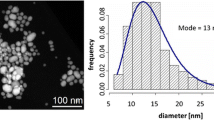
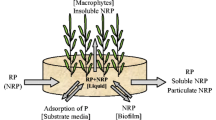
Abstract
This study investigated the effects of AgNPs on pollutant removals in constructed wetlands (CWs) with different flow patterns and spatial distributions of silver. Before exposure to AgNPs, upward flow constructed wetland (UCW) had better nitrogen removal than down-flow CW (DCW). And 0.5 mg/L AgNPs evidently inhibited nitrogen and phosphorus removal, including ammonia, nitrate, and TP (total phosphorus), with average effluent concentrations increasing by 70.83% of NH4+-N in UCW, 18.75% of TP in UCW, and 28.33% and 25.06% of NO3--N in DCW and UCW, respectively, while COD (chemical oxygen demand) was not affected. Moreover, presence of 2 mg/L AgNPs slightly inhibited organic compounds and NH4+-N removal in two systems during stage 4 (dosing 2 mg/L AgNPs). However, the response of NO3--N and TN removal to 2 mg/L AgNPs in two systems were different, and nitrogen concentrations in effluent at the end of stage 4 significantly increased in DCW. Addition of 2 mg/L AgNPs significantly affected TP removal in two systems. Two wetlands showed high removal efficiencies of about 98% on AgNPs, indicating that CWs could provide a feasible approach for ecological restoration of nanoparticles pollution. This study also found that AgNPs mainly accumulated in the upper layer with the Ag content of 17.55–20.26 mg/kg dry weight in sand layer and 7.25–10.85 mg/kg dry weight in gravel layer. Plant roots absorbed AgNPs, with Ag content at 50.80–101.40 mg/kg and bioconcentration factors 2.80–5.00. The obtained results showed that up-flow CWs had better performance and higher resistance to the exposure of AgNPs pollution, compared with down-flow CWs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Auvinen H, Sepulveda VV, Rousseau DPL, Liang GD (2016) Substrate- and plant-mediated removal of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:21920–21926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7459-6
Baalousha M, Nur Y, Romer I, Tejamaya Lead JR (2013) Effect of monovalent and divalent cations, anions and fulvic acid on aggregation of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 454:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.093
Benn TM, Westerhoff P (2008) Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ Sci Technol 42(11):4133–4139. https://doi.org/10.1021/es7032718
Cao C, Huang J, Yan CN, Liu JL, Hu Q, Guan WZ (2018) Shifts of system performance and microbial community structure in a constructed wetland after exposing silver nanoparticles. Chemosphere 199:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.031
Cao C, Huang J, Guo Y, Yan CN, Xiao J, Ma YX, Liu JL, Guan WZ (2019) Long-term effects of environmentally relevant concentration of Ag nanoparticles on the pollutant removal and spatial distribution of silver in constructed wetlands with Cyperus alternifolius and Arundo donax. Environ Pollut 252:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.144
Dan A, Yang Y, Dai YN, Chen CX, Wang SY, Tao R (2013) Removal and factors influencing removal of sulfonamides and trimethoprim from domestic sewage in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 146:363–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.050
Deng H, Yea ZH, Wong MH (2004) Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ Pollut 132:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.03.030
Deshmukhab SP, Patilac SM, Mullania SB, Delekar SD (2019) Silver nanoparticles as an effective disinfectant: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 97:954–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.102
Drizo A, Frost CA, Smith KA (1997) Phosphate and ammonium removal by constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow, using shale as a substrate. Water Sci Technol 35(5):95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00057-7
Ebbs SD, Bradfield SJ, Kumar P, White JC, Musante C, Ma X (2016) Accumulation of zinc, copper, or cerium in carrot (Daucus carota) exposed to metal oxide nanoparticles and metal ions. Environ Sci Nano 3(1):114–126. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5en00161g
Emma J, Wan-Tack I, Dong-Hoon K, Mi-Sun K, Seoktae K, Hang-Sik S, SoRyong C (2014) Different susceptibilities of bacterial community to silver nanoparticles in wastewater treatment systems. J Environ Sci Health A 49:685–693. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2014.865454
Fu GP, Yu TY, Ning KL, Guo ZP, Wong MH (2016) Effects of nitrogen removal microbes and partial nitrification-denitrification in the integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 95:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.054
Gonzalez AG, Mombo S, Leflaive J, Lamy A, Pokrovsky OS, Rols JL (2015) Silver nanoparticles impact phototrophic biofilm communities to a considerably higher degree than ionic silver. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8412–8424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3978-1
Guo Z, Zeng G, Cui K, Chen A (2019) Toxicity of environmental nanosilver: mechanism and assessment. Environ Chem Lett 17:319–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0800-1
Hannele A, Ralf K, Diederik PLR, Gijs DL (2017) Fate of silver nanoparticles in constructed wetlands-a microcosm study. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3285-9
He JZ, Wang DJ, Zhou DM (2019) Transport and retention of silver nanoparticles in soil: effects of input concentration, particle size and surface coating. Sci Total Environ 648:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.136
Huang J, Cao C, Yan CN, Hu Q, Guan WZ (2017a) Impacts of silver nanoparticles on the nutrient removal and functional bacterial community in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 243:1216–1226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.178
Huang X, Zheng J, Liu C, Liu L, Liu Y, Fan H (2017b) Removal of antibiotics and resistance genes from swine wastewater using vertical flow constructed wetlands: effect of hydraulic flow direction and substrate type. Chem Eng J 308:692–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.110
Huang J, Cao C, Yan CN, Guan WZ, Liu JL (2018) Comparison of Iris pseudacorus wetland systems with unplanted systems on pollutant removal and microbial community under nanosilver exposure. Sci Total Environ 624:1336–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.222
Huang J, Xiao J, Guo Y, Guan WZ, Cao C, Yan CN, Wang MY (2020) Long-term effects of silver nanoparticles on performance of phosphorus removal in a laboratory-scale vertical flow constructed wetland. J Environ Sci 87:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.07.012
Kaegi R, Voegelin A, Sinnet B, Zuleeg S, Hagendorfer H, Burkhardt M, Siegrist H (2011) Behavior of metallic silver nanoparticles in a pilot wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 45(9):3902–3908. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1041892
Kittler S, Greulich C, Diendorf J, Koller M, Epple M (2010) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem Mater 22(16):4548–4554. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm100023p
Kropfelova L, Vymazal J, Svehla J, Stichova J (2009) Removal of trace elements in three horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetlands in the Czech Republic. Environ Pollut 157(4):1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.12.003
Li L, Hartmann G, Doblinger M, Schuster M (2013) Quantification of nanoscale silver particles removal and release from municipal wastewater treatment plants in Germany. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7317–7323. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3041658
Li Y, Chen HY, Wang F, Zhao FR, Han XM, Geng HH, Gao L, Chen HL, Yuan RF, Yao J (2018) Environmental behavior and associated plant accumulation of silver nanoparticles in the presence of dissolved humic and fulvic acid. Environ Pollut 243:1334–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.077
Liu XB, Yang XY, Hu XB, He Q, Zhai J, Chen Y, Xiong Q, Vymazal J (2019) Comprehensive metagenomic analysis reveals the effects of silver nanoparticles on nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. Chem Eng J 358:1552–1560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.151
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311(5761):622–627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114397
Nowack B (2010) Nanosilver revisited downstream. Science 330(6007):1054–1055. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1198074
Reinsch BC, Levard C, Li Z, Ma R, Wise A, Gregory KB, Brown GE Jr, Lowry GV (2012) Sulfidation of silver nanoparticles decreases Escherichia coli growth inhibition. Environ Sci Technol 46:6992–7000. https://doi.org/10.1021/es203732x
Sgroi M, Pelissari C, Roccaro P, Sezerino PH, García J, Vagliasindi FGA, Ávila C (2018) Removal of organic carbon, nitrogen, emerging contaminants and fluorescing organic matter in different constructed wetland configurations. Chem Eng J 332:619–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.122
Sheng ZY, Liu Y (2017) Potential impacts of silver nanoparticles on bacteria in the aquatic environment. J Environ Manag 191:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.01.028
Sintubin LS, Gusseme BD, Meeren PV, Pycke BFG, Verstraete W, Boon N (2011) The antibacterial activity of biogenic silver and its mode of action. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3225-3
Sochacki A, Surmacz-Górska J, Faure O, Guy B (2014) Polishing of synthetic electroplating wastewater in microcosm upflow constructed wetlands: effect of operating conditions. Chem Eng J 237:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.015
Soda S, Hamada T, Yamaoka Y, Ike M, Nakazato H, Saeki Y, Kasamatsu T, Sakurai Y (2012) Constructed wetlands for advanced treatment of wastewater with a complex matrix from a metal-processing plant: bioconcentration and translocation factors of various metals in Acorus gramineus and Cyperus alternifolius. Ecol Eng 39:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.11.014
Sotiriou GA, Pratsinis SE (2010) Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ Sci Technol 44(14):5649–5654. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101072s
Tang SY, Liao YH, Xu YC, Dang ZZ, Zhu XF, Ji GD (2020) Microbial coupling mechanisms of nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: a review. Bioresour Technol 314:123759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123759
Tulve NS, Stefaniak AB, Vance ME, Rogers K, Mwilu S, LeBouf RF, Schwegler-Berry D, Willis R, Thomas TA, Marr LC (2015) Characterization of silver nanoparticles in selected consumer products and its relevance for predicting children's potential exposures. Int J Hyg Environ Health 218(3):345–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.02.002
Vogt R, Mozhayeva D, Steinhoff B, Schardt A, Spelz BTF, Philippe A, Kurtz S, Schaumann GE, Engelhard C, Schönherr H, Lamatsch DK, Wanzenböck J (2019) Spatiotemporal distribution of silver and silver-containing nanoparticles in a prealpine lake in relation to the discharge from a wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 696:134034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134034
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380(1-3):48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014
Vymazal J, Březinová T (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals in aboveground biomass of Phragmites australis in horizontal flow constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 290:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.108
Wang YM, Zhou J, Shi SH, Zhou J, He XJ, He L (2021) Hydraulic flow direction alters nutrients removal performance and microbial mechanisms in electrolysis-assisted constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 325:124692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124692
Xiao J, Huang J, Wang MY, Huang MJ, Wang Y (2021) The fate and long-term toxic effects of NiO nanoparticles at environmental concentration in constructed wetland: enzyme activity, microbial property, metabolic pathway and functional genes. J Hazard Mater 413:125295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125295
Xiu ZM, Zhang QB, Puppala HL, Colvin VL, Alvarez PJJ (2012) Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett 12:4271–4275. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl301934w
Yang XY, Chen Y, Guo FH, Liu XB, Su XX, He Q (2020) Metagenomic analysis of the biotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to microbial nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. J Hazard Mater 384:121376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121376
Yazdanbakhsh AR, Rafiee M, Daraei H, Amoozegar MA (2019) Responses of flocculated activated sludge to bimetallic Ag-Fe nanoparticles toxicity: performance, activity enzymatic, and bacterial community shift. J Hazard Mater 366:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.098
Zhang WZ, Yao Y, Li KG, Huang Y, Chen YS (2011) Influence of dissolved oxygen on aggregation kinetics of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 159(12):3757–3762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.013
Zhang ZH, Gao P, Li MQ, Cheng JQ, Liu W, Feng YJ (2016) Influence of silver nanoparticles on nutrient removal and microbial communities in SBR process after long-term exposure. Sci Total Environ 569:234–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.115
Zhang L, Lyu T, Zhang Y, Button M, Arias CA, Weber KP, Brix H, Carvalho PN (2018) Impacts of design configuration and plants on the functionality of the microbial community of mesocosm-scale constructed wetlands treating ibuprofen. Water Res 131:228–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.050
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51479034) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2242016R30008). The work was also supported by “The scientific research foundation of graduate school of Southeast University” (Grant No. YBPY1862).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chong Cao designed the study and analyzed the samples and wrote the manuscript; Juan Huang participated in writing through reviewing and editing; Chun-ni Yan contributed to the writing of the final version of the manuscript; Xin-xin Zhang collected the samples and analyzed the samples. All authors have read and approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All scholarly contributions by other authors, tables, graphs, data sources, etc. are cited properly. No any unethical content is added.
Consent to participate
All authors agree to participate in the revision stage of this paper and will appreciate the comments of editor and reviewers.
Consent for publication
All authors give consent to publish this paper after due process by the editorial board.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, C., Huang, J., Yan, Cn. et al. Hydraulic flow direction alters impacts of AgNPs on pollutant removal and silver spatial distribution in vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 67736–67747 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15350-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15350-y