Abstract
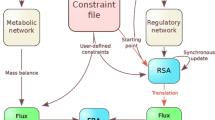
Stoichiometry-based analyses of metabolic networks have aroused significant interest of systems biology researchers in recent years. It is necessary to develop a more convenient modeling platform on which users can reconstruct their network models using completely graphical operations, and explore them with powerful analyzing modules to get a better understanding of the properties of metabolic systems. Herein, an in silico platform, FluxExplorer, for metabolic modeling and analyses based on stoichiometry has been developed as a publicly available tool for systems biology research. This platform integrates various analytic approaches, including flux balance analysis, minimization of metabolic adjustment, extreme pathways analysis, shadow prices analysis, and singular value decomposition, providing a thorough characterization of the metabolic system. Using a graphic modeling process, metabolic networks can be reconstructed and modified intuitively and conveniently. The inconsistencies of a model with respect to the FBA principles can be proved automatically. In addition, this platform supports systems biology markup language (SBML). FluxExplorer has been applied to rebuild a metabolic network in mammalian mitochondria, producing meaningful results. Generally, it is a powerful and very convenient tool for metabolic network modeling and analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varner, J., Ramdrishan D: Metabolic engineering from a cybernetic perspective I, Biotechnol. Prog., 1999, 15: 407–425.
Fell, D., Understanding the Control of Metabolism, London: Portland Press, 1996.
Varma, A., Palsson, B. O., Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, 60: 3724–3731.
Palsson, B., The challenges of in silico biology, Nature Biotechnol., 2000, 18: 1147–1150.
McAdams, H. H., Shapiro, L., A bacterial cell-cycle regulatory network operating in time and space, Science, 2003, 301: 1874–1877.
Covert, M. W., Schilling, C. H., Palsson, B., Regulation of gene expression in flux balance models of metabolism, J. Theor. Biol., 2001, 213: 73–88.
Ibarra, R.U., Edwards, J. S., Palsson, B. O., Escherichis coli K-12 undergoes adaptive evolution to achieve in silico predicted optimal growth, Nature, 2002, 420: 186–189.
Edwards, J. S., Palsson, B. O., The Escherichia coli MG1655 in silico metabolic genotype: Its definition, characteristics, and capabilities, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, 97(10): 5528–5533.
Schilling, C. H., Palsson, B. O., The underlying pathway structure of biochemical reaction networks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95: 4193–4198.
Klamt, S., Stelling, J., Ginkel, M. et al., FluxAnalyzer: Exploring structure, pathways, and flux distributions in metabolic networks on interactive flux maps, Bioinformatics, 2003, 19: 261–269.
Lee, D., Yun, H., Park, S. et al., MetaFluxNet: the management of metabolic reaction information and quantitative metabolic flux analysis, Bioinformatics, 2003, 19: 2144–2146.
Tomita, M., Hashimoto, K., Takahashi, K. et al., E-CELL: Software environment for whole-cell simulation, Bioinformatics, 1999, 15(1): 72–84.
Segrè, D., Vitkup, D., Chruch, G. M., Analysis of optimality in natural and perturbed metabolic networks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, 99: 15112–15117.
Papp, B., Pál, C., Hurst, L. D., Metabolic network analysis of the causes and evolution of enzyme dispensability in yeast, Nature, 2004, 429: 661–664.
Papin, J. A., Price, N. D., Palsson, B. O., Extreme pathway lengths and reaction participation in genome-scale metabolic networks, Genome Res., 2002, 12: 1889–1900.
Price, N. D., Reed, J. L., Papin, J. A. et al., Analysis of metabolic capabilities using singular value decomposition of extreme pathway matrices, Biophys. J., 2003, 84: 794–804.
Famili, I., Palsson, B. O., Systemic metabolic reactions are obtained by singular value decomposition of genome-scale stiochiometric matrices, J. Theor. Biol., 2003, 224: 87–96.
Schilling, C. H., Schuster, S., Palsson, B. O., Metabolic pathway analysis: Basic concepts and scientific applications in the post-genomic era, Biotechnol. Prog., 1999, 15: 296–303.
Gombert, A. K., Nielsen, J., Mathematical modeling of metabolism, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2000, 11: 180–186.
Covert, M. W., Schilling, C. H., Famili, I. et al., Metabolic modeling of microbial strains in silico, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2001, 26(3): 179–186.
Kauffman, K. J., Prakash, P., Edwards, J. S., Advances in flux balance analysis, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2003, 14: 491–496.
Schilling, C. H., Edwards, J. S., Palsson, B. O., Towards metabolic phenomics: Analysis of genomic data using flux balances, Biotechnol. Prog., 1999, 15: 288–295.
Schilling, C. H., Letscher, D., Palsson, B. O., Theory for the systemic definition of metabolic pathways and their use in interpreting metabolic function from a pathway-oriented perspective, J. Theor. Biol., 2000, 203: 229–248.
Pinney, J. W., Westhead, D. R., McConkey, G. A., Petri Net representations in systems biology, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2003, 31: 1513–1515.
Cairns, C. B., Walther, J., Harken, A. H. et al., Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation thermodynamic efficiencies reflect physiological organ roles, Am. J. Physiol., 1998, 274: R1376–R1383.
Stanley, W. C., Lopaschuk, G. D., Hall, J. L. et al., Regulation of myocardial carbohydrate metabolism under normal and ischaemic conditions, Cardiovasc. Res., 1997, 33: 243–257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, R., Liao, S., Zeng, S. et al. FluxExplorer: A general platform for modeling and analyses of metabolic networks based on stoichiometry. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 689–696 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0689-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0689-0