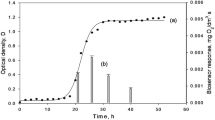
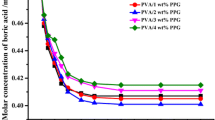
Abstract
A new approach for easy synthesis of Bacillus pseudomycoides immobilized polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/glutaraldehyde (GA) hydrogel for application in a wastewater treatment system is reported. Optimization studies revealed that GA/PVA mass ratio of 0.03 and acidic pH of 2 were required for hydrogel synthesis and eventually for bacterial cell immobilization. The synthesized crosslinked matrix possessed a pore size suitable for microbial cell entrapment while maintaining cell accessibility to external environment for bioremediation. Possible crosslinking and bacterial cell immobilization in the hydrogel were evidenced by FTIR, XRD, and SEM studies, respectively. Further, the extent of crosslinking of GA with PVA was investigated and confirmed by transmittance and permeability experiments. The viability and proliferation of hydrogel embedded cells (after 25 days) was confirmed by confocal fluorescence microscopy which also indicated that acidic pH of polymer solution did not affect the immobilized live cells. B. pseudomycoides immobilized hydrogel were demonstrated to be effective for treatment of municipal wastewater and reduced biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), and protein content below the recommended levels. Overall, the results from this bench-scale work show that employing bacteria-embedded PVA/GA hydrogel for the treatment of municipal wastewater yield promising results which should be further explored in pilot/field-scale studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews S (2010a) FASTQC package. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (last accessed: 21 September 2019)
Andrews S (2010b) Fastq-screen package. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastq_screen/ (last accessed: 21 September 2019)
Aneja KR (2005) Experiments in microbiology, plant pathology and biotechnology. New Age International.
APHA/AWWA/WEF (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater.
Bolto B, Tran T, Hoang M, Xie Z (2009) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog Polym Sci 34:969–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROGPOLYMSCI.2009.05.003
Chanthad C, Wootthikanokkhan J (2006) Effects of crosslinking time and amount of sulfophthalic acid on properties of the sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane. J Appl Polym Sci 101:1931–1936. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23660
Cho KS, Park KJ, Jeong HD, Nam SW, Lee SJ, Park TJ, Kim JK (2006) Characteristics of immobilized PVA beads in nitrate removal. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:414–422
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard J-F, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie J-M, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:W465–W469. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn180
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Figueiredo KCS, Alves TLM, Borges CP (2009) Poly(vinyl alcohol) films crosslinked by glutaraldehyde under mild conditions. J Appl Polym Sci. 111:3074–3080. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29263
Gohil JM, Bhattacharya A, Ray P (2006) Studies on the crosslinking of poly (vinyl alcohol). J Polym Res. 13:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-005-9023-9
Halma M, Mousty C, Forano C, Sancelme M, Besse-Hoggan P, Prevot V (2015) Bacteria encapsulated in layered double hydroxides: towards an efficient bionanohybrid for pollutant degradation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 126:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.11.029
Hosseinzadeh H (2013) Synthesis and swelling properties of a poly(vinyl alcohol)-based superabsorbing hydrogel. Curr Chem Lett 2:153–158. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ccl.2013.05.001
Hsia TH, Feng YJ, Ho CM, Chou WP, Tseng SK (2008) PVA-alginate immobilized cells for anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) process. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 35:721–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0336-7
Jianlong W, Xiangchun Q, Liping H, Yi Q, Hegemann W (2002) Microbial degradation of quinoline by immobilized cells of Burkholderia pickettii. Water Res. 36:2288–2296
Kang MS, Kim JH, Won J, Moon SH, Kang YS (2005) Highly charged proton exchange membranes prepared by using water soluble polymer blends for fuel cells. J Memb Sci. 247:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEMSCI.2004.09.017
Kodavaty J, Deshpande AP (2014) Mechanical and swelling properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) and hyaluronic acid gels used in biomaterial systems—a comparative study. Def Sci J 64:222–129
Labus K, Drozd A, Trusek-Holownia A (2015) Preparation and characterisation of gelatine hydrogels predisposed to use as matrices for effective immobilisation of biocatalysts. Chem Pap 70:523–530. https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0235
Lee J, Cho MH (2010) Removal of nitrogen in wastewater by polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)—immobilization of effective microorganisms. Korean J Chem Eng. 27:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0330-4
Leenen EJTM, Dos Santos VAP, Grolle KCF, Tramper J, Wijffels R (1996) Characteristics of and selection criteria for support materials for cell immobilization in wastewater treatment. Water Res. 30:2985–2996. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00209-6
Li X, Hu A, Ye L (2011) Structure and property of porous polyvinylalcohol hydrogels for microorganism immobilization. J Polym Environ. 19:398–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0289-1
Li J, Deng M, Wang Y, Chen W (2016) Production and characteristics of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus pseudomycoides BS6 utilizing soybean oil waste. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 112:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IBIOD.2016.05.002
Lin H, Yu C-P, Chen Z (2013) Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradation of TNT by newly isolated Bacillus mycoides. Ecol Eng 52:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLENG.2012.11.004
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lozinsky VI, Plieva FM (1998) Poly(vinyl alcohol) cryogels employed as matrices for cell immobilization. 3. Overview of recent research and developments. Enzyme Microb. Technol 23:227–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(98)00036-2
Luo T, Hou S, Yang L, Qi G, Zhao X (2018) Nematodes avoid and are killed by Bacillus mycoides-produced styrene. J Invertebr Pathol 159:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2018.09.006
Ma R, Xiong D (2008) Synthesis and properties of physically crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. J China Univ Min Technol 18:271–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-1266(08)60057-7
Mansur HS, Sadahira CM, Souza AN, Mansur AAP (2008) FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater Sci Eng C 28:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2007.10.088
Marin E, Rojas J, Ciro Y (2014) A review of polyvinyl alcohol derivatives: promising materials for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. African J Pharm Pharmacol 8:674–684. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajpp2013.3906
Minhas M, Ahmad M, Ali L, Sohail M (2013) Synthesis of chemically cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-co-poly (methacrylic acid) hydrogels by copolymerization; a potential graft-polymeric carrier for oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil. DARU J Pharm Sci 21:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-21-44
More SM, Kulkarni RV, Sa B, Kayane NV (2010) Glutaraldehyde-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel discs for the controlled release of antidiabetic drug. J Appl Polym Sci. 116:1732–1738. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.31627
Paula AV, Nunes GFM, de Castro HF, Santos JC (2015) Synthesis of structured lipids by enzymatic interesterification of milkfat and soybean oil in a basket-type stirred tank reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:1731–1737. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie503189e
Pramanik P, Goswami AJ, Ghosh S, Kalita C (2019) An indigenous strain of potassium-solubilizing bacteria Bacillus pseudomycoides enhanced potassium uptake in tea plants by increasing potassium availability in the mica waste-treated soil of north-east India. J Appl Microbiol 126:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14130
Rudra R, Kumar V, Kundu PP (2015) Acid catalysed cross-linking of poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) by glutaraldehyde: effect of crosslink density on the characteristics of PVA membranes used in single chambered microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv 5:83436–83447. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA16068E
Russell AD, Hopwood D (1976) 4 The biological uses and importance of glutaraldehyde. Prog Med Chem 13:271–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6468(08)70140-1
Sayre IM (1988) International standards for drinking water. J Am Water Works Assoc 80:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1551-8833.1988.tb02980.x
Seeponkai N, Wootthikanokkhan J (2007) Proton conductivity and methanol permeability of sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes modified by using sulfoacetic acid and poly(acrylic acid). J Appl Polym0 Sci 105:838–845. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.26116
Shakeel A, Singh A, Das S, Suhag D, Sharma AK, Rajput SK, Mukherjee M (2017) Synthesis and morphological insight of new biocompatible smart hydrogels. J Polym Res 24:113–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1267-7
Sharma N, Gautam N (2008) Antibacterial activity and characterization of bacteriocin of Bacillus mycoides isolated from whey. Indian J Biotechnol 7:117–121
Solmaz KB, Ozcan Y, Dogan NM, Bozkaya O, Ide S (2018) Characterization and production of extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) by Bacillus pseudomycoides U10. Environments 5:63. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5060063
Suhag D, Bhatia R, Das S, Shakeel A, Ghosh A, Singh A, Sinha OP, Chakrabarti S, Mukherjee M (2015) Physically cross-linked pH-responsive hydrogels with tunable formulations for controlled drug delivery. RSC Adv. 5:53963–53972. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA07424J
Talavera G, Castresana J (2007) Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst Biol 56:564–577. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150701472164
Tsai CE, Lin CW, Hwang BJ (2010) A novel crosslinking strategy for preparing poly(vinyl alcohol)-based proton-conducting membranes with high sulfonation. J. Power Sources 195:2166–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2009.10.055
van de Wetering P, Metters AT, Schoenmakers RG, Hubbell JA (2005) Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels formed by conjugate addition with controllable swelling, degradation, and release of pharmaceutically active proteins. J Control Release 102:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.10.029
Varshosaz J, Koopaie N (2002) Cross-linked poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel: study of swelling and drug release behaviour. Iranian Polymer J. 11:123–131
Wu J, Gong X, Fan Y, Xia H (2011) Physically crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with magnetic field controlled modulus. Soft Matter 7:6205. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1sm05386h
Xu X, Cai Y, Song Z, Qiu X, Zhou J, Liu Y, Mu T, Wu D, Guan Y, Xing J (2015) Desulfurization of immobilized sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, Thialkalivibrio versutus, by magnetic nanaoparticles under haloalkaliphilic conditions. Biotechnol Lett 37:1631–1635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1845-x
Yi Y, Kuipers OP (2017) Development of an efficient electroporation method for rhizobacterial Bacillus mycoides strains. J Microbiol Methods 133:82–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2016.12.022
Yi Y, Li Z, Kuipers OP (2018) Plant-microbe interaction: transcriptional response of Bacillus mycoides to potato root exudates. J Vis Exp 137:e57606. https://doi.org/10.3791/57606
Zhang Y, Ye L (2014) Structure and property of polyvinyl alcohol/precipitated silica composite hydrogels for microorganism immobilization. Compos Part B Eng 56:749–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2013.09.015
Zhang Y, Hui B, Ye L (2016) Preparation and structure of poly(vinyl alcohol)/polyacrylate elastomer composite hydrogels and their application in wastewater treatment by immobilizing with microorganisms. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:9934–9943. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02313
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Amity Institute of Biotechnology, Amity University Uttar Pradesh, India for providing the laboratory facilities. We would like to thank Mr. Tufail Ahmad, CIRBSc (CIF), Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi for FTIR and XRD analyses. The authors would also like to acknowledge Dr. Saras Jyoti, Research Associate, Amity Institute of Molecular Medicine & Stem Cell Research, Amity University Uttar Pradesh for confocal fluorescence microscopy. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Funding
Author S. Aggarwal acknowledges support from an early-career research fellowship from the Gulf Research Program of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (USA). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Gulf Research Program of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 734 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrotra, T., Zaman, M.N., Prasad, B.B. et al. Rapid immobilization of viable Bacillus pseudomycoides in polyvinyl alcohol/glutaraldehyde hydrogel for biological treatment of municipal wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 9167–9180 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07296-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07296-z