/10.1180/0026461036760163
Marcos C, Arango YC, Rodriguez I (2009) X-ray diffraction studies of the thermal behaviour of commercial vermiculites. Appl Clay Sci 42:368–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.03.004
Mareschal L, Ranger J, Turpault MP (2009) Stoichiometry of a dissolution reaction of a trioctahedral vermiculite at pH 2.7. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.09.036
Metcalfe CD, Chu S, Judt C, Li H, Oakes KD, Servos MR, Andrews DM (2010) Antidepressants and their metabolites in municipal wastewater, and downstream exposure in an urban watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.27
Papageorgiou M, Kosma C, Lambropoulou D (2016) Seasonal occurrence, removal, mass loading and environmental risk assessment of 55 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Central Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:547–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.047
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1024. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611
Rivagli E, Pastorello A, Sturini M, Maraschi F, Speltini A, Zampori L, Setti M, Malavasi L, Profumo A (2014) Clay minerals for adsorption of veterinary FQs: behavior and modeling. J Environ Chem Eng 2:738–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.11.017
Ruiz-Conde A, Ruiz-Amil A, Perez-Rodriguez JL, Sanchez-Soto PJ (1996) Dehydration-rehydration in magnesium vermiculite: conversion from two-one and one-two water layer hydration states through the formation of interstratified phases. J Mater Chem 6:1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1039/JM9960601557
Sakharov BA, Lindgreen H, Salyn AL, Drits VA (1999) Mixed-layer kaolinite-illite-vermiculite in North Sea shales. Clay Miner 34:333–334
Santos LH, Araujo AN, Fachini A, Pena A, Delerue-Matos C, Montenegro MC (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.100
Schoonheydt RA, Johnston CT (2006) Surface and interface chemistry of clay minerals. In: Bergaya F, Theng BKG, Lagal G (eds) Handbook of clay science, vol 1. Elsevier
Schultz MM, Furlong ET (2008) Trace analysis of antidepressant pharmaceuticals and their select degradates in aquatic matrixes by LC/ESI/MS/MS. Anal Chem 80:1756–1762. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac702154e
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495
Sposito G, Prost R (1982) Structure of water adsorbed on smectites. Chem Rev 82:553–573. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00052a001
Stawiński W, Freitas O, Chmielarz L, Węgrzyn A, Komędera K, Błachowski A, Figueiredo S (2016) The influence of acid treatments over vermiculite based material as adsorbent for cationic textile dyestuffs. Chemosphere 153:115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.004
Stawiński W, Węgrzyn A, Dańko T, Freitas O, Figueiredo S, Chmielarz L (2017a) Acid-base treated vermiculite as high performance adsorbent: insights into the mechanism of cationic dyes adsorption, regeneration, recyclability and stability studies. Chemosphere 173:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.039
Stawiński W, Węgrzyn A, Freitas O, Chmielarz L, Mordarski G, Figueiredo S (2017b) Simultaneous removal of dyes and metal cations using an acid, acid-base and base modified vermiculite as a sustainable and recyclable adsorbent. Sci Total Environ 576:398–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.120
Stefanova RY (2001) Metal removal by thermally activated clay marl. Journal of environmental science and health Part A, Toxic/hazardous substances & environmental engineering 36:293–306
Styszko K, Nosek K, Motak M, Bester K (2015) Preliminary selection of clay minerals for the removal of pharmaceuticals, bisphenol A and triclosan in acidic and neutral aqueous solutions. C R Chim 18:1134–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2015.05.015
Teng TT, Low LW (2012) Removal of dyes and pigments from industrial effluents. In: Sharma SK, Sanghi R (eds) Advances in water treatment and pollution prevention. Springer Netherlands
Thiebault T, Guégan R, Boussafir M (2015) Adsorption mechanisms of emerging micro-pollutants with a clay mineral: case of tramadol and doxepine pharmaceutical products. J Colloid Interface Sci 453:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.029
Tóth J (1971) Acta Chimica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae 69
Tsai Y-L, Chang PH, Gao ZY, Xu XY, Chen YH, Wang ZH, Chen XY, Yang ZY, Wang TH, Jean JS, Li Z, Jiang WT (2016) Amitriptyline removal using palygorskite clay. Chemosphere 155:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.062
Valcarcel Y, Gonzalez Alonso S, Rodriguez-Gil JL, Gil A, Catala M (2011) Detection of pharmaceutically active compounds in the rivers and tap water of the Madrid region (Spain) and potential ecotoxicological risk. Chemosphere 84:1336–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.014
Walker GF (1961) Vermiculite minerals. In: Brown G (ed) The X-ray identification and crystal structures of clay minerals. Mineral S Great Britain Monogr, Great Britain, pp 297–324
Wan M, Li Z, Hong H, Wu Q (2013) Enrofloxacin uptake and retention on different types of clays. J Asian Earth Sci 77:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.032
Wang C-J, Li Z, Jiang W-T (2011) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on 2:1 dioctahedral clay minerals. Appl Clay Sci 53:723–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.06.014
Worch E (2012) Adsorption technology in water treatment: fundamentals, processes, and modeling. De Gruyter
Funding
Support was provided by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), FEDER under Programme PT2020 (Project UID/QUI/50006/2013--OCI/01/0145/FEDER/007265) and Programme FCT–UT Austin, Emerging Technologies (Project UTAP-ICDT/CTM-NAN/0025/2014) for the financial funding. Stawiński (Labóratorio Associado para Química Verde–Technologia e Processos Limpos–UID/QUI/50006, POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007265) also thanks FCT/MEC for his grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Highlights
• The results prove a successful application of vermiculite for venlafaxine removal.
• Acid-base activation of vermiculite strongly increases its sorption capacity.
• Batch studies demonstrate the feasibility of the process.
• Modified vermiculite may be applied for removal of other cationic species.
• New perspectives arise for this sorbent in wastewater treatment.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, A., Martinho, S., Stawiński, W. et al. Application of vermiculite-derived sustainable adsorbents for removal of venlafaxine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 17066–17076 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1869-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1869-6