Abstract
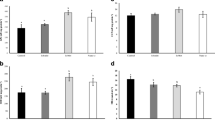
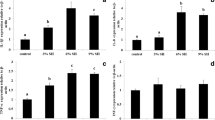
Selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) were added at 0, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg per kg diet to assess its effects on the performance, Se bioaccumulation, blood health, and antioxidant status of red sea bream. After 45 days, Se-NPs positively impacted the growth and feed efficiency of red sea bream especially by 1 mg per kg diet. No significant (P > 0.05) changes in survival and somatic indices were noticed among groups. Dietary Se-NPs significantly (P < 0.05) increased the protein, lipid, and Se contents in the whole body, muscle, and liver tissues, whereas decreasing the whole-body moisture content of treated groups compared with the Se-NP-free group. Using of Se-NPs at 2 mg per kg diet resulted in the highest Se content in the complete body, muscle, and liver. Significantly enhanced intestine protease activity and hematocrit levels accompanied with low cholesterol and triglyceride were observed in fish fed Se-NP-enriched diets. Fish fed on Se-NPs at 0.5, 1, and 2 mg Se-NPs per kg diet exhibited significantly higher values of biological antioxidant potential than the control group (P < 0.05). Therefore, the obtained results recommends adding 1 mg Se-NPs per kg diet to improve the growth, feed efficiency, blood health, and antioxidant defense system of red sea bream.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Mousa MA, Abbass FE (2007) Growth performance and physiological response of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (B.) fed organic selenium prior to the exposure to environmental copper toxicity. Aquaculture 272(1-4):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.09.004
Aliko V, Qirjo M, Sula E, Morina V, Faggio C (2018) Antioxidant defense system, immune response and erythron profile modulation in gold fish, Carassius auratus, after acute manganese treatment. Fish Shellfish Immunol 76:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.02.042
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (1998) Official methods of analysis of official analytical chemists international, 16th edn. AOAC, Washington, DC
Apines MJS, Satoh S, Kiron V, Watanabe T, Aoki T (2003) Availability of supplemental amino acid-chelated trace elements in diets containing tricalcium phosphate and phytate to rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 225(1):431–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00307-7
Ashouri S, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Johari SA, Pasha-Zanoosi H (2015) Effects of different levels of dietary selenium nanoparticles on growth performance, muscle composition, blood biochemical profiles and antioxidant status of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 446:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.04.021
Burgos-Aceves MA, Cohen A, Smith Y, Faggio C (2018) MicroRNAs and their role on fish oxidative stress during xenobiotic environmental exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.001
Celi P, Sullivan M, Evans D (2010) The stability of the reactive oxygen metabolites (d-ROMs) and biological antioxidant potential (BAP) tests on stored horse blood. Vet J 183:217–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2008.09.018
Chaudhary M, Garg AK, Mittal GK, Mudgal V (2010) Effect of organic selenium supplementation on growth, Se uptake, and nutrient utilization in guinea pigs. Biol Trace Elem Res 133(2):217–226
Dawood MAO, Koshio S (2018) Vitamin C supplementation to optimize growth, health and stress resistance in aquatic animals. Rev Aquac 10(2):334–350
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015a) Interaction effects of dietary supplementation of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-glucan on growth performance, digestibility and immune response of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(1):33–42
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015b) Effects of heat killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) supplemental diets on growth performance, stress resistance and immune response of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 442:29–36
Dawood MA, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015c) Effects of partial substitution of fish meal by soybean meal with or without heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) on growth performance, digestibility, and immune response of amberjack, Seriola dumerili juveniles. BioMed Res Int 2015:514196. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/514196
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, El-Sabagh M, Esteban MA, Zaineldin AI (2016a) Probiotics as an environment-friendly approach to enhance red sea bream, Pagrus major growth, immune response and oxidative status. Fish Shellfish Immunol 57:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.08.038
Dawood, M.A., Koshio, S., Ishikawa, M. and Yokoyama, S. (2016b) Immune responses and stress resistance in red sea bream, Pagrus major, after oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and vitamin C. Fish & shellfish immunology, 54:266–275
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama SE, Basuini MF, Hossain MS, Nhu TH, Moss AS, Dossou S, Wei H (2017) Dietary supplementation of β-glucan improves growth performance, the innate immune response and stress resistance of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquac Nutr 23(1):148–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12376
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Esteban MÁ (2018) Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Rev Aquac 10(4):950–974
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Zaineldin AI, Van Doan H, Moustafa EM, Abdel-Daim MM, Esteban MA, Hassaan MS (2019a) Dietary supplementation of selenium nanoparticles modulated systemic and mucosal immune status and stress resistance of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Fish Physiol Biochem 45(1):219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.017
Dawood MAO, Shukry M, Zayed MM, Omar AA, Zaineldin AI, El Basuini MF (2019b) Digestive enzymes, immunity and oxidative status of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared in intensive conditions. Slov Vet Res 56(22-Suppl)
Dossou S, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Dawood MA, El Basuini MF, Olivier A, Zaineldin AI (2018a) Growth performance, blood health, antioxidant status and immune response in red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed Aspergillus oryzae fermented rapeseed meal (RM-Koji). Fish Shellfish Immunol 75:253–262
Dossou S, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Dawood MA, El Basuini MF, El-Hais AM, Olivier A (2018b) Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by fermented rapeseed meal on growth, immune response and oxidative condition of red sea bream juvenile, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 490:228–235
Dossou S, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, El Basuini MF, Zaineldin AI, Mzengereza K, Moss A, Dawood MAO (2019) Effects of replacing fishmeal with fermented and non-fermented rapeseed meal on the growth, immune and antioxidant responses of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Aquac Nutr 25:508–517
El Basuini MF, El-Hais AM, Dawood MAO, Abou-Zeid AES, EL-Damrawy SZ, Khalafalla MMES, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Dossou S (2016) Effect of different levels of dietary copper nanoparticles and copper sulfate on growth performance, blood biochemical profiles, antioxidant status and immune response of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Aquaculture 455:32–40
El Basuini MF, El-Hais AM, Dawood MAO, Abou-Zeid AS, EL-Damrawy SZ, Khalafalla MS, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Dossou S (2017) Effects of dietary copper nanoparticles and vitamin C supplementations on growth performance, immune response and stress resistance of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquac Nutr 23(6):1329–1340. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12508/abstract
Ewan RC (1976) Effect of selenium on rat growth, growth hormone and diet utilization. J Nutr 106:702–709
Faggio C, Pagano M, Alampi R, Vazzana I, Felice MR (2016) Cytotoxicity, haemolymphatic parameters, and oxidative stress following exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of quaternium-15 in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 180:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.10.010
Fattman CL, Schaefer LM, Oury TD (2003) Extracellular superoxide dismutase in biology and medicine. Free Radic Biol Med 35(3):236–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00275-2
Gobi N, Vaseeharan B, Rekha R, Vijayakumar S, Faggio C (2018) Bioaccumulation, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress of the acute exposure selenium in Oreochromis mossambicus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.070
Hao X, Ling Q, Hong F (2014) Effects of dietary selenium on the pathological changes and oxidative stress in loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus). Fish Physiol Biochem 40(5):1313–1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-014-9926-7
Hefnawy AEG, Tórtora-Pérez JL (2010) The importance of selenium and the effects of its deficiency in animal health. Small Rumin Res 89(2):85–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2009.12.042
Hilton JW, Hodson PV, Slinger SJ (1980) The requirement and toxicity of selenium in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Nutr 110(12):2527–2535
Hodkovicova N, Chmelova L, Sehonova P, Blahova J, Doubkova V, Plhalova L, Fiorino E, Vojtek L, Vicenova V, Siroka Z, Enevova V, Berlinska J, Faldyna M, Svobodova Z, Faggio C (2019) The effects of a therapeutic formalin bath on selected immunological and oxidative stress parameters in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Sci Total Environ 653:1120–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.035
Hodson PV, Spry DJ, Blunt BR (1980) Effects on rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) of a chronic exposure to waterborne selenium. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37(2):233–240
Hossain MS, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Sony NM, Dawood MAO, Kader MA, Bulbul M, Fujieda T (2016) Efficacy of nucleotide related products on growth, blood chemistry, oxidative stress and growth factor gene expression of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 464:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.004
Khan KU, Zuberi A, Nazir S, Ullah I, Jamil Z, Sarwar H (2017) Synergistic effects of dietary nano selenium and vitamin C on growth, feeding, and physiological parameters of mahseer fish (Tor putitora). Aquac Rep 5:70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2017.01.002
Kim JH, Kang JC (2014) The selenium accumulation and its effect on growth, and haematological parameters in red sea bream, Pagrus major, exposed to waterborne selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:96–102
Kim JH, Kang JC (2015) Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and non-specific immune responses in juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major, exposed to different waterborne selenium concentrations. Chemosphere 135:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.062
Köhrle J, Brigelius-Flohé R, Böck A, Gärtner R, Meyer O, Flohé L (2000) Selenium in biology: facts and medical perspectives. Biol Chem 381(9-10):849–864
Le KT, Fotedar R (2013) Dietary selenium requirement of yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi). Agric Sci 4(6A):68–75
Lee S, Lee JH, Bai SC (2008) Effects of different levels of dietary selenium (Se) on growth, tissue Se accumulations and histopathological changes in black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Asian-Australian J Anim Sci 21:1794–1799
Lee S, Nambi RW, Won S, Katya K, Bai SC (2016) Dietary selenium requirement and toxicity levels in juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 464:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.06.027
Lemaire P, Drai P, Mathieu A, Lemaire S, Carriere S, Giudicelli J, Lafaurie M (1991) Changes with different diets in plasma enzymes (GOT, GPT, LDH, ALP) and plasma lipids (cholesterol, triglycerides) of sea-bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 93(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(91)90205-L
Lin YH, Shiau SY (2005) Dietary selenium requirements of juvenile grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus. Aquaculture 250(1):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.03.022
Lin CT, Lee TL, Duan KJ, Su JC (2001) Purification and characterization of Black porgy muscle Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. ZOOLOGICAL STUDIES-TAIPEI 40(2):84–90
Lin YH, Shih CC, Kent M, Shiau SY (2010) Dietary copper requirement reevaluation for juvenile grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus, with an organic copper source. Aquaculture 310(1):173–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.10.004
Liu K, Wang XJ, Ai Q, Mai K, Zhang W (2010) Dietary selenium requirement for juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum L. Aquac Res 41(10):e594–e601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02562.x
McCarty LS, Mackay D (1993) Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment. Body residues and modes of toxic action. Environ Sci Technol 27(9):1718–1728
Morganti P, Bruno C, Guarneri F, Cardillo A, Del Ciotto P, Valenzano F (2002) Role of topical and nutritional supplement to modify the oxidative stress. Int J Cosmet Sci 24:331–339
Naderi M, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Ghaedi A (2017a) Combined or individual effects of dietary vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles on humoral immune status and serum parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high stocking density. Aquaculture 474:40–47
Naderi M, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Ghaedi A (2017b) Effects of dietary vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles supplementation on acute stress responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) previously subjected to chronic stress. Aquaculture 473:215–222
Naderi M, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Ghaedi A (2017c) Proteomic analysis of liver tissue from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high rearing density after administration of dietary vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D: Genomics Proteomics 22:10–19
Pacitti D, Lawan MM, Feldmann J, Sweetman J, Wang T, Martin SAM, Secombes CJ (2016) Impact of selenium supplementation on fish antiviral responses: a whole transcriptomic analysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed supranutritional levels of Sel-Plex®. BMC Genomics 17(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2418-7
Pham HD, Fotedar R (2017) Do the dietary ingredients of low-protein formulated diet provide a sufficient selenium source in Australian snapper Pagrus auratus diet (Bloch & Schneider 1801)? Anim Feed Sci Technol 223:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.11.012
Rider SA, Davies SJ, Jha AN, Fisher AA, Knight J, Sweetman JW (2009) Supranutritional dietary intake of selenite and selenium yeast in normal and stressed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): implications on selenium status and health responses. Aquaculture 295:282–291
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra W (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179(4073):588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Saffari S, Keyvanshokooh S, Zakeri M, Johari SA, Pasha-Zanoosi H (2017) Effects of different dietary selenium sources (sodium selenite, selenomethionine and nanoselenium) on growth performance, muscle composition, blood enzymes and antioxidant status of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac Nutr 23(3):611–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12428
Saffari S, Keyvanshokooh S, Zakeri M, Johari SA, Pasha-Zanoosi H, Mozanzadeh MT (2018) Effects of dietary organic, inorganic, and nanoparticulate selenium sources on growth, hemato-immunological, and serum biochemical parameters of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Physiol Biochem 44(4):1087–1097
Salahuddin NA, El-Kemary M, Ibrahim EM (2017) High-performance flexible epoxy/ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Polym Eng Sci 57(9):932–946
Sarkar B, Bhattacharjee S, Daware A, Tribedi P, Krishnani KK, Minhas PS (2015) Selenium nanoparticles for stress-resilient fish and livestock. Nanoscale Res Lett 10(1):371
Shenkin A (2006) Micronutrients in health and disease. Postgrad Med J 82(971):559–567. https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.2006.047670
Shi L, Xun W, Yue W, Zhang C, Ren Y, Liu Q, Wang Q, Shi L (2011) Effect of elemental nano-selenium on feed digestibility, rumen fermentation, and purine derivatives in sheep. Anim Feed Sci Technol 163(2-4):136–142
Song SK, Beck BR, Kim D, Park J, Kim J, Kim HD, Ringø E (2014) Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 40(1):40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.06.016
Tashjian DH, Teh SJ, Sogomonyan A, Hung SS (2006) Bioaccumulation and chronic toxicity of dietary l-selenomethionine in juvenile white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Aquat Toxicol 79(4):401–409
Tatsumi N, Tsuji R, Yamada T, Kubo K, Matsuda T (2000) Spot chem. EZ SP- 4430 no kisotekikento. J Clin Lab Instrum Reagents 23(6):427–433
Wang Y, Han J, Li W, Xu Z (2007) Effect of different selenium source on growth performances, glutathione peroxidase activities, muscle composition and selenium concentration of allogynogenetic crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Anim Feed Sci Technol 134(3):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.12.007
Wang Y, Yan X, Fu L (2013) Effect of selenium nanoparticles with different sizes in primary cultured intestinal epithelial cells of crucian carp, Carassius auratus gibelio. Int J Nanomedicine 8:4007
Wang L, Zhang X, Wu L, Liu Q, Zhang D, Yin J (2018) Expression of selenoprotein genes in muscle is crucial for the growth of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed diets supplemented with selenium yeast. Aquaculture. 492:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.03.054
Watanabe T, Kiron V, Satoh S (1997) Trace minerals in fish nutrition. Aquaculture 151(1):185–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01503-7
Yan J, Li Y, Liang X, Zhang Y, Dawood MAO, Matuli'c D, Gao J (2017) Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth performance, fatty acid composition and antioxidant-related gene expressions in juvenile loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. Aquac Res 48(10):5385–5393. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13352
Yang Q, Yang R, Li M, Zhou Q, Liang X, Elmada ZC (2014) Effects of dietary fucoidan on the blood constituents, anti-oxidation and innate immunity of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellfish Immunol 41(2):264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.09.003
Zaineldin AI, Hegazi S, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Bakr A, El-Keredy AM, Dawood MA, Dossou S, Wang W, Yukun Z (2018) Bacillus subtilis as probiotic candidate for red sea bream: Growth performance, oxidative status, and immune response traits. Fish Shellfish Immunol 79:303–312
Zhou X, Wang Y, Gu Q, Li W (2009) Effects of different dietary selenium sources (selenium nanoparticle and selenomethionine) on growth performance, muscle composition and glutathione peroxidase enzyme activity of crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquaculture 291:78–81
Zhu Y, Chen Y, Liu Y, Yang H, Liang G, Tian L (2012) Effect of dietary selenium level on growth performance, body composition and hepatic glutathione peroxidase activities of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoide. Aquac Res 43(11):1660–1668. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2011.02972
Zhu L, Han D, Zhu X, Yang Y, Jin J, Liu H, Xie S (2016) Dietary selenium requirement for on-growing gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio var. CAS III). Aquac Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 580 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dawood, M.A.O., Koshio, S., Zaineldin, A.I. et al. An evaluation of dietary selenium nanoparticles for red sea bream (Pagrus major) aquaculture: growth, tissue bioaccumulation, and antioxidative responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 30876–30884 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06223-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06223-6