Abstract
The ban and restriction of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and major brominated flame retardants (BFRs), including hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), due to their confirmed detrimental effects on wildlife and humans have paved the way for the wide application of organophosphate esters (OPEs). OPEs have been extensively used as alternative flame retardants, plasticizer, and antifoaming agents in various industrial and consumer products, which leads to an increase in production, usage, and discharge in the environment. We compile recent information on the production/usage and physicochemical properties of OPEs and discussed and compared the available sample treatment and analysis techniques of OPEs, including extraction, clean-up, and instrumental analysis. The occurrence of OPEs in sediment, aquatic biota, surface, and drinking water is documented. Toxicity, human exposure, and ecological risks of OPEs were summarized; toxicological data of several OPEs shows different adverse health effects on aquatic organisms and humans. Much attention was given to document evidence regarding the bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of OPEs in aquatic organisms. Finally, identified research gaps and avenues for future studies are forwarded.
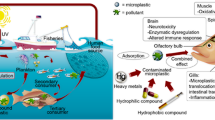
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abafe OA, Martincigh BS (2019) Concentrations, sources and human exposure implications of organophosphate esters in indoor dust from South Africa. Chemosphere 230:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.175
Abbasi G, Saini A, Goosey E, Diamond ML (2016) Product screening for sources of halogenated flame retardants in Canadian house and office dust. Sci Total Environ 545:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.028
Abdallah MAE, Covaci A (2014) Organophosphate flame retardants in indoor dust from Egypt: Implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 48:4782–4789. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501078s
Alaee M, Arias P, Sjödin A, Bergman Å (2003) An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ Int 29:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00121-1
Ali N, Alhakamy NA, Ismail IMI et al (2021) Exposure to phthalate and organophosphate esters via indoor dust and pm10 is a cause of concern for the exposed saudi population. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18042125
Andresen JA, Grundmann A, Bester K (2004) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticisers in surface waters. Sci Total Environ 332:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.021
Arnot JA, Gobas FAPC (2006) A review of bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) assessments for organic chemicals in aquatic organisms. Environ Rev 14:257–297. https://doi.org/10.1139/A06-005
Arukwe A, Carteny CC, Eggen T, Möder M (2018) Novel aspects of uptake patterns, metabolite formation and toxicological responses in Salmon exposed to the organophosphate esters—Tris(2-butoxyethyl)- and tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate. Aquat Toxicol 196:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.014
Behl M, Hsieh JH, Shafer TJ et al (2015) Use of alternative assays to identify and prioritize organophosphorus flame retardants for potential developmental and neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 52:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2015.09.003
Bekele TG, Zhao H, Wang Y et al (2018) Measurement and prediction of bioconcentration factors of organophosphate flame retardants in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.089
Bekele TG, Zhao H, Wang Q, Chen J (2019) Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of emerging organophosphate flame retardants in the marine food webs of Laizhou Bay, North China. Environ Sci Technol 53:13417–13426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03687
Bekele TG, Zhao H, Wang Q (2021) Tissue distribution and bioaccumulation of organophosphate esters in wild marine fish from Laizhou Bay, North China: implications of human exposure via fish consumption. J Hazard Mater 401:123410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123410
Björklund J, Isetun S, Nilsson U (2004) Selective determination of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor air by gas chromatography, positive-ion chemical ionization and collision-induced dissociation mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:3079–3083. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.1721
Borga K, Fjeld E, Kierkegaard A, Mclachlan MS (2013) Consistency in trophic magnification factors of cyclic methyl siloxanes in pelagic freshwater food webs leading to brown trout. Environ Sci Technol 47:1439–1402. https://doi.org/10.1021/es404374j
Brandsma SH, Leonards PEGG, Leslie HA et al (2015) Tracing organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants and plasticizers in an estuarine food web. Sci Total Environ 505:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.072
Cao D, Guo J, Wang Y et al (2017) Organophosphate esters in sediment of the great lakes. Environ Sci Technol 51:1441–1449. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05484
Cao D, Lv K, Gao W et al (2019) Presence and human exposure assessment of organophosphate flame retardants (OPEs) in indoor dust and air in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 169:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.038
Carson R (1962) Silent spring. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin 1962:34–42
Cequier E, Ionas AC, Covaci A et al (2014) Occurrence of a broad range of legacy and emerging flame retardants in indoor environments in Norway. Environ Sci Technol 48:6827–6835. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500516u
Cequier E, Kaur A, Maria R et al (2015) Human exposure pathways to organophosphate triesters — a biomonitoring study of mother–child pairs. Environ Int 75:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.11.009
Chapin RE, Sloane RA, Haseman JK (1997) The relationships among reproductive endpoints in Swiss mice, using the reproductive assessment by continuous breeding database. Fundam Appl Toxicol 38:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1006/faat.1997.2341
Chen D, Letcher RJ, Chu S (2012) Determination of non-halogenated, chlorinated and brominated organophosphate flame retardants in herring gull eggs based on liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1220:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.11.046
Chen M, Jiang J, Gan Z et al (2019) Grain size distribution and exposure evaluation of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in indoor and outdoor dust and PM10 from Chengdu, China. J Hazard Mater 365:280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.082
Choo G, Cho H, Park K et al (2018) Tissue-specific distribution and bioaccumulation potential of organophosphate flame retardants in crucian carp*. Environ Pollut 239:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.104
Chu S, Letcher RJ (2015) Determination of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in lipid-rich matrices using dispersive solid-phase extraction as a sample cleanup step and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass. Anal Chim Acta 885:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.024
CPSC (2017) Commission guidance document on hazardous additive, non-polymeric organohalogen flame retardants in certain consumer products. https://www.cpsc.gov/Business%2D%2DManufacturing/Business-Education/Business-Guidance/flame-retardants. Accessed 10 Jan 2021
Cristale J, Katsoyiannis A, Sweetman AJ et al (2013) Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in the River Aire (UK). Environ Pollut 179:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.001
Cristale J, Hurtado A, Gómez-Canela C, Lacorte S (2016) Occurrence and sources of brominated and organophosphorus flame retardants in dust from different indoor environments in Barcelona, Spain. Environ Res 149:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.05.001
Cristale J, Aragão Belé TG, Lacorte S, de Marchi MRR (2019) Occurrence of flame retardants in landfills: a case study in Brazil. Environ Res 168:420–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.10.010
Cui K, Wen J, Zeng F et al (2017) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in urban soils of the subtropical city, Guangzhou, China. Chemosphere 175:514–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.070
De la Torre A, Navarro I, Sanz P, de los Ángeles Martínez M (2020) Organophosphate compounds, polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in European indoor house dust: use, evidence for replacements and assessment of human exposure. J Hazard Mater 382:121009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121009
Ding J, Shen X, Liu W et al (2015) Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in drinking water from Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 538:959–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.101
Ding J, Xu Z, Huang W et al (2016) Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in human placenta in Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 554–555:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.171
Ding J, Deng T, Xu M et al (2018) Residuals of organophosphate esters in foodstuffs and implication for human exposure. Environ Pollut 233:986–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.092
Dionex ASE (2011) 350 Accelerated solvent extractor operator’s Manual. Document 065207. Sunnyvale, CA, USA
Du Z, Wang G, Gao S, Wang Z (2015) Aryl organophosphate flame retardants induced cardiotoxicity during zebrafish embryogenesis: by disturbing expression of the transcriptional regulators. Aquat Toxicol 161:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.01.027
Endo S, Escher BI, Goss KU (2011) Capacities of membrane lipids to accumulate neutral organic chemicals. Environ Sci Technol 45:5912–5921. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200855w
European Commission (2014) Commission directive 2014/79/EU of 20 June 2014 amending appendix C of annex II to directive 2009/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the council on the safety of toys, as regards TCEP, TCPP and TDCP
Fabiańska MJ, Kozielska B, Konieczyński J, Bielaczyc P (2019) Occurrence of organic phosphates in particulate matter of the vehicle exhausts and outdoor environment – a case study. Environ Pollut 244:351–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.060
Farhat A, Crump D, Chiu S et al (2013) In ovo effects of two organophosphate flame retardants-TCPP and TDCPP-on pipping success, development, mRNA expression, and thyroid hormone levels in chicken embryos. Toxicol Sci 134:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kft100
Fisk AT, Norstrom RJ, Cymbalisty CD, Muir DCG (1998) Dietary accumulation and depuration of hydrophobic organochlorines: bioaccumulation parameters and their relationship with the octanol/water partition coefficient. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:951–961. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170526
Frederiksen M, Stapleton HM, Vorkamp K et al (2018) Dermal uptake and percutaneous penetration of organophosphate esters in a human skin ex vivo model. Chemosphere 197:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.032
Fries E, Püttmann W (2001) Occurrence of organophosphate esters in surface water and ground water in Germany. J Environ Monit 3:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1039/b105072a
Fries E, Püttmann W (2003) Monitoring of the three organophosphate esters TBP, TCEP and TBEP in river water and ground water (Oder, Germany). J Environ Monit 5:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1039/b210342g
Gao Z, Deng Y, Yuan W et al (2014) Determination of organophosphorus flame retardants in fish by pressurized liquid extraction using aqueous solutions and solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-flame photometric detector. J Chromatogr A 1366:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.028
Gao D, Yang J, Bekele TG et al (2019) Organophosphate esters in human serum in Bohai Bay, North China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2721–2729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07204-5
Giulivo M, Capri E, Kalogianni E et al (2017) Occurrence of halogenated and organophosphate flame retardants in sediment and fish samples from three European river basins. Sci Total Environ 586:782–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.056
Gobas FAPC, Opperhuizen A, Hutzinger O (1986) Bioconcentration of hydrophobic chemicals in fish: relationship with membrane permeation. Environ Toxicol Chem 5:637–646. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620050704
Gobas FAPC, De Wolf W, Burkhard LP et al (2009) Revisiting bioaccumulation criteria for POPs and PBT assessments. Integr Environ Assess Manag 5:624–637. https://doi.org/10.1897/IEAM_2008-089.1
Government of Canada (2010) Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (S.C. 2010, c. 21). https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/c-1.68/FullText.html. Accessed 26 Dec 2020
Greaves AK, Letcher RJ (2014) Comparative body compartment composition and in ovo transfer of organophosphate flame retardants in North American Great Lakes herring gulls. Environ Sci Technol 48:7942–7950. https://doi.org/10.1021/es501334w
Greaves AK, Letcher RJ, Chen D et al (2016) Retrospective analysis of organophosphate flame retardants in herring gull eggs and relation to the aquatic food web in the Laurentian Great Lakes of North America. Environ Res 150:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.06.006
Guo J, Venier M, Salamova A, Hites RA (2017) Bioaccumulation of Dechloranes, organophosphate esters, and other flame retardants in Great Lakes fish. Sci Total Environ 583:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.063
Guo H, Zheng X, Ru S et al (2019) Size-dependent concentrations and bioaccessibility of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in indoor dust: a comparative study from a megacity and an e-waste recycling site. Sci Total Environ 650:1954–1960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.340
Gustavsson J, Wiberg K, Ribeli E et al (2018) Screening of organic flame retardants in Swedish river water. Sci Total Environ 625:1046–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.281
Hallanger IG, Sagerup K, Evenset A et al (2015) Organophosphorous flame retardants in biota from Svalbard, Norway. MPB 101:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.049
Han X, Hao Y, Li Y et al (2020) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in the air and soils of Ny-Ålesund and London Island, Svalbard, Arctic. Environ Pollut 263:114495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114495
He CT, Zheng J, Qiao L et al (2015) Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants in indoor dust in multiple microenvironments of southern China and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 133:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.043
He H, Gao Z, Zhu D et al (2017a) Assessing bioaccessibility and bioavailability of chlorinated organophosphorus flame retardants in sediments. Chemosphere 189:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.017
He MJ, Yang T, Yang ZH et al (2017b) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in surface soil and street dust from Chongqing, China: implications for human exposure. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73:349–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0432-7
He C, English K, Baduel C et al (2018a) Concentrations of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in urine from young children in Queensland, Australia and associations with environmental and behavioural factors. Environ Res 164:262–270.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.02.040
He C, Toms LML, Thai P et al (2018b) Urinary metabolites of organophosphate esters: concentrations and age trends in Australian children. Environ Int 111:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.11.019
He MJ, Lu JF, Wei SQ (2019) Organophosphate esters in biota, water, and air from an agricultural area of Chongqing, western China: concentrations, composition profiles, partition and human exposure. Environ Pollut 244:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.085
Heindel JJ, Blumberg B, Cave M et al (2017) Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod Toxicol 68:3–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.10.001
Hou R, Xu Y, Wang Z (2016) Review of OPFRs in animals and humans: absorption, bioaccumulation, metabolism, and internal exposure research. Chemosphere 153:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.003
Hou R, Liu C, Gao X et al (2017) Accumulation and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants (PFRs) and their di-alkyl phosphates (DAPs) metabolites in different freshwater fish from locations around Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 229:548–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.097
Hou L, Jiang J, Gan Z et al (2019) Spatial distribution of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in surface water, sediment, groundwater, and wild fish in Chengdu, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 77:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00624-x
Hou M, Shi Y, Jin Q, Cai Y (2020a) Organophosphate esters and their metabolites in paired human whole blood, serum, and urine as biomarkers of exposure. Environ Int 139:105698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105698
Hou R, Xu Y, Rao K et al (2020b) Tissue-specific bioaccumulation, metabolism and excretion of tris (2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TEHP) in rare minnow (Gobiocyprisrarus). Environ Pollut 261:114245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114245
Hou M, Shi Y, Na G, Cai Y (2021) A review of organophosphate esters in indoor dust, air, hand wipes and silicone wristbands: implications for human exposure. Environ Int 146:106261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106261
Hu M, Li J, Zhang B et al (2014) Regional distribution of halogenated organophosphate flame retardants in seawater samples from three coastal cities in China. Mar Pollut Bull 86:569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.009
Hu YX, Sun YX, Xu WH et al (2017) Organophosphorus flame retardants in mangrove sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 181:433–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.117
Jarema KA, Hunter DL, Shaffer RM et al (2015) Acute and developmental behavioral effects of flame retardants and related chemicals in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 52:194–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2015.08.010
Kajiwara N, Noma Y, Takigami H (2011) Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in selected consumer products on the Japanese market in 2008. J Hazard Mater 192:1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.043
Kelly BC, Ikonomou MG, Blair JD et al (2007) Food web specific biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants. Science (80) 317(5835):236–239. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1138275
Khan MU, Li J, Zhang G, Malik RN (2016) First insight into the levels and distribution of flame retardants in potable water in Pakistan: an underestimated problem with an associated health risk diagnosis. Sci Total Environ 565:346–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.173
Kim UJ, Kannan K (2018) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in surface waters, tap water, and rainwater: implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 52:5625–5633. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00727
Kim JW, Isobe T, Chang KH et al (2011) Levels and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in fishes from Manila Bay, the Philippines. Environ Pollut 159:3653–3659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.020
Kojima H, Takeuchi S, Van den Eede N, Covaci A (2016) Effects of primary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants on transcriptional activity via human nuclear receptors. Toxicol Lett 245:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.01.004
Lai NLS, Kwok KY, Xhong W et al (2019) Assessment of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in aquatic environments of China (Pearl River Delta, South China Sea, Yellow River Estuary) and Japan (Tokyo Bay). J Hazard Mater 371:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.029
Lee S, Jeong W, Kannan K, Moon HB (2016) Occurrence and exposure assessment of organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) through the consumption of drinking water in Korea. Water Res 103:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.034
Lee S, Cho HJ, Choi W, Moon HB (2018) Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in water and sediment: occurrence, distribution, and hotspots of contamination of Lake Shihwa, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 130:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.03.009
Lee JS, Morita Y, Kawai YK et al (2020) Developmental circulatory failure caused by metabolites of organophosphorus flame retardants in zebrafish, Danio rerio. Chemosphere 246:125738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125738
Li J, Yu N, Zhang B et al (2014) Occurrence of organophosphate flame retardants in drinking water from China. Water Res 54:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.031
Li G, Du Y, Liang J et al (2018) Characteristics of gasoline–air mixture explosions with different obstacle configurations. J Energy Inst 91:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2017.01.001
Li J, He J, Li Y et al (2019a) Assessing the threats of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) to drinking water safety based on USEPA oral reference dose (RfD) and oral cancer slope factor (SFO). Water Res 154:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.035
Li J, Zhao L, Letcher RJ et al (2019b) A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions. Environ Int 127:35–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.009
Li Y, Fu Y, Hu K et al (2020) Positive correlation between human exposure to organophosphate esters and gastrointestinal cancer in patients from Wuhan, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 196:110548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110548
Liang Y, Wang H, Yang Q et al (2020) Spatial distribution and seasonal variations of atmospheric organophosphate esters (OPEs) in Tianjin, China based on gridded field observations. Environ Pollut 263:114460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114460
Liu S, Bekele T-G, Zhao H et al (2018a) Bioaccumulation and tissue distribution of antibiotics in wild marine fish from Laizhou Bay. North China Sci Total Environ:631–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.139
Liu YE, Huang LQ, Luo XJ et al (2018b) Determination of organophosphorus flame retardants in fish by freezing-lipid precipitation, solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1532:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.12.001
Liu Y, Luo X, Zapata P et al (2019a) Organophosphorus flame retardants in a typical freshwater food web: Bioaccumulation factors, tissue distribution, and trophic transfer *. Environ Pollut 255:113286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113286
Liu YE, Luo XJ, Huang LQ et al (2019b) Organophosphorus flame retardants in fish from Rivers in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci Total Environ 663:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.344
Luo P, Bao LJ, Guo Y et al (2016) Size-dependent atmospheric deposition and inhalation exposure of particle-bound organophosphate flame retardants. J Hazard Mater 301:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.014
Ma Y, Cui K, Zeng F et al (2013) Microwave-assisted extraction combined with gel permeation chromatography and silica gel cleanup followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 786:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.062
Ma Y, Xie Z, Lohmann R et al (2017) Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in ocean sediments from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 51:3809–3815
Mackintosh CE, Maldonado J, Hongwu J et al (2004) Distribution of phthalate esters in a marine aquatic food web: comparison to polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ Sci Technol 38:2011–2020. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034745r
Makinen MSE, Makinen MRA, Koistinen JTB et al (2009) Respiratory and dermal exposure to organophosphorus flame retardants and tetrabromobisphenol A at five work environments. Environ Sci Technol 43:941–947. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802593t
Marklund A, Andersson B, Haglund P (2003) Screening of organophosphorus compounds and their distribution in various indoor environments. Chemosphere 53:1137–1146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00666-0
Marklund A, Andersson B, Haglund P (2005) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in Swedish sewage treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 39:7423–7429. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051013l
McGoldrick DJ, Letcher RJ, Barresi E et al (2014) Organophosphate flame retardants and organosiloxanes in predatory freshwater fish from locations across Canada. Environ Pollut 193:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.024
MD (2013) Public health - child care products containing flame-retardant chemicals (TCEP) - prohibition. https://mgaleg.maryland.gov/mgawebsite/legislation/details/hb0099?ys=2013rs. Accessed 17 Sep 2020
Meeker JD, Stapleton HM (2010) House dust concentrations of organophosphate flame retardants in relation to hormone levels and semen quality parameters. Environ Health Perspect 118:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901332
Mo L, Zheng J, Wang T et al (2019) Legacy and emerging contaminants in coastal surface sediments around Hainan Island in South China. Chemosphere 215:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.022
Möller A, Sturm R, Xie Z et al (2012) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in airborne particles over the Northern Pacific and Indian Ocean toward the polar regions: Evidence for global occurrence. Environ Sci Technol 46:3127–3134. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204272v
Muir DCG, Yarechewski AL, Grift NP (1983) Environmental dynamics of phosphate esters III. Comparison of the bioconcentration of four triaryl phosphates by fish. Chemosphere 12:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(83)90159-5
Nguyen TMD, Chang S, Condon B et al (2012) Synthesis and characterization of a novel phosphorus-nitrogen-containing flame retardant and its application for textile. Polym Adv Technol 23:1036–1044. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.2008
Noyes PD, Haggard DE, Gonnerman GD, Tanguay RL (2015) Advanced morphological - behavioral test platform reveals neurodevelopmental defects in embryonic zebrafish exposed to comprehensive suite of halogenated and organophosphate flame retardants. Toxicol Sci 145:177–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv044
Pantelaki I, Voutsa D (2019) Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs): a review on analytical methods and occurrence in wastewater and aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 649:247–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.286
Percy Z, Vuong AM, Ospina M et al (2020) Organophosphate esters in a cohort of pregnant women: variability and predictors of exposure. Environ Res 184:109255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109255
Poma G, Glynn A, Malarvannan G et al (2017) Dietary intake of phosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) using Swedish food market basket estimations. Food Chem Toxicol 100:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.12.011
Poma G, Sales C, Bruyland B et al (2018) Occurrence of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers (PFRs) in Belgian foodstuff and estimation of the dietary exposure of the adult population. Environ Sci Technol 52:2331–2338. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06395
Qiao L, Zheng XB, Zheng J et al (2016) Analysis of human hair to assess exposure to organophosphate flame retardants: influence of hair segments and gender differences. Environ Res 148:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.03.032
Quintana JB, Rodil R, Reemtsma T et al (2008) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in water and air II. Analytical methodology TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 27:904–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2008.08.004
REACH (2015) The prohibition of TCEP. https://echa.europa.eu/authorisation-list. Accessed 2 Oct 2020
Reemtsma T, Quintana B, Rodil R et al (2008) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in water and air I. Occurrence and fate. Trends Anal Chem 27:727–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2008.07.002doi:10.1016/j.trac.2008.07.002
Regnery J, Püttmann W (2010) Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in urban and remote surface waters in Germany. Water Res 44:4097–4104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.024
Ren G, Chu X, Zhang J et al (2019) Organophosphate esters in the water, sediments, surface soils, and tree bark surrounding a manufacturing plant in north China. Environ Pollut 246:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.020
Richter BE, Jones BA, Ezzell JL et al (1996) Accelerated solvent extraction: a technique for sample preparation. Anal Chem 68:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9508199
RSD (Research and Statistics Department) (2010) Economic and Industrial Policy Bureau, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Tokyo J Yearbook of Chemical Industry Statistics
Salamova A, Ma Y, Venier M, Hites RA (2013) High levels of organophosphate flame retardants in the Great Lakes atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/ez400034n
Santín G, Eljarrat E, Barceló D (2016) Simultaneous determination of 16 organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in fish by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1441:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.02.058
Schang G, Robaire B, Hales BF (2016) Organophosphate flame retardants act as endocrine-disrupting chemicals in MA-10 mouse tumor Leydig cells. Toxicol Sci 150:499–509
Shi Y, Gao L, Li W et al (2016) Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in urban surface water in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 209:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.008
Shi Q, Wang M, Shi F et al (2018) Developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae. Aquat Toxicol 203:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.08.001
Stasinska A, Heyworth J, Reid A et al (2014) Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) concentrations in plasma of pregnant women from Western Australia. Sci Total Environ 493:554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.001
Su G, Greaves AK, Gauthier L, Letcher RJ (2014) Liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of organophosphate diesters in biotic samples including Great Lakes herring gull plasma. J Chromatogr A 1374:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.11.022
Sun Y, Zhang Z, Xu X et al (2015) Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of halogenated organic pollutants in mangrove biota from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Mar Pollut Bull 99:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.041
Sun R, Luo X, Tang B et al (2017) Bioaccumulation of short chain chlorinated paraffins in a typical freshwater food web contaminated by e-waste in south china: bioaccumulation factors, tissue distribution, and trophic transfer *. Environ Pollut 222:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.060
Sun Y, Guo JQ, Liu LY et al (2020) Seasonal variation and influence factors of organophosphate esters in air particulate matter of a northeastern Chinese test home. Sci Total Environ 740:140048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140048
Sundkvist AM, Olofsson U, Haglund P (2010) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in marine and fresh water biota and in human milk. J Environ Monit 12:943. https://doi.org/10.1039/b921910b
Sutton R, Chen D, Sun J et al (2019) Characterization of brominated, chlorinated, and phosphate flame retardants in San Francisco Bay, an urban estuary. Sci Total Environ 652:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.096
Tang B, Poma G, Bastiaensen M et al (2019) Bioconcentration and biotransformation of organophosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environ Int 126:512–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.063
Teo TLL, Mcdonald JA, Coleman HM, Khan SJ (2015) Analysis of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticisers in water by isotope dilution gas chromatography-electron ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 143:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.091
UNEP (2019) Stockholm convention on POPs, Governments unite to step-up reduction on global DDT reliance and add nine new chemicals under international treaty
USEPA (2014) HPV chemical hazard characterizations. http://iaspub.epa.gov/oppthpv/hpv_hc_characterization.get_report. Accessed 2 Oct 2020
Van Den Eede N, Maho W, Erratico C et al (2013) First insights in the metabolism of phosphate flame retardants and plasticizers using human liver fractions. Toxicol Lett 223:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.08.012
Van den Eede N, Erratico C, Exarchou V et al (2015) In vitro biotransformation of tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate (TBOEP) in human liver and serum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 284:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.01.021
van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Velázquez-Gómez M, Hurtado-Fernández E, Lacorte S (2019) Differential occurrence, profiles and uptake of dust contaminants in the Barcelona urban area. Sci Total Environ 648:1354–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.058
Walters DM, Jardine TD, Cade BS, Kidd KA (2016) Trophic magnification of organic chemicals : a global synthesis. Environ Sci Technol 50:4650–4658. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00201
Wang Y, Kannan K (2018) Concentrations and dietary exposure to organophosphate esters in foodstuffs from Albany, New York, United States. J Agric Food Chem 66:13525–13532. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06114
Wang X, Liu J, Yin YG (2010) The pollution status and research progress on organophosphate esters flame retardants. Prog Chem 22:1983–1992 (in Chinese)
Wang Q, Lai NLS, Wang X et al (2015a) Bioconcentration and transfer of the organophorous flame retardant 1,3-dichloro-2-propyl phosphate causes thyroid endocrine disruption and developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae. Environ Sci Technol 49:5123–5132. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00558
Wang Q, Lam JCW, Man YC et al (2015b) Bioconcentration, metabolism and neurotoxicity of the organophorous flame retardant 1,3-dichloro 2-propyl phosphate (TDCPP) to zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 158:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.11.001
Wang R, Tang J, Xie Z et al (2015c) Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in 40 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea, north China. Environ Pollut 198:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.037
Wang G, Du Z, Chen H et al (2016) Tissue-specific accumulation, depuration, and transformation of triphenyl phosphate (TPHP) in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Technol 50:13555–13564. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04697
Wang G, Chen H, Du Z et al (2017a) In vivo metabolism of organophosphate flame retardants and distribution of their main metabolites in adult zebrafish. Sci Total Environ 590–591:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.038
Wang G, Shi H, Du Z et al (2017b) Bioaccumulation mechanism of organophosphate esters in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 229:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.075
Wang Y, Wu X, Zhang Q et al (2017c) Organophosphate esters in sediment cores from coastal Laizhou Bay of the Bohai Sea China. Sci Total Environ 607–608:103–108
Wang D, Zhu W, Chen L et al (2018a) Neonatal triphenyl phosphate and its metabolite diphenyl phosphate exposure induce sex- and dose-dependent metabolic disruptions in adult mice. Environ Pollut 237:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.047
Wang X, Zhu L, Zhong W, Yang L (2018b) Partition and source identification of organophosphate esters in the water and sediment of Taihu Lake, China. J Hazard Mater 66:13525–13532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.082
Wang Y, Wu X, Zhang Q et al (2018c) Occurrence , distribution , and air-water exchange of organophosphorus fl ame retardants in a typical coastal area of China. Chemosphere 211:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.062
Wang X, Zhong W, Xiao B et al (2019a) Bioavailability and biomagnification of organophosphate esters in the food web of Taihu Lake, China: impacts of chemical properties and metabolism. Environ Int 125:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.018
Wang Y, Yao Y, Li W et al (2019b) A nationwide survey of 19 organophosphate esters in soils from China: spatial distribution and hazard assessment. Sci Total Environ 671:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.335
Wang Q, Zhao H, Bekele TG et al (2020a) Organophosphate esters (OPEs) in wetland soil and Suaeda salsa from intertidal Laizhou Bay. Levels, distribution, and soil-plant transfer model. Sci Total Environ, North China. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142891
Wang X, Zhu Q, Yan X et al (2020b) A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: analysis, occurrence and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 731:139071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139071
Wang Y, Yao Y, Han X et al (2020c) Organophosphate di- and tri-esters in indoor and outdoor dust from China and its implications for human exposure. Sci Total Environ 700:134502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134502
Wei GL, Li DQ, Zhuo MN et al (2015) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ Pollut 196:29–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.012
Weisbrod AV, Burkhard LP, Arnot J et al (2007) Workgroup report: review of fish bioaccumulation databases used to identify persistent, bioaccumlative, toxic substances. Environ Health Perspect 115:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9424
Wolschke H, Sühring R, Xie Z, Ebinghaus R (2015) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the aquatic environment: a case study of the Elbe River, Germany. Environ Pollut 206:488–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.08.002
Wolschke H, Sühring R, Mi W et al (2016) Atmospheric occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizer at the German coast. Atmos Environ 137:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.04.028
Wolschke H, Sühring R, Massei R et al (2018) Regional variations of organophosphorus flame retardants - fingerprint of large river basin estuaries/deltas in Europe compared with China. Environ Pollut 236:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.061
World Health Organization (1991) Triphenyl phosphate. Environmental Health Criteria 111; World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
World Health Organization (1998) Flame retardants: Tris-(chloropropyl) phosphate and tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate. Environmental Health Criteria 209; World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
World Health Organization (2000) Flame retardants: Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate, tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate and tetrakis- (hydroxymethyl) phosphonium salts. Environmental Health Criteria 209; World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Xu F, Giovanoulis G, Van Waes S et al (2016) Comprehensive study of human external exposure to organophosphate flame retardants via air, dust, and hand wipes: the importance of sampling and assessment strategy. Environ Sci Technol 50:7752–7760. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00246
Xu F, Eulaers I, Alves A et al (2019a) Human exposure pathways to organophosphate flame retardants: associations between human biomonitoring and external exposure. Environ Int 127:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.053
Xu L, Hu Q, Liu J et al (2019b) Occurrence of organophosphate esters and their diesters degradation products in industrial wastewater treatment plants in China: implication for the usage and potential degradation during production processing. Environ Pollut 250:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.058
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Zhong G et al (2017) Occurrence and fate of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor air and dust of Nepal: implication for human exposure. Environ Pollut 229:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.089
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Li J et al (2018) Concentration and spatial distribution of organophosphate esters in the soil-sediment profile of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: implication for risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 613–614:502–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.039
Yang J, Zhao Y, Li M et al (2019) A review of a class of emerging contaminants: the classification, distribution, intensity of consumption, synthesis routes, environmental effects and expectation of pollution abatement to organophosphate flame retardants (opfrs). Int J Mol Sci 20:1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122874
Yu L, Jia Y, Su G et al (2017) Parental transfer of tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate and transgenerational inhibition of growth of zebrafish exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Pollut 220:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.039
Yuan S, Li H, Dang Y, Liu C (2018) Effects of triphenyl phosphate on growth, reproduction and transcription of genes of Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 195:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.12.009
Zeng X, Hu Q, He L et al (2018) Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks of organophosphate esters and synthetic musks in sediments from the Hun River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.034
Zha D, Li Y, Yang C, Yao C (2018) Assessment of organophosphate flame retardants in surface water and sediment from a freshwater environment (Yangtze River, China). Environ Monit Assess 190:222
Zhang X, Zou W, Mu L et al (2016) Rice ingestion is a major pathway for human exposure to organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in China. J Hazard Mater 318:686–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.055
Zhang W, Wang P, Zhu Y et al (2020) Occurrence and human exposure assessment of organophosphate esters in atmospheric PM2.5 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111399
Zhao H, Zhao F, Liu J et al (2018) Trophic transfer of organophosphorus flame retardants in a lake food web. Environ Pollut 242:1887–1893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.077
Zhao L, Zhang Y, Deng Y et al (2020) Traditional and emerging organophosphate esters (OPEs) in indoor dust of Nanjing, eastern China: occurrence, human exposure, and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 712:136494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136494
Zhong M, Tang J, Mi L et al (2017) Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the Bohai and Yellow Seas. China Mar Pollut Bull 121:331–338
Zhong M, Wu H, Mi W et al (2018) Occurrences and distribution characteristics of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Sci Total Environ 615:1305–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.272
Zhu H, Al-Bazi MM, Kumosani TA, Kannan K (2020) Occurrence and profiles of organophosphate esters in infant clothing and raw textiles collected from the United States. Environ Sci Technol Lett 7:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00221
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Arba Minch University, Ethiopia (GOV/AMU/TH4/COA/NaRM/01/2010), the National Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Grant 2019-MS-057), and the Petro China Innovation Foundation (2019D-5007-0502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TGB: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, and writing—original draft.
HZ: Funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, and writing—reviewing and editing.
JY: Writing (reviewing and editing) and resources.
RGC: Data curation, investigation, and writing—reviewing and editing.
JC: Project administration, resources, validation, and supervision.
SM: Writing—reviewing and editing.
AQ: Writing—reviewing and editing.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hongwen Sun
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bekele, .G., Zhao, H., Yang, J. et al. A review of environmental occurrence, analysis, bioaccumulation, and toxicity of organophosphate esters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 49507–49528 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15861-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15861-8