Abstract
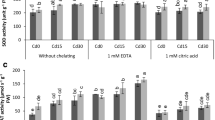
In order to explore the influence of C14 alkane on physiological stress responses, mineral nutrient elements uptake, cadmium (Cd) transfer, and uptake characteristics of Lolium perenne L. (ryegrass), a series of pot trials were conducted which included a moderate level of Cd (2.182 mg·kg−1) without (control) and with five levels of C14 alkane (V/m, 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%). Biomass and Cd content in the root and shoot, chlorophyll content, antioxidant enzymes activity, and mineral nutrient elements in the shoot of ryegrass were determined at the end of the experiment. The results indicated that Cd uptake significantly elevated at 0.1% C14 alkane treatment, then gradually decreased with the increase of C14 alkane concentration. Compared with the control, chlorophyll content was significantly suppressed and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration obviously increased. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and catalase (CAT) activity significantly increased to prevent the C14 alkane stress. With the increase of C14 alkane, the Mn concentration gradually increased; Mg and Fe significantly decreased. Correlation analysis showed that Mn was positively correlated with SOD (with the exception of 2% treatment) and CAT (p < 0.01), and negatively correlated with Cd uptake (p < 0.01). It implied that the increase of Mn induced by C14 alkane stress was an important reason for the decrease of Cd uptake.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that (the/all other) data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Adam G, Duncan H (2002) Influence of diesel fuel on seed germination. Environ Pollut 120:363–370
Agnello AC, Bagard M, van Hullebusch ED, Esposito G, Huguenot D (2016) Comparative bioremediation of heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons co-contaminated soil by natural attenuation, phytoremediation, bioaugmentation and bioaugmentation-assisted phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 563–564:693–703
Ahammed GJ, Li X, Xia X-J, Shi K, Zhou Y-H, Yu J-Q (2015) Enhanced photosynthetic capacity and antioxidant potential mediate brassinosteriod-induced phenanthrene stress tolerance in tomato. Environ Pollut 201:58–66
Ahammed GJ, Wang M-M, Zhou Y-H, Xia X-J, Mao W-H, Shi K, Yu J-Q (2012) The growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant defense responses of five vegetable crops to phenanthrene stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 80:132–139
Alkio M, Tabuchi TM, Wang X, Colón-Carmona A (2005) Stress responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Arabidopsis include growth inhibition and hypersensitive response-like symptoms. J Exp Bot 56:2983–2994
Baruah P, Saikia RR, Baruah PP, Deka S (2014) Effect of crude oil contamination on the chlorophyll content and morpho-anatomy of Cyperus brevifolius (Rottb.) Hassk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12530–12538
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Carvalho MEA, Piotto FA, Franco MR, Rossi ML, Martinelli AP, Cuypers A, Azevedo RA (2019) Relationship between Mg, B and Mn status and tomato tolerance against Cd toxicity. J Environ Manage 240:84–92
Chaney RL, Malik M, Li YM, Brown SL, Brewer EP, Angle JS, Baker AJM (1997) Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:279–284
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153
Chen YX, Lin Q, He YF, Tian GM (2004) Behavior of Cu and Zn under combined pollution of 2,4-dichlorophenol in the planted soil. Plant Soil 261:127–134
Chigbo C, Batty L, Bartlett R (2013) Interactions of copper and pyrene on phytoremediation potential of Brassica juncea in copper–pyrene co-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 90:2542–2548
Choudhary SP, Kanwar M, Bhardwaj R, Gupta BD, Gupta RK (2011) Epibrassinolide ameliorates Cr (VI) stress via influencing the levels of indole-3-acetic acid, abscisic acid, polyamines and antioxidant system of radish seedlings. Chemosphere 84:592–600
Cramer GR, Nowak RS (1992) Supplemental manganese improves the relative growth, net assimilation and photosynthetic rates of salt-stressed barley. Physiol Plantarum 84:600–605
Cui B, Zhang X, Han G, Li K (2016) Antioxidant defense response and growth reaction of amorpha fruticosa seedlings in petroleum-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Poll 227:121
Dong Z-Y, Huang W-H, Xing D-F, Zhang H-F (2013) Remediation of soil co-contaminated with petroleum and heavy metals by the integration of electrokinetics and biostimulation. J Hazard Mater 260:399–408
Gao M, Dong Y, Zhang Z, Song W, Qi Y (2017) Growth and antioxidant defense responses of wheat seedlings to di-n-butyl phthalate and di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate stress. Chemosphere 172:418–428
Gao M, Liu Y, Dong Y, Song Z (2018) Photosynthetic and antioxidant response of wheat to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) contamination in the soil. Chemosphere 209:258–267
Gao Y, Zhu L (2004) Plant uptake, accumulation and translocation of phenanthrene and pyrene in soils. Chemosphere 55:1169–1178
Habibul N, Chen J-J, Hu Y-Y, Hu Y, Yin H, Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q (2019) Uptake, accumulation and metabolization of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide by ryegrass from water: prospects for phytoremediation. Water Res 156:82–91
Harayama S, Kishira H, Kasai Y, Shutsubo K (1999) Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments. J Mol Microb Biotechnol 1:63–70
Heenan DP, Campbell LC (1981) Influence of potassium and manganese on growth and uptake of magnesium by soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr. cv. Bragg). Plant Soil 61:447–456
Hodges DM, DeLong JM, Forney CF, Prange RK (1999) Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 207:604–611
Huang R, Dong M, Mao P, Zhuang P, Paz-Ferreiro J, Li Y, Li Y, Hu X, Netherway P, Li Z (2020) Evaluation of phytoremediation potential of five Cd (hyper)accumulators in two Cd contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ. 721:137581
Li L, Yi H (2012) Effect of sulfur dioxide on ROS production, gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 58:46–53
Li Y, Xie T, Zha Y, Du W, Yin Y, Guo H (2021) Urea-enhanced phytoremediation of cadmium with willow in pyrene and cadmium contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 405:124257
Lichtenthaler H, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Lin Q, Shen K-L, Zhao H-M, Li W-H (2008) Growth response of Zea mays L. in pyrene–copper co-contaminated soil and the fate of pollutants. J Hazard Mater 150:515–521
Liu H, Zhang C, Wang J, Zhou C, Feng H, Mahajan MD, Han X (2017) Influence and interaction of iron and cadmium on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymes in two rice cultivars. Chemosphere 171:240–247
Lu M, Zhang Z-Z, Wang J-X, Zhang M, Xu Y-X, Wu X-J (2014) Interaction of heavy metals and pyrene on their fates in soil and tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Environ Sci Technol 48:1158–1165
McSwain BD, Tsujimoto HY, Arnon DI (1976) Effects of magnesium and chloride ions on light-induced electron transport in membrane fragments from a blue-green alga. BBA-Biomembranes 423:313–322
Millaleo R, Reyes-Díaz M, Ivanov A, Mora M, Alberdi M (2010) Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:470–481
Mitsou K, Koulianou A, Lambropoulou D, Pappas P, Albanis T, Lekka M (2006) Growth rate effects, responses of antioxidant enzymes and metabolic fate of the herbicide Propanil in the aquatic plant Lemna minor. Chemosphere 62:275–284
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Khan MIR, Syeed S, Khan NA (2012) Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Am J Plant Sci 3:1476–1489
Peng K, Luo C, You W, Lian C, Li X, Shen Z (2008) Manganese uptake and interactions with cadmium in the hyperaccumulator—Phytolacca Americana L. J Hazard Mater 154:674–681
Pittman JK (2005) Managing the manganese: molecular mechanisms of manganese transport and homeostasis. New Phytol 167:733–742
Rahman A, Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2016) Manganese-induced cadmium stress tolerance in rice seedlings: coordinated action of antioxidant defense, glyoxalase system and nutrient homeostasis. Cr Biol 339:462–474
Ramos I, Esteban E, Lucena JJ, Gárate, A.n., (2002) Cadmium uptake and subcellular distribution in plants of Lactuca sp. Cd–Mn interaction. Plant Sci 162:761–767
Rees F, Germain C, Sterckeman T, Morel J-L (2015) Plant growth and metal uptake by a non-hyperaccumulating species (Lolium perenne) and a Cd-Zn hyperaccumulator (Noccaea caerulescens) in contaminated soils amended with biochar. Plant Soil 395:57–73
Rojo F (2009) Degradation of alkanes by bacteria. Environ Microbiol 11:2477–2490
Savage KN, Krumholz LR, Gieg LM, Parisi VA, Suflita JM, Allen J, Philp RP, Elshahed MS (2010) Biodegradation of low-molecular-weight alkanes under mesophilic, sulfate-reducing conditions: metabolic intermediates and community patterns. Fems Microbiol Ecol 72:485–495
Shentu J, He Z, Yang X-E, Li T (2008) Accumulation properties of cadmium in a selected vegetable-rotation system of southeastern china. J Agr Food Chem 56:6382–6388
Steliga T, Kluk D (2020) Application of Festuca arundinacea in phytoremediation of soils contaminated with Pb, Ni, Cd and petroleum hydrocarbons. Ecotox Environ Safe 194:110409
Varjani SJ (2017) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour Technol 223:277–286
Wang C, Zhao Y, Zheng R, Ding X, Wei W, Zuo Z, Chen Y (2006) Effects of tributyltin, benzo[a]pyrene, and their mixture on antioxidant defense systems in Sebastiscus marmoratus. Ecotox Environ Safe 65:381–387
Wang J, Chen X, Chi Y, Chu S, Hayat K, Zhi Y, Hayat S, Terziev D, Zhang D, Zhou P (2020) Optimization of NPK fertilization combined with phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated soil by orthogonal experiment. Ecotox Environ Safe 189:109997
Wang K, Zhu Z, Huang H, Li T, He Z, Yang X, Alva A (2012a) Interactive effects of Cd and PAHs on contaminants removal from co-contaminated soil planted with hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. J Soil Sediment 12:556–564
Wang L, Huang X, Ma F, Ho S-H, Wu J, Zhu S (2017) Role of Rhizophagus irregularis in alleviating cadmium toxicity via improving the growth, micro- and macroelements uptake in Phragmites australis. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:3593–3607
Wang P, Zhang S, Wang C, Lu J (2012b) Effects of Pb on the oxidative stress and antioxidant response in a Pb bioaccumulator plant Vallisneria natans. Ecotox Environ Safe 78:28–34
Wang Z, Xu Y, Zhao J, Li F, Gao D, Xing B (2011) Remediation of petroleum contaminated soils through composting and rhizosphere degradation. J Hazard Mater 190:677–685
Xi Y, Song Y, Liu H, Johnson DM, Huang Y (2018) Selenium enhanced degradation of diesel by Erigeron annuus. J Soil Sediment 18:1906–1914
Xia W, Du Z, Cui Q, Dong H, Wang F, He P, Tang Y (2014) Biosurfactant produced by novel Pseudomonas sp. WJ6 with biodegradation of n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mater 276:489–498
Xie W, Li R, Li X, Liu P, Yang H, Wu T, Zhang Y (2018) Different responses to soil petroleum contamination in monocultured and mixed plant systems. Ecotox Environ Safe 161:763–768
Xie W, Zhang Y, Li R, Yang H, Wu T, Zhao L, Lu Z (2017) The responses of two native plant species to soil petroleum contamination in the Yellow River Delta. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24438–24446
Yuan L, Guo P, Guo S, Wang J, Huang Y (2021) Influence of electrical fields enhanced phytoremediation of multi-metal contaminated soil on soil parameters and plants uptake in different soil sections. Environ Res 198:111290
Zembala M, Filek M, Walas S, Mrowiec H, Kornaś A, Miszalski Z, Hartikainen H (2010) Effect of selenium on macro- and microelement distribution and physiological parameters of rape and wheat seedlings exposed to cadmium stress. Plant Soil 329:457–468
Zeng P, Guo Z, Xiao X, Peng C, Liu L, Yan D, He Y (2020) Physiological stress responses, mineral element uptake and phytoremediation potential of Morus alba L. in cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotox Environ Safe 189:109973
Zhang F-Q, Wang Y-S, Lou Z-P, Dong J-D (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere 67:44–50
Zhang H, Jiang Y, He Z, Ma M (2005) Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum). J Plant Physiol 162:977–984
Zhang Z, Rengel Z, Meney K, Pantelic L, Tomanovic R (2011) Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) mediate cadmium toxicity to an emergent wetland species. J Hazard Mater 189:119–126
Zhao Z-Q, Zhu Y-G, Li H-Y, Smith SE, Smith FA (2004) Effects of forms and rates of potassium fertilizers on cadmium uptake by two cultivars of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum, L.). Environ Int 29:973–978
Zhou L, Xia M, Wang L, Mao H (2016) Toxic effect of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Chemosphere 159:420–425
Funding
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019M652453), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977140), Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences) Youth Doctoral Cooperation Fund Project (No. 2018BSHZ0016), and Liao Ning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1802111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lizhu Yuan: performed the experiments, data processing, draft preparation. Penghong Guo: reviewing, revising, editing the manuscript. Shuhai Guo: conceived and designed experiments. Jianing Wang: conceptualization, methodology. Yujie Huang: participated in some tests. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Gangrong Shi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Guo, P., Guo, S. et al. Influence of C14 alkane stress on antioxidant defense capacity, mineral nutrient element accumulation, and cadmium uptake of ryegrass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 13857–13868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16806-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16806-x