Abstract
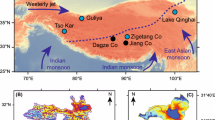
Widespread lakes on the Tibetan Plateau (TP) are valuable archives for investigating climate and environment changes, which could provide essential information on the mechanisms of past climate changes on the TP and their interaction with the global climate systems. However, there is a lack of in-depth investigation of modern limnological processes in the Tibetan lakes, which hampers the understanding of paleolimnological records and lake ecosystem succession. In this study, we performed continuous temperature monitoring at two lakes, Bangong Co, a freshwater lake in the western TP, and Dagze Co, a brackish lake in the central TP, in order to characterize the patterns of seasonal temperature variability, stratification, and mixing. Temperature data for an entire hydrological year demonstrate that Bangong Co is a dimictic lake and that Dagze Co is a meromictic lake. The higher salinity in the deep water at Dagze Co prevents the lake from overturning completely, and this finding is supported by simulations using a physical limnological model Lake Analyzer. Continuous lake water temperature monitoring provides fundamental data for classifying Tibetan lakes, as well as the hydrological basis for understanding their paleolimnological records and ecosystem succession.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems. Elsevier, San Diego
Kalff J (2002) Limnology: inland water ecosystems. Prentice Hall, NJ
Likens GE (ed) (2010) Biogeochemistry of inland waters: a derivative of encyclopedia of inland waters. Academic Press, Amsterdam
MacIntyre S, Flynn KM, Jellison R et al (1999) Boundary mixing and nutrient fluxes in Mono Lake, California. Limnol Oceanogr 44:512–529
Lewis WM Jr (2011) Global primary production of lakes: 19th Baldi Memorial Lecture. Inland Waters 1:1–28
Li WC, Li SJ, Yin Y et al (2001) Meromixis in Zige Tangco, central Tibetan Plateau—discovery and significance. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 44:338–342
Brauer A (2004) Annually laminated lake sediments and their palaeoclimatic relevance. In: Fischer H, Kumke T, Lohmann G et al (eds) The climate in historical times. Towards a synthesis of Holocene proxy data and climate models. Springer, Berlin, pp 109–128
Mischke S, Zhang CJ, Borner A et al (2010) Lateglacial and Holocene variation in aeolian sediment flux over the northeastern Tibetan Plateau recorded by laminated sediments of a saline meromictic lake. J Quat Sci 25:162–177
Yao TD, Thompson L, Yang W et al (2012) Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat Clim Chang 2:663–667
Yao TD, Masson-Delmotte V, Gao J et al (2013) A review of climatic controls on δ 18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: observations and simulations. Rev Geophys. doi:10.1002/rog.20023
Ma R, Yang G, Duan H et al (2011) China’s lakes at present: number, area and spatial distribution. Sci China Earth Sci 54:283–289
Wang SM, Dou HS (1998) Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Gasse F, Arnold M, Fontes JC et al (1991) A 13,000-year climate record from western Tibet. Nature 353:742–745
Fontes JC, Gasse F, Gibert E (1996) Holocene environmental changes in Lake Bangong basin (Western Tibet). Part 1: chronology and stable isotopes of carbonates of a Holocene lacustrine core. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 120:25–47
Morrill C, Overpeck JT, Cole JE et al (2006) Holocene variations in the Asian monsoon inferred from the geochemistry of lake sediments in central Tibet. Quat Res 65:232–243
Wu YH, Lucke A, Jin ZD et al (2006) Holocene climate development on the central Tibetan Plateau: a sedimentary record from Cuoe Lake. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 234:328–340
Zhu LP, Wu YH, Wang JB et al (2008) Environmental changes since 8.4 ka reflected in the lacustrine core sediments from Nam Co, central Tibetan Plateau, China. Holocene 18:831–839
An ZS, Colman SM, Zhou WJ et al (2012) Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka. Sci Rep 2:619. doi:10.1038/srep00619
Henderson ACG, Holmes JA, Leng MJ (2010) Late Holocene isotope hydrology of Lake Qinghai, NE Tibetan Plateau: effective moisture variability and atmospheric circulation changes. Quat Sci Rev 29:2215–2223
Wang HY, Liu WG, Zhang CL et al (2013) Assessing the ratio of archaeol to caldarchaeol as a salinity proxy in highland lakes on the northeastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Org Geochem 54:69–77
Murakami T, Terai H, Yoshiyama Y et al (2007) The second investigation of Lake Puma Yum Co located in the Southern Tibetan Plateau, China. Limnology 8:331–335
Wang JB, Zhu LP, Daut G et al (2009) Investigation of bathymetry and water quality of Lake Nam Co, the largest lake on the central Tibetan Plateau, China. Limnology 10:149–158
Ju JT, Zhu LP, Wang JB et al (2010) Water and sediment chemistry of Lake Pumayum Co, South Tibet, China: implications for interpreting sediment carbonate. J Paleolimnol 43:463–474
Zhu LP, Ju JT, Wang JB et al (2010) Further discussion about the features of Lake Puma Yum Co, South Tibet, China. Limnology 11:281–287
Khan A, Richards K, Parker G et al (2013) How large is the Upper Indus Basin? The pitfalls of auto-delineation using DEMs. J Hydrol 509:442–453
Wan W, Xiao P, Feng X et al (2014) Monitoring lake changes of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau over the past 30 years using satellite remote sensing data. Chin Sci Bull 59:1021–1035
Guan ZH, Chen CY, Qu YX et al (1984) Rivers and lakes of Xizang. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Gasse F, Fontes JC, Van Campo E et al (1996) Holocene environmental changes in Bangong Co basin (Western Tibet). Part 4: discussion and conclusions. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 120:79–92
Liu SS, Jia QX, Liu XF et al (2013) The depositional environment and organic sediment component of Dagze Co, a saline lake in Tibet, China. Acta Ecol Sin 33:5785–5793 (in Chinese)
Qiao C, Luo JC, Sheng YW et al (2010) Lake shrinkage analysis using spectral-spatial coupled remote sensing on Tibetan Plateau. In: IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, 25–30 July 2010
Zhu DQ (2010) Chinese water illustrated. Qingdao Press, Qingdao (in Chinese)
Millero FJ, Chen CT, Schleicher K et al (1980) A new high-pressure equation of state for seawater. Deep Sea Res Pt I 27:255–264
Boehrer B, Schultze M (2008) Stratification of lakes. Rev Geophys 46:RG2005. doi:10.1029/2006RG000210
Dietz S, Lessmann D, Boehrer B (2012) Contribution of solutes to density stratification in a meromictic lake (Waldsee/Germany). Mine Water Environ 31:129–137
Boehrer B, Herzsprung P, Schultze M et al (2010) Calculating density of water in geochemical lake stratification models. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 8:567–574
Millero FJ, Poisson A (1981) International one-atmosphere equation of state of seawater. Deep Sea Res 28:625–629
Read JS, Hamilton DP, Jones ID et al (2011) Derivation of lake mixing and stratification indices from high-resolution lake buoy data. Environ Model Softw 26:1325–1336
Kling GW (1988) Comparative transparency, depth of mixing, and stability of stratification in lakes of Cameroon, West Africa. Limnol Oceanogr 33:27–40
Hutchinson GE, Löffler H (1956) The thermal classification of lakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 42:84–86
Lewis WM Jr (1983) A revised classification of lakes based on mixing. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 40:1779–1787
Walker K, Likens G (1975) Meromixis and a reconsidered typology of lake circulation patterns. Verh Int Ver Limnol 19:442–458
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41072120, 41321061). The authors thank Prof. Tian Lide for providing meteorological data of NASDE, Dr. Wang Junbo for providing bathymetry data of Bangong Co, and Zhang Hongbo for his help in processing the meteorological data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Hou, J. & Lei, Y. Classification of Tibetan lakes based on variations in seasonal lake water temperature. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 4847–4855 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0588-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0588-8