Abstract
Purpose
Although biological nitrogen fixation is an important nitrogen source for agroecosystem, the knowledge of their response to long-term fertilization under neutral soil is limited. The aims of this study were to explore the effects of different fertilization treatments on diversity and compositions of diazotrophic community in a neutral black soil in northeast China.
Materials and methods
The long-term fertilization experiment under monoculture maize was established in a neutral black soil since 1979. Soil samples from four treatments were collected in September 2014: non-fertilization (NoF), chemical fertilization (CF), manure fertilization (M), and chemical fertilization plus manure (CFM). qPCR and Illumina MiSeq sequencing were used to assess the abundance and compositions of diazotrophic community targeting nifH gene.
Results and discussion
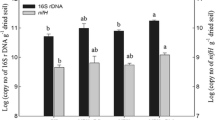
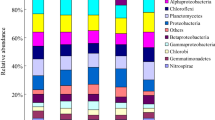
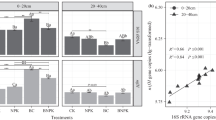
M treatment significantly increased the nifH gene abundance, but inverse trends were found in the CF and CFM treatments when compared with NoF. The diazotrophic community was overwhelmingly dominated by Alphaproteobacteria with relative higher abundance in manure-added treatments. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) indicated that the total diazotrophic community was separated into two groups with and without manure addition, and soil available P was the most influential factor on the changes of diazotrophic community.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that soil nutrients rather than soil pH were the main influential factors on the changes of diazotrophic communities and manure addition had a greater effect than chemical fertilization on diazotrophic community structure in neutral black soil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron AR, Wurzburger N, Bellenger JP, Wright SJ, Kraepiel AML, Hedin L (2008) Molybdenum limitation of asymbiotic nitrogen fixation in tropical forest soils. Nat Geosci 2:42–45
Belnap J (2002) Nitrogen fixation in biological soil cursts from southeast Utah, USA. Biol Fertil Soils 35:128–135
Berthrong ST, Yeager CM, Gallegos-Graves L, Steven B, Eichorst SA, Jackson RB (2014) Nitrogen fertilization has a stronger effect on soil nitrogen-fixing bacterial communities than elevated atmospheric CO2. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:3103–3112
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Coelho MRR, de Vos M, Carneiro NP, Marriel IE, Paiva E, Seldin L (2008) Diversity of nifH gene pools in the rhizosphere of two cultivars of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) treated with contrasting levels of nitrogen fertilizer. FEMS Microbiol Lett 279:15–22
Coelho MRR, Marriel IE, Jenkins SN, Lanyon CV, Seldin L, O’Donnell AG (2009) Molecular detection and quantification of nifH gene sequences in the rhizosphere of sorghum (Sorghum biocolor) sown with two levels of nitrogen fertilizer. Appl Soil Ecol 42:48–53
De Cáceres M, Legendre P, Moretti M (2010) Improving indicator species analysis by combining groups of sites. Oikos 119:1674–1684
DeLuca TH, Drinkwater LE, Wiefing BA, DeNicola DM (1996) Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria in temperate cropping systems: influence of nitrogen source. Biol Fertil Soils 23:140–144
Dufrêne M, Legendre P (1997) Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecol Monogr 67:345–366
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Eilers KG, Lauber CL, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Shifts in bacterial community structure associated with inputs of low molecular weight carbon compounds to soil. Soil Biol Biochem 42:896–903
Epstein W (2003) The roles and regulation of potassium in bacteria. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Bio 75:293
Fish JA, Chai B, Wang Q, Sun Y, Brown CT, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2013) FunGene: the functional gene pipeline and repository. Front Microbiol 4:291
Francioli D, Schulz E, Lentendu G, Wubet T, Buscot F, Reitz T (2016) Mineral vs. organic amendments: microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front Microbiol 7:289
García-Orenes F, Roldán A, Morugán A, Pérez CL, Cerdà A, Caravaca F (2016) Organic fertilization in traditional Mediterranean grapevine orchards mediates changes in soil microbial community structure and enhances soil fertility. Land Degrad Dev 27:1622–1628
Geisseler D, Scow KM (2014) Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—a review. Soil Biol Biochem 75:54–63
Guan TY, Holley RA (2003) Pathogen survival in swine manure environments and transmission of human enteric illness—a review. J Environ Qual 32:383–392
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Goulding KWT, Vitousek PM, Zhang FS (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327:1008–1010
Halbleib CM, Ludden PW (2000) Regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. J Nutr 130:1081–1084
Hamman S, Burke IC, Stromberger ME (2007) Relationships between microbial community structure and soil environmental conditions in a recently burned system. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1703–1711
Hsu SF, Buckley DH (2009) Evidence for the functional significance of diazotroph community structure in soil. ISME J 3:124–136
Hu X, Liu J, Wei D, Zhu P, Cui X, Zhou B, Chen X, Jin J, Liu X, Wang G (2017) Effects of over 30-year of different fertilization regimes on fungal community compositions in the black soils of northeast China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 248:113–122
Juraeva D, George E, Davranov K, Ruppel S (2006) Detection and quantification of the nifH gene in shoot and root of cucumber plants. Can J Microbiol 52:731–739
Kellar PE, Goldman CR (1979) A comparative study of nitrogen fixation by the Anabaena-Azolla symbiosis and free-living populaltions of Anabaena spp. Oecologia 43:269–281
Kuczynski J, Liu Z, Lozupone C, McDonald D, Fiere N, Knight R (2010) Microbial community resemblance methods differ in their ability to detect biologically relevant patterns. Nat Methods 7:813–819
Kumar U, Panneerselvam P, Govindasamy V, Vithalkumar L, Senthilkumar M, Banik A, Annapurna K (2017) Long-term aromatic rice cultivation effect on frequency and diversity of diazotrophs in its rhizosphere. Ecol Eng 10:227–236
Lassaletta L, Billen G, Grizzetti B, Anglade J, Garnier J (2014) 50 year trends in nitrogen use efficiency of world cropping systems: the relationship between yield and nitrogen input to cropland. Environ Res Lett 9:105011
Liang Q, Chen H, Gong Y, Fan M, Yang H, Lal R, Kuzyakov Y (2012) Effects of 15 years of manure and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon fractions in a wheat-maize system in the North China Plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 92:21–33
Limmer C, Drake HL (1996) Non-symbiotic N2-fixation in acidic and pH-neutral forest soils: aerobic and anaerobic differentials. Soil Biol Biochem 28:177–183
Ludwig B, Geisseler G, Michel K, Joergensen RG, Schulz E, Merbach I, Raupp J, Rauber R, Hu K, Niu L, Liu X (2011) Effect of fertilization and soil management on crop yields and carbon stabilization in soils. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 31:361–372
Luo G, Shi Z, Wang H, Wang G (2012) Skermanella stibiiresistens sp. nov., a highly antimony-resistant bacterium isolated from coal-mining soil, and emended description of the genus Skermanella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1271–1276
Mårtensson L, Díez B, Wartiainen I, Zheng W, El-Shehawy R, Rasmussen U (2009) Diazotrophic diversity, nifH gene expression and nitrogenase activity in a rice paddy field in Fujian, China. Plant Soil 325:207–218
Meng X, Wang L, Long X, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zed R (2012) Influence of nitrogen fertilization on diazotrophic communities in the rhizosphere of the Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) Res Microbiol 163:349–356
Milligan GW (1985) Cluster-analysis for researchers—Romesburg, Hc. J Classif 2:133–137
Mirza BS, Potisap C, Nüsslein K, Bohannan BJ, Rodrigues JL (2014) Response of free-living nitrogen-fixing microorganisms to land use change in the Amazon rainforest. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:281–288
Orr CH, James A, Leifert C, Cooper JM, Cummings SP (2011) Diversity and activity of free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria and total bacteria in organic and conventionally managed soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:911–919
Orr CH, Leifert C, Cumings SP, Cooper JM (2012) Impact of organic and conventional crop management on diversity and activity of free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria and total bacteria are subsidiary to temporal effects. PLoS One 7:e52891
Pereira e Silva MC, Semenov AV, van Elsas JD, Salles JF (2011) Seasonal variations in the diversity and abundance of diazotrophic communities across soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:57–68
Pereira e Silva MC, Schloter-Hai B, Schloter M, van Elsas JD, Salles JF (2013) Temporal dynamics of abundance and composition of nitrogen-fixing communities across agricultural soils. PLoS One 8:1–15
Piceno YM, Lovell CR (2000) Stability in natural bacterial communities: I. Nutrient addition effects on rhizosphere diazotrophic assemblage composition. Microb Ecol 39:32–40
R Development Core Team (2016) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria
Rösch C, Mergel A, Bothe H (2002) Biodiversity of denitrifying and dinitrogen-fixing bacteria in an acid forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3818–3829
Rousk J, Bååth E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351
Rousk K, Jones DL, DeLuca TH (2014) The resilience of nitrogen fixation in feather moss (Pleurozium schreberi)-cyanobacteria associations after a drying and rewetting cycle. Plant Soil 377:159–167
Rousk K, Sorensen PL, Lett S, Michelsen A (2015) Across-habitat comparison of diazotroph activity in the subarctic. Microb Ecol 69:778–787
Różycki H, Dahm H, Strzelczyk E, Li CY (1999) Diazotrophic bacteria in root-free soil and in the root zone of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and oak (Quercus robur L.) Appl Soil Ecol 12:239–250
Soil Survey Staff (2003) Keys to soil taxonomy, 9th edn. United States Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington
Subhash Y, Yoon DE, Lee SS (2017) Skermanella mucosa sp. nov., isolated from crude oil contaminated soil. Anton Leeuw 110:1–8
Sun R, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang D, Chu H (2015) Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 88:9–18
Sun L, Xun W, Huang T, Zhang G, Gao J, Ran W, Li D, Shen Q, Zhang R (2016a) Alteration of the soil bacterial community during parent material maturation driven by different fertilization treatments. Soil Biol Biochem 96:207–215
Sun R, Dsouza M, Gilber JA, Guo X, Wang D, Guo Z, Ni Y, Chu H (2016b) Fungal community composition in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization is most influenced by the type of organic matter. Environ Microbiol 18:5137–5150
Tan Z, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2003) Effect of N-fertilization, plant genotype and environmental conditions on nifH gene pools in roots of rice. Environ Microbiol 5:1009–1015
Tang H, Yu M, Wang Y, Han X, Wang X, Jin W, Chi F, Wei D (2012) Effects of long-term fertilization on nifH gene diversity in agricultural black soil. Afr J Microbiol Res 6:2659–2666
Tang Y, Zhang M, Chen A, Zhang W, Wei W, Sheng R (2017) Impact of fertilization regimes on diazotroph community compositions and N2-fixation activity in paddy soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 247:1–8
Vitousek PM, Cassman K, Cleveland C, Crews T, Field CB, Grimm NB, Howarth RW, Marino R, Martinelli L, Rastetter EB, Sprent JI (2002) Towards an ecological understanding of biological nitrogen fixation. Biogeochemistry 57:1–45
Wang S, Gonzalez PP, Ye J, Huang D (2012) Abundance and diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in rhizosphere and bulk paddy soil under different duration of organic management. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:493–503
Wang C, Zheng M, Song W, Wen S, Wang B, Zhu C, Shen R (2017a) Impact of 25 inorganic fertilization on diazotrophic abundance and community structure in an acidic soil in sourthern China. Soil Biol Biochem 113:240–249
Wang Y, Li H, Li J, Li X (2017b) The diversity and co-occurrence patterns of diazotrophs in the steppes of Inner Mongolia. Catena 157:130–180
Yousuf B, Kumar R, Mishra A, Jha B (2015) Differential distribution and abundance of diazotrophic bacterial communities across different soil niches using a gene-targeted clone library approach. FEMS Microbiol Lett 360:117–125
Zhang Y, Dong J, Yang Z, Zhang S, Wang Y (2008) Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in mangrove sediments assessed by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Arch Microbiol 190:19–28
Zhong W, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang B, Lin X, Huang Q, Shen W (2010) The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 326:523
Zhu W, Huang J, Li M, Li X, Wang G (2014) Genomic analysis of Skermanella stibiiresistens type strain SB22T. Stand Geonomic Sci 9:1211–1220
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15010103) and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0200604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jizheng He
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
Fig. S1. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) of diazotrophic community composition associated with soil properties following long-term fertilization treatments in neutral black soil of northeast China. NoF, non-fertilization; CF, chemical fertilization, M, manure fertilization; CFM, chemical fertilization plus manure. (PDF 597 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Liu, J., Zhu, P. et al. Long-term manure addition reduces diversity and changes community structure of diazotrophs in a neutral black soil of northeast China. J Soils Sediments 18, 2053–2062 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1975-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1975-6