Abstract
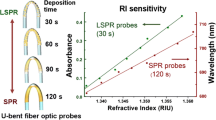
The refractive index (RI) sensitivity of a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR)-based fiber-optic probes is dependent on surface coverage of gold nanoparticles (GNP), fiber core diameter, and probe geometry. For U-bent LSPR fiber-optic probes, which demonstrated an order higher absorption sensitivity over straight probes, bend diameter and probe length may also have a significant influence on the sensitivity. This study on U-bent fiber-optic LSPR probes is aimed at optimizing these parameters to obtain highest possible RI sensitivity. RI sensitivity increases linearly as a function of surface coverage of GNP in the range of 2–22 %. U-bent fiber-optic probes made of 200-, 400-, and 600-μm fiber core diameter show optimum bend diameter value as ∼1.4 mm. In addition, RI sensitivity is almost the same irrespective of fiber core diameter demonstrating flexibility in choice of the fiber and ease in optical coupling. The length of the probe preceding and succeeding the bend region has significantly less influence on RI sensitivity allowing miniaturization of these probes. In addition to these experimental studies, we present a theoretical analysis to understand the relative contribution of evanescent wave absorbance of GNP and refractive losses in the fiber due to GNP, towards the RI sensitivity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borisov SM, Wolfbeis OS (2008) Optical biosensors. Chem Rev 108:423–461
Fan X, White IM, Shopova SI, Zhu H, Suter JD, Sun Y (2008) Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: a review. Anal Chim Acta 620:8–26
Velasco-Garcia MN (2009) Optical biosensors for probing at the cellular level: a review of recent progress and future prospects. Sem Cell Dev Biol 20:27–33
DeLisa MP, Zhang Z, Shiloach M, Pilevar S, Davis CC, Sirkis JS, Bentley WE (2000) Evanescent wave long-period fiber Bragg grating as an immobilized antibody biosensor. Anal Chem 72:2895–2900
Wolfbeis OS (2008) Fiber-optic chemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 80:4269–4283
Tierney S, Falch BMH, Hjelme DR, Stokke BT (2009) Determination of glucose levels using a functionalized hydrogel-optical fiber biosensor: toward continuous monitoring of blood glucose in vivo. Anal Chem 81:3630–3636
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110:7238–7248
Satija J, Bharadwaj R, Sai VVR, Mukherji S (2010) Emerging use of nanostructure films containing capped gold nanoparticles in biosensors. Nanotech Sci Appl 3:171–188
Mayer KM, Hafner JH (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111:3828–3857
Mitsui K, Handa Y, Kajikawa K (2004) Optical fiber affinity biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance. Appl Phy Lett 85:4231–4233
Chau L-K, Lin Y-F, Cheng S-F, Lin T-J (2006) Fiber-optic chemical and biochemical probes based on localized surface plasmon resonance. Sens Actuat B Chem 113:100–105
Cao J, Tu MH, Sun T, Grattan KTV (2013) Wavelength-based localized surface plasmon resonance optical fiber biosensor. Sens Actuat B Chem 181:611–619
Jeong H-H, Erdene N, Lee S-K, Jeong D-H, Park J-H (2011) Fabrication of fiber-optic localized surface plasmon resonance sensor and its application to detect antibody-antigen reaction of interferon-gamma. Opt Eng 50:124405
Sai VVR, Kundu T, Mukherji S (2009) Novel U-bent fiber optic probe for localized surface plasmon resonance based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2804–2809
Gupta BD, Dodeja H, Tomar AK (1996) Fibre-optic evanescent field absorption sensor based on a U-shaped probe. Opt Quant Electron 28:1629–1639
Simsek E (2009) Effective refractive index approximation and surface plasmon resonance modes of metal nanoparticle chains and arrays. PIERS Online 5:629–632
Degrandpre MD, Burgess LW (1990) A fiber-optic FT-NIR evanescent field absorbance sensor. Appl Spectrosc 44:273–279
Conzen J-P, Bürck J, Ache H-J (1993) Characterization of a fiber-optic evanescent wave absorbance sensor for nonpolar organic compounds. Appl Spectrosc 47:753–763
Moon JH, Shin JW, Kim SY, Park JW (1996) Formation of uniform aminosilane thin layers: an imine formation to measure relative surface density of the amine group. Langmuir 12:4621–4624
Chen M, Horn RG (2007) Refractive index of sparse layers of adsorbed gold nanoparticles. J Colloid Interf Sci 315:814–817
Prabhakar A, Mukherji S (2012) Investigation of the effect of curvature on sensitivity of bio/chemical sensors based on embedded polymer semicircular waveguides. Sens Actuat B Chem 171–172:1303–1311
Sai VVR, Kundu T, Deshmukh C, Titus S, Kumar P, Mukherji S (2010) Label-free fiber optic biosensor based on evanescent wave absorbance at 280 nm. Sens Actuat B Chem 143:724–730
Cras JJ, Rowe-Taitt CA, Nivens DA, Ligler FS (1999) Comparison of chemical cleaning methods of glass in preparation for silanization. Biosens Bioelectron 14:683–688
Bhagwati P (1999) Capacitive immunosensors for fibronectin. Ph.D. Thesis, IIT Bombay
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Grabar KC, Smith PC, Musick MD, Davis JA, Walter DG, Jackson MA, Guthrie AP, Natan MJ (1996) Kinetic control of interparticle spacing in Au colloid-based surfaces: rational nanometer-scale architecture. J Am Chem Soc 118:1148–1153
Su K-H, Wei Q-H, Zhang X, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Schultz S (2003) Interparticle coupling effects on plasmon resonances of nanogold particles. Nano Lett 3:1087–1090
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2004) Label-free biosensing by surface plasmon resonance of nanoparticles on glass: optimization of nanoparticle size. Anal Chem 76:5370–5378
Cheng S, Chau L-K (2003) Colloidal gold-modified optical fiber for chemical and biochemical sensing. Anal Chem 75:16–21
Tou ZQ, Chan CC, Wong WC, Chen LH (2013) Fiber optic refractometer based on cladding excitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. IEEE Photonic Technol Lett 25:556–559
Yamamichi J, Iida M, Ojima T, Handa Y, Yamada T, Kuroda R, Imamura T, Yano T (2009) The mesoscopic effect on label-free biosensors based on localized surface plasmon resonance of immobilized colloidal gold. Sens Actuat B Chem 143:349–356
Srivastava SK, Arora V, Sapra S, Gupta BD (2012) Localized surface plasmon resonance-based fiber optic U-shaped biosensor for the detection of blood glucose. Plasmon 7:261–268
Khijwania SK, Gupta BD (1999) Fiber optic evanescent field absorption sensor: effect of fiber parameters and geometry of the probe. Opt Quant Electron 31:625–636
Khijwania SK, Srinivasan KL, Singh JP (2005) An evanescent-wave optical fiber relative humidity sensor with enhanced sensitivity. Sens Actuat B Chem 104:217–222
Leung A, Shankar PM, Mutharasan R (2007) A review of fiber-optic biosensors. Sens Actuat B Chem 125:688–703
Acknowledgments
We thank the Centre for Research in Nanotechnology and Science and Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility, IIT Bombay for FE-TEM and FE-SEM images acquired in support of this study. Authors also thank Bhuvaneshwari K. for helping in FE-SEM image analysis using MATLB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 2,801 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satija, J., Punjabi, N.S., Sai, V.V.R. et al. Optimal Design for U-bent Fiber-optic LSPR Sensor Probes. Plasmonics 9, 251–260 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9618-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-013-9618-7