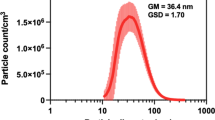
Abstract
With the rapid development in nanoscience and nanotechnology, rare earth oxide nanomaterials (REO-NMs) have been increasingly used due to their unique physical and chemical characteristics. Despite the increasing applications of REO NPs, scarce information is available on their detrimental effects. In the current study, we investigate the toxic effect of ytterbium oxide nanoparticles (Yb2O3 NPs) in mouse model by using various techniques including inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis over 30 days of exposure. Furthermore, we elucidated lung lavage fluid of mice for biochemical and cytological analysis, and lung tissues for histopathology to interpret the NP side effects. We observed a significant concentration of Yb2O3 NPs accumulated in the lung, liver, kidney, and heart tissues. Similarly, increased bioaccumulation of Yb content was found in the olfactory bulb compared to other reigns of brain. The cytological analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) revealed a significant elevation in the percentage of neutrophils and lymphocytes. Biochemical analysis showed an instilled Yb2O3 NPs, showing signs of oxidative damage through up-regulation of 60–87% of MDA while down-regulation of 20–40% of GSH-PX and GSH content. The toxicity pattern was more evident from histopathological observations. These interpretations provide enough evidence of bioaccumulation of Yb2O3 NPs in mice tissues. Overall, our findings reveal that acute exposure of Yb2O3 NPs through intranasal inhalation may cause toxicity via oxidative stress, which leads to a chronic inflammatory response.

Graphical illustrations of experimental findings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeel M, Song X, Wang Y, Francis D, Yang Y (2017) Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: a critical review. Environ Int 99:107–119
Adeel M, Lee JY, Zain M, Rizwan M, Nawab A, Ahmad MA, Shafiq M, Yi H, Jilani G, Javed R, Horton R, Rui Y, Tsang DCW, Xing B (2019a) Cryptic footprints of rare earth elements on natural resources and living organisms. Environ Int 127:785–800
Adeel M, Ma C, Ullah S, Rizwan M, Hao Y, Chen C, Jilani G, Shakoor N, Li M, Wang L, Tsang DCW, Rinklebe J, Rui Y, Xing B (2019b) Exposure to nickel oxide nanoparticles insinuates physiological, ultrastructural and oxidative damage: a life cycle study on Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 254, ISSN 0269-7491:113032
Akanuma S-I, Yamazaki Y, Kubo Y, Hosoya K-I (2018) Role of cationic drug-sensitive transport systems at the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in para-tyramine elimination from rat brain. Fluids Barriers CNS 15:1
Anna Antsiferova MYK, Kochkin VN, Kashkarov PK, Kovalchuk MV (2019) Accumulation of silver nanoparticles in mice brain parts and the harmful effects. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 10(524):1–7
Bakand S, Hayes A (2016) Toxicological considerations, toxicity assessment, and risk management of inhaled nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 17:929
Bona A, Pecho O, Alessandretti R (2015) Zirconia as a dental biomaterial. Materials. 8:4978–4991
Bouzigues C, Gacoin T, Alexandrou A (2011) Biological applications of rare-earth based nanoparticles. ACS Nano 5:8488–8505
Boyes WK, Chen R, Chen C, Yokel RA (2012) The neurotoxic potential of engineered nanomaterials. NeuroToxicology. 33:902–910
Bundschuh M, Filser J, Lüderwald S, Mckee MS, Metreveli G, Schaumann GE, Schulz R, Wagner S (2018) Nanoparticles in the environment: where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ Sci Eur 30:6
Coccini T, Grandi S, Lonati D, Locatelli C, De Simone U (2015) Comparative cellular toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on human astrocyte and neuronal cells after acute and prolonged exposure. NeuroToxicology. 48:77–89
Dumala N, Mangalampalli B, Kalyan Kamal SS, Grover P (2019) Repeated oral dose toxicity study of nickel oxide nanoparticles in Wistar rats: a histological and biochemical perspective. J Appl Toxicol 0
Dunnick KM, Morris AM, Badding MA, Barger M, Stefaniak AB, Sabolsky EM, Leonard SS (2016) Evaluation of the effect of valence state on cerium oxide nanoparticle toxicity following intratracheal instillation in rats. Nanotoxicology. 10:992–1000
Gao C, Jin Y, Jia G, Suo X, Liu H, Liu D, Yang X, Ge K, Liang X-J, Wang S (2018a) Y2O3 nanoparticles caused bone tissue damage by breaking the intracellular phosphate balance in bone marrow stromal cells. ACS Nano 13:313–323
Gao Y, Ma X, Kang F, Yang W, Liu Y, Wang Z, Ma W, Wang Z, Li G, Cao X (2018b) Enhanced Cerenkov luminescence tomography analysis based on Y 2 O 3: Eu 3+ rare earth oxide nanoparticles. Biomed Opt Express 9:6091–6102
Geiser M, Jeannet N, Fierz M, Burtscher H (2017) Evaluating adverse effects of inhaled nanoparticles by realistic in vitro technology. Nanomaterials. 7:49
Han H, Ziegler SF (2013) Bronchoalveolar lavage and lung tissue digestion. Bio-protocol 3(16):e859. https://doi.org/10.21769/bioprotoc.859
Han Y, Lee D-K, Kim S-H, Lee S, Jeon S, Cho W-S (2018) High inflammogenic potential of rare earth oxide nanoparticles: the new hazardous entity. Nanotoxicology. 12:712–728
He X, Zhang H, Ma Y, Bai W, Zhang Z, Lu K, Ding Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2010) Lung deposition and extrapulmonary translocation of nano-ceria after intratracheal instillation. Nanotechnology. 21:285103
Ho E, Galougahi KK, Liu C-C, Bhindi R, Figtree GA (2013) Biological markers of oxidative stress: applications to cardiovascular research and practice. Redox Biol 1(1):483–491
Hochella MF, Mogk DW, Ranville J, Allen IC, Luther GW, Marr LC, Mcgrail BP, Murayama M, Qafoku NP, Rosso KM (2019) Natural, incidental, and engineered nanomaterials and their impacts on the Earth system. Science 363:eaau8299
Kannan S, Sundrarajan M (2015) Biosynthesis of yttrium oxide nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extract. Bull Mater Sci 38:945–950
Kumar V, Choudhary AK, Kumar P, Sharma S (2019) Nanotechnology: nanomedicine, nanotoxicity and future challenges. Nanosci Nanotechnol-Asia 9:64–78
Li R, Ji Z, Chang CH, Dunphy DR, Cai X, Meng H, Zhang H, Sun B, Wang X, Dong J (2014) Surface interactions with compartmentalized cellular phosphates explain rare earth oxide nanoparticle hazard and provide opportunities for safer design. ACS Nano 8:1771–1783
Lin C-H, Liu G-F, Chen J, Chen Y, Lin R-H, He H-X, Chen J-P (2017) Rare-earth nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity on spatial cognition memory of mouse brain. Chin Med J 130:2720
Liu J-H, Ma X, Xu Y, Tang H, Yang S-T, Yang Y-F, Kang D-D, Wang H, Liu Y (2017) Low toxicity and accumulation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice after 270-day consecutive dietary supplementation. Toxicol Res 6:134–143
Ma Y, Kuang L, He X, Bai W, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2010) Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on root elongation of plants. Chemosphere. 78:273–279
Ma L, Zhai X, Du G, Zhou J (2019) Orthogonal shortwave infrared emission based on rare earth nanoparticles for interference-free logical codes and bio-imaging. Chem Sci 10:3281–3288
Mehta A, Singh S, Ganguly NK (1998) Impairment of intestinal mucosal antioxidant defense system during Salmonella typhimurium infection. Dig Dis Sci 43(3):646–651
Mohammed A, Gutta V, Ansari MS, Venkata RS, Jamil K (2017) Altered antioxidant enzyme activity with severity and comorbidities of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in South Indian population. COPD Res Pract 3(1):4
Neacsu IA, Stoica AE, Vasile BS, Andronescu E (2019) Luminescent hydroxyapatite doped with rare earth elements for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials. 9:239
Ober JA (2018) Mineral commodity summaries 2018. US Geological Survey
Ostovan MA, Khanian MS, Hamidi S, Fattahi M, Dehghani P (2016) Spontaneous multi-focal coronary artery spasm: a case report. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res 8(3):137–139
Panyala A, Chinde S, Kumari SI, Grover P (2017a) Assessment of genotoxicity and biodistribution of nano- and micron-sized yttrium oxide in rats after acute oral treatment. J Appl Toxicol 37:1379–1395
Panyala A, Chinde S, Kumari SI, Grover P (2017b) Assessment of genotoxicity and biodistribution of nano-and micron-sized yttrium oxide in rats after acute oral treatment. J Appl Toxicol 37:1379–1395
Panyala A, Chinde S, Kumari SI, Rahman MF, Mahboob M, Kumar JM, Grover P (2019) Comparative study of toxicological assessment of yttrium oxide nano-and microparticles in Wistar rats after 28 days of repeated oral administration. Mutagenesis 34:181–201
Pardridge WM (2011) Drug transport in brain via the cerebrospinal fluid. Fluids Barriers CNS 8:7–7
Peng L, He X, Zhang P, Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang J, Ma Y, Ding Y, Wu Z, Chai Z, Zhang Z (2014) Comparative pulmonary toxicity of two ceria nanoparticles with the same primary size. Int J Mol Sci 15:6072–6085
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A, Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD, Remacle J (1990) Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech Ageing Dev 51(3):283–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-6374(90)90078-t
Saravanan T, Anandan P, Azhagurajan M, Arivanandhan M, Pazhanivel K, Hayakawa Y, Jayavel R (2016) Synthesis and characterization of Y2O3-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for photocatalytic applications. Mater Res Express 3:075502
Sayour H, Kassem S, Canfarotta F, Czulak J, Mohamed M, Piletsky S (2019) Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-modified yttrium oxide nanoparticles for potential theranostic applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13
Sharma V, Saha J, Patnaik S, Kuanr BK (2017) Synthesis and characterization of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) nanoparticles-microwave material. AIP Adv 7:056405
Srinivas A, Rao PJ, Selvam G, Murthy PB, Reddy PN (2011) Acute inhalation toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles in rats. Toxicol Lett 205:105–115
Tao J, Yang Z, Wang J-M, Wang L-C, Luo C, Tang A, Dong Y, Ma H (2007) Shear stress increases Cu/Zn SOD activity and mRNA expression in human endothelial progenitor cells. J Hum Hypertens 21(5):353–358
Teleanu D, Chircov C, Grumezescu A, Volceanov A, Teleanu R (2018) Impact of nanoparticles on brain health: an up to date overview. J Clin Med 7:490
Teng X, Zhu Y, Wei W, Wang S, Huang J, Naccache R, Hu W, Tok AIY, Han Y, Zhang Q (2012) Lanthanide-doped Na × ScF3+ × nanocrystals: crystal structure evolution and multicolor tuning. J Am Chem Soc 134:8340–8343
Teodoro JS, Silva R, Varela AT, Duarte FV, Rolo AP, Hussain S, Palmeira CM (2016) Low-dose, subchronic exposure to silver nanoparticles causes mitochondrial alterations in Sprague–Dawley rats. Nanomedicine. 11:1359–1375
Xue Y, Zhang T, Zhang B, Gong F, Huang Y, Tang M (2016) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by silver nanoparticles in human liver HepG2 cells in different dispersion media. J Appl Toxicol 36:352–360
Yang L, Kuang H, Zhang W, Aguilar ZP, Wei H, Xu H (2017) Comparisons of the biodistribution and toxicological examinations after repeated intravenous administration of silver and gold nanoparticles in mice. Sci Rep 7:3303
Zhang H, Ji Z, Xia T, Meng H, Low-Kam C, Liu R, Pokhrel S, Lin S, Wang X, Liao Y-P (2012a) Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 6:4349–4368
Zhang P, Ma Y, Zhang Z, He X, Guo Z, Tai R, Ding Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2012b) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate/bulk Yb2O3 and YbCl3 to cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Environ Sci Technol 46:1834–1841
Zhou G, Li Y, Ma Y, Liu Z, Cao L, Wang D, Liu S, Xu W, Wang W (2016) Size-dependent cytotoxicity of yttrium oxide nanoparticles on primary osteoblasts in vitro. J Nanopart Res 18:135
Funding
The project was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Nos. 2017YFD0801300 and 2017YFD0801103), the NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund (Grant No. U1401234), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41371471 and 31501791), and the Key National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41130526).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Adeel, Jin Tingting, and Muhammad kashif Irshad designed and performed experiment. Xie Changjian, Muhammad Arslan Ahmad, Yi Hao, Muhammad Adeel, and Tariq Hussain drafted the article. Xiao He, Yukui Rui, Rabia Javed, and Zhang Zhiyong critically evaluated and approved final version of draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adeel, M., Tingting, J., Hussain, T. et al. Bioaccumulation of ytterbium oxide nanoparticles insinuate oxidative stress, inflammatory, and pathological lesions in ICR mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 32944–32953 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09565-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09565-8