Abstract
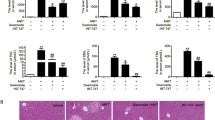
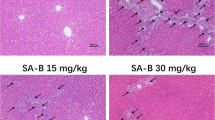
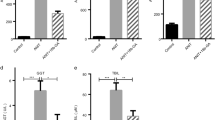
To investigate if andrographolide impairs cholestatic liver injury. All rats were randomly divided into six groups—(1) control (n = 6), (2) control + 200 mg/kg andrographolide (n = 6), (3) alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT)-control (n = 6), (4) ANIT + 50 mg/kg andrographolide (n = 6), (5) ANIT + 100 mg/kg andrographolide (n = 6), and (6) ANIT + 200 mg/kg andrographolide (n = 6). We gavaged 50 mg/kg ANIT to mimic cholestatic liver injury in rats. Seven days after treatment, all the rats were killed. Serum biochemistry and hepatic histopathological assays were performed to evaluate liver injury. We observed that 200 mg/kg andrographolide significantly decreased the level of alanine transaminase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, γ-glutamyltranspeptidase, total bilirubin, and total bile acid in the blood. It also markedly decreased hepatic interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α. Furthermore, 200 mg/kg andrographolide significantly decreased malondialdehyde but increased superoxide dismutase, glutathione, and erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. Moreover, 200 mg/kg andrographolide effectively increased the accumulation of sirtuin 1 and nuclear erythroid 2-related factor-2. It also attenuated the level of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B and cyclooxygenase-2. These data suggest that andrographolide may impair cholestatic liver injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu L, Liu X, Yuan Z, Li X, Yang H, Yuan Z, Sun L, Zhang L, Jiang Z (2017) SRT1720 alleviates ANIT-induced cholestasis in a mouse model. Front Pharmacol 8:256
Kang YZ, Sun XY, Liu YH, Shen ZY (2015) Autoimmune hepatitis-primary biliary cirrhosis concurrent with biliary stricture after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 21:2236–2241
Liu J, Lu YF, Zhang Y, Wu KC, Fan F, Klaassen CD (2013) Oleanolic acid alters bile acid metabolism and produces cholestatic liver injury in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:816–824
Feng C, Li WJ, He RH, Sun XW, Wang G, Wang LQ (2018) Impacts of different methods of conception on the perinatal outcome of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in twin pregnancies. Sci Rep 8:3985
Riverso M, Chang M, Soldevila-Pico C, Lai J, Liu X (2018) Histologic characterization of kratom use-associated liver injury. Gastroenterol Res 11:79–82
Wu JS, Li YF, Li YY, Dai Y, Li WK, Zheng M, Shi ZC, Shi R, Wang TM, Ma BL, Liu P, Ma YM (2017) Huangqi decoction alleviates alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate induced intrahepatic cholestasis by reversing disordered bile acid and glutathione homeostasis in mice. Front Pharmacol 8:938
Yan JY, Ai G, Zhang XJ, Xu HJ, Huang ZM (2015) Investigations of the total flavonoids extracted from flowers of Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 172:202–213
Arauz J, Zarco N, Hernandez-Aquino E, Galicia-Moreno M, Favari L, Segovia J, Muriel P (2017) Coffee consumption prevents fibrosis in a rat model that mimics secondary biliary cirrhosis in humans. Nutr Res 40:65–74
Wang L, Wu G, Wu F, Jiang N, Lin Y (2017) Geniposide attenuates ANIT-induced cholestasis through regulation of transporters and enzymes involved in bile acids homeostasis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 196:178–185
Dai M, Hua H, Lin H, Xu G, Hu X, Li F, Gonzalez FJ, Liu A, Yang J (2018) Targeted metabolomics reveals a protective role for basal PPARalpha in cholestasis induced by alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate. J Proteome Res 17(4):1500–1508
Li YF, Wu JS, Li YY, Dai Y, Zheng M, Zeng JK, Wang GF, Wang TM, Li WK, Zhang XY, Gu M, Huang C, Yang L, Wang ZT, Ma YM (2017) Chicken bile powder protects against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in mice. Oncotarget 8(57):97137–97152
Lee TY, Chang HH, Wen CK, Huang TH, Chang YS (2014) Modulation of thioacetamide-induced hepatic inflammations, angiogenesis and fibrosis by andrographolide in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 158(Pt A):423–430
Gehrke N, Nagel M, Straub BK, Worns MA, Schuchmann M, Galle PR, Schattenberg JM (2018) Loss of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein promotes acute cholestatic liver injury and inflammation from bile duct ligation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 314(3):G319–G333
Chavez E, Segovia J, Shibayama M, Tsutsumi V, Vergara P, Castro-Sanchez L, Salazar EP, Moreno MG, Muriel P (2010) Antifibrotic and fibrolytic properties of celecoxib in liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in the rat. Liver Int 30(7):969–978
Yao H, Xu Y, Yin L, Tao X, Xu L, Qi Y, Han X, Sun P, Liu K, Peng J (2017) Dioscin protects ANIT-induced intrahepatic cholestasis through regulating transporters, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Front Pharmacol 8:116
Rudraiah S, Moscovitz JE, Donepudi AC, Campion SN, Slitt AL, Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE (2014) Differential Fmo3 gene expression in various liver injury models involving hepatic oxidative stress in mice. Toxicology 325:85–95
Tsai MS, Lee PH, Sun CK, Chiu TC, Lin YC, Chang IW, Chen PH, Kao YH (2018) Nerve growth factor upregulates sirtuin 1 expression in cholestasis: a potential therapeutic target. Exp Mol Med 50(1):e426
Abd El Motteleb DM, Ibrahim I, Elshazly SM (2017) Sildenafil protects against bile duct ligation induced hepatic fibrosis in rats: potential role for silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 335:64–71
Cabrera D, Wree A, Povero D, Solis N, Hernandez A, Pizarro M, Moshage H, Torres J, Feldstein AE, Cabello-Verrugio C, Brandan E, Barrera F, Arab JP, Arrese M (2017) Andrographolide ameliorates inflammation and fibrogenesis and attenuates inflammasome activation in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Rep 7(1):3491
Li M, Zhang T, Zhu L, Wang R, Jin Y (2017) Liposomal andrographolide dry powder inhalers for treatment of bacterial pneumonia via anti-inflammatory pathway. Int J Pharm 528(1–2):163–171
Feng B, Zhang Q, Wang X, Sun X, Mu X, Dong H (2017) Effect of andrographolide on gene expression profile and intracellular calcium in primary rat myocardium microvascular endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 70(6):369–381
Ambili R, Janam P, Saneesh Babu PS, Prasad M, Vinod D, Anil Kumar PR, Kumary TV, Asha Nair S, Radhakrishna Pillai M (2017) An ex vivo evaluation of the efficacy of andrographolide in modulating differential expression of transcription factors and target genes in periodontal cells and its potential role in treating periodontal diseases. J Ethnopharmacol 196:160–167
Wu KC, McDonald PR, Liu J, Klaassen CD (2014) Screening of natural compounds as activators of the keap1-nrf2 pathway. Planta Med 80(1):97–104
Panraksa P, Ramphan S, Khongwichit S, Smith DR (2017) Activity of andrographolide against dengue virus. Antiviral Res 139:69–78
Yang Y, Yan H, Jing M, Zhang Z, Zhang G, Sun Y, Shan L, Yu P, Wang Y, Xu L (2016) Andrographolide derivative AL-1 ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in mice: involvement of NF-small ka, CyrillicB and PPAR-gamma signaling pathways. Sci Rep 6:29716
Ding Y, Shi C, Chen L, Ma P, Li K, Jin J, Zhang Q, Li A (2017) Effects of andrographolide on postoperative cognitive dysfunction and the association with NF-kappaB/MAPK pathway. Oncol Lett 14(6):7367–7373
Tan WSD, Liao W, Zhou S, Wong WSF (2017) Is there a future for andrographolide to be an anti-inflammatory drug? Deciphering its major mechanisms of action. Biochem Pharmacol 139:71–81
Wang T, Zhou ZX, Sun LX, Li X, Xu ZM, Chen M, Zhao GL, Jiang ZZ, Zhang LY (2014) Resveratrol effectively attenuates alpha-naphthyl-isothiocyanate-induced acute cholestasis and liver injury through choleretic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35(12):1527–1536
Nie X, Chen SR, Wang K, Peng Y, Wang YT, Wang D, Wang Y, Zhou GC (2017) Attenuation of innate immunity by andrographolide derivatives through NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7(1):4738
Chen HW, Huang CS, Li CC, Lin AH, Huang YJ, Wang TS, Yao HT, Lii CK (2014) Bioavailability of andrographolide and protection against carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative damage in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280(1):1–9
Yan J, Xie G, Liang C, Hu Y, Zhao A, Huang F, Hu P, Liu P, Jia W, Wang X (2017) Herbal medicine Yinchenhaotang protects against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in rats. Sci Rep 7(1):4211
Peng S, Hang N, Liu W, Guo W, Jiang C, Yang X, Xu Q, Sun Y (2016) Andrographolide sulfonate ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by down-regulating MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(3):205–211
Cao WR, Ge JQ, Xie X, Fan ML, Fan XD, Wang H, Dong ZY, Liao ZH, Lan XZ, Chen M (2017) Protective effects of petroleum ether extracts of Herpetospermum caudigerum against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced acute cholestasis of rats. J Ethnopharmacol 198:139–147
Chen KL, Bi KS, Han F, Zhu HY, Zhang XS, Mao XJ, Yin R (2015) Evaluation of the protective effect of Zhi-Zi-da-Huang decoction on acute liver injury with cholestasis induced by alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 172:402–409
Yang H, Bi Y, Xue L, Wang J, Lu Y, Zhang Z, Chen X, Chu Y, Yang R, Wang R, Liu G (2015) Multifaceted Modulation of SIRT1 in cancer and inflammation. Crit Rev Oncog 20(1–2):49–64
Ishii T, Itoh K, Takahashi S et al (2000) Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem 275:16023–16029
Xue F, Huang JW, Ding PY, Zang HG, Kou ZJ, Li T, Fan J, Peng ZW, Yan WJ (2016) Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathway is involved in the neuroprotective effects of Sirt1 against focal cerebral ischemia in rats after hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Behav Brain Res 309:1
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81473504) and the China Scholarship Council (no. 201708080032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG and ZW carried out the research; LW, FC, LZ, PL and WL provided Figs. 1, 2 and 4; XD and YS provided Fig. 3; HB was responsible for the reagents and animals; LW and FC wrote the paper. All of the authors listed have revised and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Cao, F., Zhu, Ll. et al. Andrographolide impairs alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in vivo. J Nat Med 73, 388–396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-01275-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-01275-3