Abstract
Purpose
Paulownia, one of the fastest growing broad-leaved tree species in the world, is widely distributed in the warm temperate regions of China. However, there are few commercial-scale Paulownia plantations, and there is only limited information available about the most suitable soil quality for Paulownia fortunei growth in mid-subtropical, Hunan Province, China.
Materials and methods
To understand the effect of the growth of P. fortunei on soil conditions, 25 soil property parameters under Paulownia plantations were studied in Hunan Province, China. Seventy-two standard plots of eight different stand types were analyzed by three statistical approaches to assess soil quality (SQ) in the different P. fortunei plantations.
Results and discussion
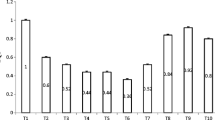
The results revealed that a majority of the soil characteristics when intercropping with oilseed rape and the pure P. fortunei (plantation III) were better than intercropping with Camellia oleifera, orange trees, and Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.). Available calcium, available magnesium, available potassium, available phosphorus, soil thickness, slope, soil organic matter, available sulfur, available copper, dehydrogenase, and available zinc were selected as the minimum data set (MDS). The SQ index (SQI) showed that three classes for soil quality among the eight P. fortunei plantations ranged from 0.48 to 0.88 and these were correlated with standing volume (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
From the results, we concluded that selected MDS indicators can describe the soil fertility quality of P. fortunei plantations, and that the relationship between SQI and standing volume has a biological significance. P. fortunei plantations intercropped with Camellia oleifera, orange trees, and Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) caused a deterioration in SQ, but intercropping oilseed rape and pure P. fortunei plantations produced an improvement in SQ.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews SS, Karlen DL, Mitchell JP (2002) A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric Ecosyst Environ 90:25–45
Arun Jyoti N, Lal R, Das AK (2015) Ethnopedology and soil quality of bamboo (Bambusa sp.) based agroforestry system. Sci Total Environ 521–522:372–379
Barbosa ER, Tomlinson KW, Carvalheiro LG, Kirkman K, de Bie S, Prins HH, van Langevelde F (2014) Short-term effect of nutrient availability and rainfall distribution on biomass production and leaf nutrient content of savanna tree species. Plos One 9:e92619
Bond CR, Maguire RO, Havlin JL (2006) Change in soluble phosphorus in soils following fertilization is dependent on initial Mehlich-3 phosphorus. J Environ Qual 35:1818–1824
Caparrós S, Díaz M, Ariza J, López F, Jiménez L (2008) New perspectives for Paulownia fortunei L. valorisation of the autohydrolysis and pulping processes. Bioresour Technol 99:741–749
Chen M, Cao Z (2015) Genome-wide expression profiling of microRNAs in poplar upon infection with the foliar rust fungus Melampsora larici-populina. BMC Genomics 16:696
Daniels MB, Delaune P, Moore PA, Mauromoustakos A, Chapman SL, Langston JM (2001) Soil phosphorus variability in pastures: implications for sampling and environmental management strategies. J Environ Qual 30:2157–2165
Ditzler CA, Tugel AJ (2002) Soil quality field tools. Agron J 94:33–38
Fox TR (2000) Sustained productivity in intensively managed forest plantations. For Ecol Manag 138:187–202
Franzmeier D, Pedersen E, Longwell T, Byrne J, Losche C (1969) Properties of some soils in the Cumberland Plateau as related to slope aspect and position. Soil Sci Soc Am J 33:755–761
Ge XG, Huang ZL, Cheng RM, Zeng LX, Xiao WF, Tan BW (2012) Effects of litterfall and root input on soil physical and chemical properties in Pinus massoniana plantations in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 23:3301–3308
Gonzalez-Delgado AM, Ashigh J, Shukla MK, Perkins R (2015) Mobility of indaziflam influenced by soil properties in a semi-arid area. Plos One 10:e0126100
Huang ZQ, He ZM, Wan XH, Hu ZH, Fan SH, Yang YS (2013) Harvest residue management effects on tree growth and ecosystem carbon in a Chinese fir plantation in subtropical China. Plant Soil 364:303–314
Hussain I, Olson KR, Wander MM, Karlen DL (1999) Adaptation of soil quality indices and application to three tillage systems in southern Illinois. Soil Tillage Res 50:237–249
Kader M, Lamb DT, Correll R, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2015) Pore-water chemistry explains zinc phytotoxicity in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:252–259
Kandeler E, Gerber H (1988) Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol Fertil Soils 6:68–72
Karlen D, Mausbach M, Doran J, Cline R, Harris R, Schuman G (1997) Soil quality: a concept, definition, and framework for evaluation (a guest editorial). Soil Sci Soc Am J 61:4–10
Lee IS, Kim OK, Chang YY, Bae B, Kim HH, Baek KH (2002) Heavy metal concentrations and enzyme activities in soil from a contaminated Korean shooting range. J Biosci Bioeng 94:406–411
Liebig MA, Varvel G, Doran J (2001) A simple performance-based index for assessing multiple agroecosystem functions. Agron J 93:313–318
Liu A, Ming J, Ankumah RO (2005) Nitrate contamination in private wells in rural Alabama, United States. Sci Total Environ 346:112–120
Lucas-Borja ME, Wic-Baena C, Moreno JL, Dadi T, García C, Andrés-Abellán M (2011) Microbial activity in soils under fast-growing Paulownia (Paulownia elongata & fortunei) plantations in Mediterranean areas. Appl Soil Ecol 51:42–51
Madejon P, Dominguez MT, Diaz MJ, Madejon E (2016) Improving sustainability in the remediation of contaminated soils by the use of compost and energy valorization by Paulownia fortunei. Sci Total Environ 539:401–409
Masto RE, Chhonkar PK, Singh D, Patra AK (2008) Alternative soil quality indices for evaluating the effect of intensive cropping, fertilisation and manuring for 31 years in the semi-arid soils of India. Environ Monit Assess 136:419–435
Morris J, Ningnan Z, Zengjiang Y, Collopy J, Daping X (2004) Water use by fast-growing Eucalyptus urophylla plantations in southern China. Tree Physiol 24:1035–1044
Ngo-Mbogba M, Yemefack M, Nyeck B (2015) Assessing soil quality under different land cover types within shifting agriculture in South Cameroon. Soil Tillage Res 150:124–131
Nielsen B, Albregtsen F, Danielsen HE (2004) Low dimensional adaptive texture feature vectors from class distance and class difference matrices. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:73–84
Ojekanmi AA, Chang SX (2014) Soil quality assessment for peat-mineral mix cover soil used in oil sands reclamation. J Environ Qual 43:1566–1575
Ouyang W, Wei X, Hao F (2013) Long-term soil nutrient dynamics comparison under smallholding land and farmland policy in northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 450–451:129–139
Ownley BH, Duffy BK, Weller DM (2003) Identification and manipulation of soil properties to improve the biological control performance of phenazine-producing Pseudomonas fluorescens. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3333–3343
Peng G, Bing W, Guangcan Z (2013) Influence of sub-surface irrigation on soil conditions and water irrigation efficiency in a cherry orchard in a hilly semi-arid area of northern China. Plos One 8:e73570
Reichmann H, Pette D (1982) A comparative microphotometric study of succinate dehydrogenase activity levels in type I, IIA and IIB fibres of mammalian and human muscles. Histochem 74:27–41
Saaty TL (1994) How to make a decision—the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 24:19–43
Sharpley A (1985) Depth of surface soil-runoff interaction as affected by rainfall, soil slope, and management. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:1010–1015
Sparling GP, Schipper LA (2002) Soil quality at a national scale in New Zealand. J Environ Qual 31:1848–1857
Tsiknia M, Tzanakakis VA, Oikonomidis D, Paranychianakis NV, Nikolaidis NP (2014) Effects of olive mill wastewater on soil carbon and nitrogen cycling. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:2739–2749
Tu J, Shen AR, Wu TL, Wu LC, Wu JP (2013) Effects of different fertilization treatments on stand growth of Paulownia fortunei and soil quality. Hunan For Sci Technol 40:20–24 (in Chinese)
van Gaans PF, Vriend SP, Bleyerveld S, Schrage G, Vos A (1995) Assessing environmental soil quality in rural areas: a base line study in the province of Zeeland, the Netherlands and reflections on soil monitoring network designs. Environ Monit Assess 34:73–102
Wang Q, Shogren JF (1992) Characteristics of the crop-paulownia system in China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 39:145–152
Waskiewicz A (2015) Mineral supplements’ effect on total nutrient intake in Warsaw adult population; cross-sectional assessment. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 66:123–128 (http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.agro-a706f8de-f928-40f9-9aa1-d82bd60f3b31/c/4.pdf)
Wu L, Wang B, Qiao J, Zhou H, Wen R, Xue J, Li Z (2014) Effects of trunk-extension pruning at different intensities on the growth and trunk form of Paulownia fortunei. For Ecol Manag 327:128–135
Xu JW, Zhao HE (1997) Growth analysis of Paulownia high-yield plantation in Heze. Shandong For Sci Technol 109:34–36 (in Chinese)
Xue YJ, Liu SG, Hu YM, Yang JF (2010) Soil quality assessment using weighted fuzzy association rules. Pedosphere 20:334–341
Yanu P, Jakmunee J (2015) Flow injection with in-line reduction column and conductometric detection for determination of total inorganic nitrogen in soil. Talanta 144:263–267
Acknowledgments
We thank all the staff of Xiang Yin County Forestry Bureau and Hunan Forestry Bureau for assistance in the field census. Financial support was partly provided by the National Science and Technology Support Project of China (Grant No. 2015BAD09B0204), the Central Government Forestry S & T Achievement Extension Project of China (Grant No. 2014XT009), and the National Agricultural Science and Technology Achievements Transformation Project of China (Grant No. 2011GB24320015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhiqun Huang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, J., Wang, B., McGrouther, K. et al. Soil quality assessment under different Paulownia fortunei plantations in mid-subtropical China. J Soils Sediments 17, 2371–2382 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1478-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1478-2