Abstract
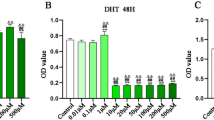
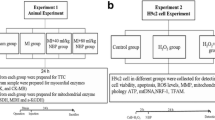
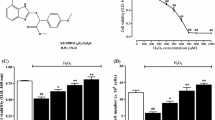
Polydatin is a traditional Chinese medicine that provides myocardial protection after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The study aim was to investigate the myocardial protection polydatin in H9c2 myocardial cells cultured in a hypoxic atmosphere and in a rat AMI model induced by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery and treated with polydatin 100 mg/kg/day for 30 days. The involvement of Nrf2 in mediating the effects of polydatin was investigated in H9c2 cells following Nrf2 knockdown by transfection of siRNA. Polydatin suppressed hypoxia-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by promoting Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Nrf2 knockdown reversed the protective effects of polydatin against hypoxia-induced myocardial cell injury. The in vivo results were consistent with polydatin suppression of apoptosis and ROS generation in myocardial tissue by promotion of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. In conclusion, polydatin effectively inhibited hypoxia- and AMI-induced myocardial damage by promotion of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han A et al (2018) Qiliqiangxin attenuates cardiac remodeling via inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad3 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem 45:1797–1806
Farah E et al (2012) Prevalence and predictors of ventricular remodeling after anterior myocardial infarction in the era of modern medical therapy. Med Sci Monit 18:CR276–CR281
Li XZ et al (2017) Astragaloside IV prevents cardiac remodeling in the apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by regulating cardiac homeostasis and oxidative stress. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:2422–2438
Hong YM, Lee H, Cho MS, Kim KC (2017) Apoptosis and remodeling in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy rat model. Korean J Pediatr 60:365–372
Chakraborti S et al (2018) Atypical G protein β5 promotes cardiac oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrotic remodeling in response to multiple cancer chemotherapeutics. Cancer Res 78:528–541
Jiao Y, Wu Y, Du D (2018) Polydatin inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and induces cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Braz J Med Biol Res 51:e6867
Tang S et al (2018) Polydatin inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and ameliorates murine osteoarthritis. Food Funct 9:1701–1712
Pang N et al (2017) Polydatin prevents methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis through reducing oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7180943
Gugliandolo E et al (2017) Palmitoylethanolamide and polydatin combination reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in vascular injury. Pharmacol Res 123:83–92
Chen S et al (2017) Polydatin down-regulates the phosphorylation level of creb and induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cell. PLoS One 12:e0176501
Zhang M et al (2017) Polydatin protects cardiomyocytes against myocardial infarction injury by activating Sirt3. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:1962–1972
Gao Y et al (2015) Cardioprotective effect of polydatin on ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in coronary artery ligation rats. Planta Med 81:568–577
Liu SX et al (2012) Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression by hydroxysafflor yellow A conferring protection from anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Int J Cardiol 160:95–101
Huang QH et al (2017) Polydatin protects rat liver against ethanol-induced injury: involvement of CYP2E1/ROS/Nrf2 and TLR4/NF-kappaB p65 pathway. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7953850
Gong W et al (2017) Polydatin promotes Nrf2-ARE anti-oxidative pathway through activating CKIP-1 to resist HG-induced up-regulation of FN and ICAM-1 in GMCs and diabetic mice kidneys. Free Radic Biol Med 106:393–405
Liang M et al (2018) L-Arginine induces antioxidant response to prevent oxidative stress via stimulation of glutathione synthesis and activation of Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 115:315–328
Ali T et al (2018) Natural dietary supplementation of anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 55:6076–6093
Xin Y et al (2018) Sulforaphane prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiomyopathy by activation of Nrf2 via stimulating the Akt/GSK-3ss/Fyn pathway. Redox Biol 15:405–417
Han D et al (2017) Cytoprotective effect of chlorogenic acid against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8:14680–14692
Lee YJ et al (2012) Reactive oxygen species and PI3K/Akt signaling play key roles in the induction of Nrf2-driven heme oxygenase-1 expression in sulforaphane-treated human mesothelioma MSTO-211H cells. Food Chem Toxicol 50:116–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
All animals were treated following the ethical guidelines of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The study was approved by, and conducted following the guidelines, of the Ethics Committee of Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai, China. All surgical procedures were performed under anesthesia, and every effort was made to minimize suffering.
Additional information
Guo Chen and Guorong Liu are co-first author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Liu, G., Cao, D. et al. Polydatin protects against acute myocardial infarction-induced cardiac damage by activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. J Nat Med 73, 85–92 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1241-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-018-1241-7