Abstract
Purpose
The development of rapid, accurate, and cost-effective methods to determine forest soil properties such as visible and near infrared (Vis-NIR) spectroscopy is important for sustainable land management. The main objective of this study was to assess the suitability of Vis-NIR spectroscopy coupled with partial least squares regression (PLSR) to determine some forest soil properties such as organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), pH, and soil texture (sand, silt, and clay) for a representative forest area in southern Italy.
Materials and methods
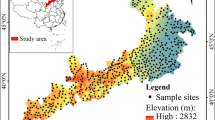
Soil samples (0–20 cm depth) were collected at 267 locations, oven-dried and passed through a 2-mm sieve, and analyzed for some chemical and physical soil properties using conventional laboratory methods. Vis-NIR reflectance of each soil sample was measured in laboratory under artificial light using an ASD FieldSpec IV 350–2500 nm spectroradiometer. Partial least squares regression (PLSR) was used to develop a calibration model for SOC, TN, pH, sand, silt, and clay. Samples were split into a calibration set (187 samples) to develop the models and a validation set (80 samples) to assess the prediction accuracy of the calibration models.
Results and discussion
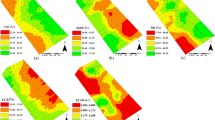
Results showed a good agreement between measured and predicted values with high R 2 and low root mean square error (RMSE) values. Model validation using independent data was satisfactory for all the studied soil properties. Finally, findings confirmed that laboratory Vis–NIR spectroscopy has the potential to be a non-destructive and cost-effective tool for rapid determination of many soil properties.
Conclusions
The spectral data collected in this study could contribute to build a regional soil spectral library to be used advantageously in support to soil survey in other areas of the Calabria region (southern Italy).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARSSA (2003) Carta dei suoli della regione Calabria — scala 1:250000, Monografia divulgativa ARSSA – Agenzia Regionale per lo Sviluppo e per i Servizi in Agricoltura, Servizio Agropedologia, Rubbettino
Barnes RJ, Dhanoa MS, Lister SJ (1989) Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl Spec 43:772–777
Barthes BG, Brunet D, Ferrer H, Chotte JL, Feller C (2006) Determination of total carbon and nitrogen content in a range of tropical soils using near infrared spectroscopy: influence of replication and sample grinding and drying. J Near Infrared Spec 14:341–348
Bellon-Maurel V, Fernandez-Ahumada E, Palagos B, Roger JM, McBratney A (2010) Critical review of chemometric indicators commonly used for assessing the quality of the prediction of soil attributes by NIR spectroscopy. Trends Anal Chem 29:1073–1081
Bellon-Maurel V, McBratney A (2011) Near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopic techniques for assessing the amount of carbon stock in soils—critical review and research perspectives. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1398–1410
Ben-Dor E, Irons JR, Epema GF (1999) Soil reflectance. In: “Remote Sensing for the Earth Sciences” (Rencz AN ed.). Manual of Remote Sensing, vol. 3, Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, pp 111–188
Ben-Dor E (2002) Quantitative remote sensing of soil properties. Adv Agron 75:173–243
Ben-Dor E, Banin A (1995) Near infrared analysis as a rapid method to simultaneously evaluate several soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:364–372
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle-size analyses of soils. Agron J 54:464–465
Brady NC, Weil RR (2002) The nature and properties of soils. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey
Brown DJ, Shepherd KD, Walsh MG, Dewayne Mays M, Reinsch TG (2006) Global soil characterization with VNIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 132:273–290
Brunet D, Barthès B, Chotte JL, Feller C (2007) Determination of carbon and nitrogen contents in Alfisols, Oxisols and Ultisols from Africa and Brazil using NIRS analysis: effects of sample grinding and set heterogeneity. Geoderma 139:106–117
Calcaterra D, Parise M, Dattola L (1996) Caratteristiche dell’alterazione e franosità di rocce granitoidi nel bacino del torrente Alaco (Massiccio della Serre, Calabria). Boll Soc Geol It 115:3–28
Cécillon L, Cassagnec N, Czarnesd S, Grose R, Vennetierf M, Brun JJ (2009) Predicting soil quality indices with near infrared analysis in a wildfire chronosequence. Sci Total Environ 407:1200–1205
Chang CW, Laird DA, Mausbach MJ, Hurburgh CR Jr (2001) Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—principal components regression analysis of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:480–490
Clark RN (1999) Spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Conforti M, Buttafuoco G, Leone AP, Aucelli PPC, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F (2013) Studying the relationship between water-induced soil erosion and soil organic matter using Vis-NIR spectroscopy and geomorphological analysis: a case study in a southern Italy area. Catena 110:44–58
Conforti M, Castrignanò A, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F, Stelluti M, Buttafuoco G (2015a) Laboratory-based Vis-NIR spectroscopy and partial least square regression with spatially correlated errors for predicting soil organic matter content. Catena 124:60–67
Conforti M, Froio R, Matteucci G, Buttafuoco G (2015b) Visible and near infrared spectroscopy for predicting texture in forest soil: an application in Southern Italy. iForest 8:339–347
Conforti M, Lucà F, Scarciglia F, Matteucci G, Buttafuoco G (2016) Soil carbon stock in relation to soil properties and landscape position in a forest ecosystem of southern Italy (Calabria region). Catena 144:23–33
Conforti M, Matteucci G, Buttafuoco G (2017) Organic carbon and total nitrogen topsoil stocks, biogenetic natural reserve “Marchesale” (Calabria region, southern Italy). J Maps 13:91–99
Cozzolino D, Moron A (2003) The potential of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy to analyze soil chemical and physical characteristics. J Agric Sci 140:65–71
Curcio D, Ciraolo G, D’Asaro F, Minacapilli M (2013) Prediction of soil texture distributions using VNIR-SWIR reflectance spectroscopy. Procedia Environ Sci 19:494–503
Demattê JAM, Terra FS (2014) Spectral pedology: a new perspective on evaluation of soils along pedogenetic alterations. Geoderma 217-218:190–200
Demattê JAM, Sousa AA, Alves MC, Nanni MR, Fiorio PR, Campos RC (2006) Determining soil water status and other soil characteristics by spectral proximal sensing. Geoderma 135:179–195
Dwivedi RS (2002) Spatio-temporal characterization of soil degradation. Trop Ecol 43:75–90
Ehsani MR, Upadhyaya SK, Slaughter D, Shafii S, Pelletier M (1999) A NIR technique for rapid determination of soil mineral nitrogen. Precis Agric 1:217–234
Farifteh J, Van Der Meer F, Atzberger C, Carranza EJM (2007) Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: a comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens Environ 110:59–78
Fernandes RBA, Barrón V, Torrent J, Fontes MPF (2004) Quantification of iron oxides in Brazilian latosols by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 28:245–257
Fontes MPF, Carvalho IA Jr (2005) Color attributes and mineralogical characteristics, evaluated by radiometry, of highly weathered tropical soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:1162–1172
Ge Y, Thomasson JA, Morgan CL, Searcy SW (2007) VNIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for agricultural soil property determination based on regression-kriging. T ASABE 50:1081–1092
Gomez C, Lagacherie P, Coulouma G (2008) Continuum removal versus PLSR method for clay and calcium carbonate content estimation from laboratory and airborne hyperspectral measurements. Geoderma 148:141–148
Hill J (1994) Spectral properties of soils and the use of optical remote sensing systems for soil erosion mapping. In: Bidoglio G, Stumm W (eds) Chemistry of aquatic systems: local and global perspectives. ECSC, EEC, EAEC, Brussels and Luxembourg, pp 497–526
Kinoshita R, Moebius-Clune BN, van Es HM, Hively WD, Bilgili AV (2012) Strategies for soil quality assessment using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy in a western Kenya chronosequence. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1779–1788
Konen M, Burras C, Sandor J (2003) Organic carbon, texture, and quantitative color measurement relationships for cultivated soils in north central Iowa. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:1823–1830
Krishnan P, Alexander J, Butler B, Hummel J (1980) Reflectance technique for predicting soil organic matter. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:1282–1285
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 304:1623–1627
Latz K, Wesimiller RA, Van Scoyoc GE, Baumgarnder MF (1984) Characteristic variation in spectral reflectance of selected eroded Alfisols. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:1130–1134
Leone AP, Viscarra-Rossel RA, Amenta P, Buondonno A (2012) Prediction of soil properties with PLSR and vis-NIR spectroscopy: application to Mediterranean soils from Southern Italy. Curr Anal Chem 8:283–299
Lucà F, Conforti M, Castrignanò AM, Matteucci G, Buttafuoco G (2017) Effect of calibration set size on prediction at local scale of soil carbon by Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 288:175–183
Lucà F, Robustelli G, Conforti M, Fabbricatore D (2011) Geomorphological map of the Crotone Province (Calabria, South Italy). J Maps 7:375–390
Martens H, Naes T (1989) Multivariate Calibration. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Næs T, Isaksson T, Fearn T, Davies T (2004) A user-friendly guide to multivariate calibration and classification, Chichester, p Reprinted with corrections. NIR Publications
Nanni MR, Demattê JAM (2006) Spectral reflectance methodology in comparison to traditional soil analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:393–407
Nocita M, Stevens A, Noon C, Van Wesemael B (2013) Prediction of soil organic carbon for different levels of soil moisture using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 199:37–42
Pagliai M (1997) Metodi di Analisi Fisica del Suolo (physical methods of soil analysis). Italian Ministry of Agriculture, Franco Angeli, Milan (in Italian)
Palacios-Orueta A, Ustin SL (1998) Remote sensing of soil properties in the Santa Monica mountains I. Spectral analysis. Remote Sens Environ 65:170–183
Reeves JB, McCarty GW, Reeves VB (2001) Mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for the quantitative analysis of agricultural soils. J Agric Food Chem 49:766–772
Schoenholtz SH, Van Miegroet H, Burger JA (2000) A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: challenges and opportunities. For Ecol Manag 138:335–356
Schwanghart W, Jarmer T (2011) Linking spatial patterns of soil organic carbon to topography—a case study from south-eastern Spain. Geomorphology 126:252–263
Shepherd KD, Walsh MG (2002) Development of reflectance spectral libraries for characterization of soil properties. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:988–998
Six J, Callewaert P, Lenders S, Degryze S, Morris SJ, Gregorich EG, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002) Measuring and understanding carbon storage in afforested soils by physical fractionation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1981–1987
Sorensen LK, Dalsgaard S (2005) Determination of clay and other soil properties by near infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:159–167
Stenberg B, Viscarra Rossel RA, Mouazen AM, Wetterlind J (2010) Visible and near infrared spectroscopy in soil Science. Adv Agron 107:163–215
Stevens A, Nocita M, Tóth G, Montanarella L, Van Wesemael B (2013) Prediction of soil organic carbon at the European scale by visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. PLoSOne 8:e66409
Stevens A, Wesemael B, Vandenschrick G, Touré S, Tychon B (2006) Detection of carbon stock change in agricultural soils using spectroscopic techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:844–850
Telles ECC, Camargo PB, Martinelli LA, Trumbore SE, Costa ES, Santos J, Higuchi N, Oliveira RCJ (2003) Influence of soil texture on carbon dynamics and storage potential in tropical forest soils of Amazonia. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 17:1040
Tian Y, Zhang J, Yao X, Cao W, Zhu Y (2013) Laboratory assessment of three quantitative methods for estimating the organic matter content of soils in China based on visible/near-infrared reflectance spectra. Geoderma 202–203:161–170
Udelhoven T, Emmerling C, Jarmer T (2003) Quantitative analysis of soil chemical properties with diffuse reflectance spectrometry and partial least-square regression: a feasibility study. Plant Soil 251:319–329
USDA (2010) Keys to soil taxonomy, 11th edit. Soil Survey Staff. USDA, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, DC, p 372
Varmuza K, Filzmoser P (2009) Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis in chemometrics. Taylor & Francis - CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 336
Vendrame PRS, Marchao RL, Brunet D, Becquer T (2012) The potential of NIR spectroscopy to predict soil texture and mineralogy in Cerrado.Latosols. Eur J Soil Sci 6:743–753
Violante P (2000) Metodi di Analisi Chimica del Suolo (Chemical methods of soil analysis). Italian Ministry of Agriculture, Franco Angeli, Milan (in Italian)
Viscarra Rossel RA (2008) ParLeS: software for chemometric analysis of spectroscopic data. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 90:72–83
Viscarra Rossel RA, Walvoort DJJ, McBratney AB, Janik LJ, Skjemstad JO (2006) Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 131:59–75
Volkan Bilgili A, Van Es HM, Akbas F, Durak A, Hively WD (2010) Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for assessment of soil properties in a semiarid area of Turkey. J Arid Environ 74:229–238
White K, Walden J, Drake N, Eckardt F, Settle J (1997) Mapping the iron oxide content of dune sands, Namib Sand Sea, Namibia, using Landsat Thematic Mapper data. Remote Sens Environ 62:30–39
Yang H, Griffiths PR, Tate JD (2003) Comparison of partial least squares regression and multi-layer neural networks for quantification of nonlinear systems and application to gas phase Fourier transform infrared spectra. Anal Chim Acta 489:125–136
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the projects LIFE09 ENV/IT/000078 ManFor C.BD. “Managing forests for multiple purposes: carbon, biodiversity and socio-economic wellbeing” and PONa3_00363 Infrastruttura AMICA: “Infrastruttura di Alta Tecnologia per il Monitoraggio Integrato Climatico-Ambientale.”
The authors thank the reviewers for providing constructive comments, which have contributed to the improvement of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jun Zhou
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conforti, M., Matteucci, G. & Buttafuoco, G. Using laboratory Vis-NIR spectroscopy for monitoring some forest soil properties. J Soils Sediments 18, 1009–1019 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1766-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1766-5