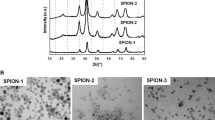
Abstract
Although iron oxide occurs naturally in the environment, iron oxide nanoparticles have distinct mobility, reactivity, and toxicity, which can harm the human health and nature. This scenario has motivated the investigation of the toxic effects of iron oxide nanoparticles (akaganeite predominance + hematite) on the aquatic plant Lemna minor. First, nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized; then, different iron oxide NP concentrations were added to Lemna minor culture. After 7 days, all the Lemna minor leaves died, irrespective of the added NP concentration. The iron oxide NP impact on the plant was evaluated based on malondialdehyde (MDA) production from thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), which was dose-dependent; i.e., lipid peroxidation in the plant increased with rising iron oxide NP concentration. The chlorophyll content decreased at high iron oxide NP concentrations, which disrupted the light absorption mechanism. Fe accumulation in Lemna minor roots also occurred, which can harm nutrient uptake. Therefore, the iron oxide NP toxic impact on plants and related ecosystems requires further studies in order to prevent environmental damage.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kady AS, Gaber M, Hussein MM, Ebeid EZM (2011) Structural and fluorescence quenching characterization of hematite nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 83:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.08.052
Anjum NA, Sofo A, Scopa A et al (2015) Lipids and proteins—major targets of oxidative modifications in abiotic stressed plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4099–4121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3917-1
Asenath-smith E, Estroff LA (2015) Role of akaganeite ( β -FeOOH) in the growth of hematite ( α -Fe 2 O 3 ) in an inorganic silica hydrogel. Cryst Growth Des 15:3388–3398. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b00475
Chernyshova IV, Hochella MF, Madden AS (2007) Size-dependent structural transformations of hematite nanoparticles. 1. Phase transition. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:1736–1750. https://doi.org/10.1039/b618790k
Clément B, Bouvet Y (1993) Assessment of landfill leachate toxicity using the duckweed Lemna minor. Sci Total Environ 134:1179–1190
Colombo C, Palumbo G, Di Iorio E et al (2015) Influence of hydrothermal synthesis conditions on size, morphology and colloidal properties of hematite nanoparticles. Nano-Structures and Nano-Objects 2:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2015.07.004
Cox A, Venkatachalam P, Sahi S, Sharma N (2016) Silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticle toxicity in plants: a review of current research. Plant Physiol Biochem 107:147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.022
da Silva BF, Pérez S, Gardinalli P et al (2011) Analytical chemistry of metallic nanoparticles in natural environments. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 30:528–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.01.008
Dale M, Causton D (1992) Use of the chlorophyll a/b ratio as a bioassay for the light environment of a plant. Funct Ecol 6:190–196. https://doi.org/10.2307/2389754
de la Rosa G, García-Castañeda C, Vázquez-Núñez E et al (2017) Physiological and biochemical response of plants to engineered NMs: implications on future design. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.014
Dinali R, Ebrahiminezhad A, Manley-Harris M et al (2017) Iron oxide nanoparticles in modern microbiology and biotechnology. Crit Rev Microbiol 43:493–507. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2016.1267708
Dissanayake NM, Current KM, Obare SO (2015) Mutagenic effects of Iron oxide nanoparticles on biological cells. Int J Mol Sci 16:23482–23516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023482
dos Reis DA, da Fonseca Santiago A, Nascimento LP, Roeser HMP (2017) Influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors at the bottom sediments in a Doce River tributary in Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7456–7467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8443-5
Drost W, Matzke M, Backhaus T (2007) Heavy metal toxicity to Lemna minor: studies on the time dependence of growth inhibition and the recovery after exposure. Chemosphere 67:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.10.018
Duarte AL, Daboit K, Oliveira MLS, et al (2018) Geoscience Frontiers Hazardous elements and amorphous nanoparticles in historical estuary coal mining area. Geosci Front https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2018.05.005
Emerit J, Beaumont C, Trivin F (2001) Iron, free radicals, and oxidative injury. Biomed Pharmacother 55:333–339 S0753-3322(01)00068-3 [pii]
Escobar H (2015) Mud tsunami wreaks ecological havoc in Brazil. Science (80- ) 350:1138–1139
Fu PP, Xia Q, Hwang HM et al (2014) Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: generation of reactive oxygen species. J Food Drug Anal 22:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.005
Gottschalk F, Sondere T, Schols R, Nowack B (2009) Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials for different regions. Environ Sci Technol 43:9216–9222. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9015553
Gottschalk F, Sun T, Nowack B (2013) Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ Pollut 181:287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.06.003
Gregor C, Hermanek M, Jancik D et al (2010) The effect of surface area and crystal structure on the catalytic efficiency of Iron(III) oxide nanoparticles in hydrogen peroxide decomposition. Eur J Inorg Chem:2343–2351. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200901066
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Cytotoxicity suppression and cellular uptake enhancement of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 26:1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.05.022
Gustafsson Å, Bergström U, Ågren L et al (2015) Differential cellular responses in healthy mice and in mice with established airway inflammation when exposed to hematite nanoparticles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 288:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.07.001
He YT, Wan J, Tokunaga T (2008) Kinetic stability of hematite nanoparticles: the effect of particle sizes. J Nanopart Res 10:321–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9255-1
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hu J, Guo H, Li J et al (2017) Comparative impacts of iron oxide nanoparticles and ferric ions on the growth of Citrus maxima. Environ Pollut 221:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.064
Keck CM, Müller RH (2013) Nanotoxicological classification system (NCS) - a guide for the risk-benefit assessment of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 84:445–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.01.001
Laloi C, Havaux M (2015) Key players of singlet oxygen-induced cell death in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00039
Lei C, Zhang L, Yang K et al (2016) Toxicity of iron-based nanoparticles to green algae: effects of particle size, crystal phase, oxidation state and environmental aging. Environ Pollut:4–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.030
Li J, Hu J, Ma C et al (2016) Uptake , translocation and physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide. Chemosphere 159:326–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.083
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and carotenoids : measurement and characterization by UV-VIS. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, Hoboken
Lu L, Li L, Wang X, Li G (2005) Understanding of the finite size effects on lattice vibrations and electronic transitions of, pp 17151–17156
Maczka E, Kosmulski M (2015) Hematite and hematite – akageneite composites. XRD and electrokinetic study and interaction with ionic surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci 458:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.07.050
Martínez-fernández D, Barroso D, Komárek M (2016) Root water transport of Helianthus annuus L. under iron oxide nanoparticle exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1732–1741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5423-5
Melis A, Harvey GW (1981) Regulation of photosystem stoichiometry, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b content and relation to chloroplast ultrastructure. BBA - Bioenerg 637:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2728(81)90219-X
Miller GW, Pushnik JC, Welkie GW (1984) Iron chlorosis, a world wide problem the relation of chlorophyll biosynthesis to iron. J Plant Nutr 7:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168409363172
Naumann B, Eberius M, Appenroth KJ (2007) Growth rate based dose-response relationships and EC-values of ten heavy metals using the duckweed growth inhibition test (ISO 20079) with Lemna minor L. clone St. J Plant Physiol 164:1656–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2006.10.011
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.006
Oukarroum A, Bras S, Perreault F, Popovic R (2012) Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles in two green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.012
Pariona N, Martinez AI, Hdz-García HM et al (2017) Effects of hematite and ferrihydrite nanoparticles on germination and growth of maize seedlings. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:1547–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.06.004
Pereira EG, Oliva MA, Rosado-Souza L et al (2013) Iron excess affects rice photosynthesis through stomatal and non-stomatal limitations. Plant Sci 201–202:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.12.003
Petering HG, Wolman W, Hibbard RP (1940) Determination of chlorophyll and carotene in plant tissue. Ind Eng Chem - Anal Ed 12:148–151. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50143a011
Petticrew EL, Albers SJ, Baldwin SA et al (2015) The impact of a catastrophic mine tailings impoundment spill into one of North America’s largest fjord lakes: Quesnel Lake, British Columbia, Canada. Geophys Res Lett 42:3347–3355. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL063345
Ramazanov MA, Ahmadov IS, Ramazanli VN, Agayeva NJ (2015) Trends in Nanotechnology & Material Science Effect of nanoparticles on the activity of the electrone ion pumps in plasmatic membrane of plant cells. Trends Nanotechnol Mater Sci 1:1–5
Reddy AVB, Yusop Z, Jaafar J et al (2016) Recent progress on Fe-based nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, characterization and environmental applications. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3537–3553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.035
Ribeiro AR, Leite PE, Falagan-Lotsch P et al (2017) Challenges on the toxicological predictions of engineered nanoparticles. NanoImpact 8:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2017.07.006
Ševců A, El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ, Černík M (2011) Oxidative stress induced in microorganisms by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Microbes Environ 26:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME11126
Tanaka A, Ito H, Tanaka R et al (1998) Chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) is involved in chlorophyll b formation from chlorophyll a. Plant Biol 95:12719–12723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.21.12719
Tsikas D (2017) Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem 524:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Turrens JF (2003) Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J Physiol 552:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049478
Velichkova F, Julcour-Lebigue C, Koumanova B, Delmas H (2013) Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of paracetamol using iron oxide (nano)particles. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1214–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.09.011
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164:645–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(03)00022-0
Voinov MA, Pagán JOS, Morrison E et al (2011) Supporting information for surface-mediated production of hydroxyl radicals as a mechanism of iron oxide nanoparticle biotoxicity. Analysis:1–9
Wang W, Howe JY, Gu B (2008) Structure and morphology evolution of hematite (α-Fe 2 O 3 ) nanoparticles in forced hydrolysis of ferric chloride. J Phys Chem C 112:9203–9208. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp800683j
Wang B, Yin J-J, Zhou X et al (2013) Physicochemical origin for free radical generation of iron oxide nanoparticles in biomicroenvironment-- catalytic activities mediated by surface chemical states.Pdf. J Phys Chem C 117:383–392
Wang T, Zhou S, Zhang C et al (2014) Facile synthesis of hematite nanoparticles and nanocubes and their shape-dependent optical properties. New J Chem 38:46–49. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nj01060k
Zhang Z, He X, Zhang H et al (2011) Uptake and distribution of ceria nanoparticles in cucumber plants. Metallomics 3:816–822. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1mt00049g
Zia-ur-rehman M, Naeem A, Khalid H et al (2018) Responses of plants to iron oxide. In: Tripathi DK, Ahmad P, Sharma S et al (eds) Nanomaterials in plants, algae, and microorganisms, First. Elsevier Inc., Oxford, pp 221–238
Zou XY, Xu B, Yu CP, Zhang HW (2013) Combined toxicity of ferroferric oxide nanoparticles and arsenic to the ciliated protozoa Tetrahymena pyriformis. Aquat Toxicol 134–135:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.03.006
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the research group of Prof. Dr. Luiz Alberto Beraldo de Moraes, from the University of São Paulo, for supplying the Lemna minor samples. We are also grateful to Cynthia M. C. Prado Manso for reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are very grateful to the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the scholarship, Finance Code 001, and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP: 2016/13951-1) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3087 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souza, L.R.R., Bernardes, L.E., Barbetta, M.F.S. et al. Iron oxide nanoparticle phytotoxicity to the aquatic plant Lemna minor: effect on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and chlorophyll a/chlorophyll b ratio. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24121–24131 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05713-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05713-x