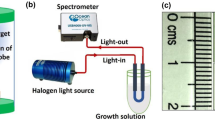
Abstract
This study describes fabrication of highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance (SPR) as well as localized SPR (LSPR) dominant fiber optic plasmonic probes by controlled sputtering of gold thin films on the fiber core surface. Compact U-bent probes of 750 μm plastic optical fibers (made of poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA)) were used for efficient evanescent wave excitation of plasmonic substrates to achieve high sensitivity. U-bent probes with 2.25-mm bend diameter were sputter coated for deposition times of 30, 60, 90, and 120 s to obtain gold thin films with nanovoids on the U-bent region. As deposition time increased, a significant transition from LSPR to SPR characteristics was observed in the overall UV-visible spectral characteristics with a clear shift in the plasmon peak from 520 to 650 nm. Probes sputtered for 30 and 120 s show excellent LSPR- and SPR-based characteristics with a sensitivity of 15.5 ∆Abs/RIU and 1040 nm/RIU, respectively (for refractive index variation from 1.333 to 1.361 RIU). The high sensitivity of the probes in addition to other advantages, including ease of fabrication, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for in situ monitoring, demonstrates their potential for bio/chemical sensing applications.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsushio M, Miyashita K, Higo M (2006) Sensor properties and surface characterization of the metal-deposited SPR optical fiber sensors with Au, Ag, Cu, and Al. Sensors Actuators A Phys 125:296–303. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2005.08.019
Kundu T, Sai VVR, Dutta R et al (2010) Development of evanescent wave absorbance-based fibre-optic biosensor. Pramana - J Phys 75:1099–1113
Sai VVR, Kundu T, Mukherji S (2009) Novel U-bent fiber optic probe for localized surface plasmon resonance based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2804–2809. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.02.007
Caucheteur C, Guo T, Albert J (2015) Review of plasmonic fiber optic biochemical sensors: improving the limit of detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:3883–3897. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8411-6
Cennamo N, D’Agostino G, Pesavento M, Zeni L (2014) High selectivity and sensitivity sensor based on MIP and SPR in tapered plastic optical fibers for the detection of l-nicotine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 191:529–536. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2013.10.067
Grassini S, Ishtaiwi M, Parvis M, Vallan A (2015) Design and deployment of low-cost plastic optical fiber sensors for gas monitoring. Sensors (Basel) 15:485–498. doi:10.3390/s150100485
Zeni L, Auria SD, Pesavento M et al (2015) Sensing platforms exploiting surface plasmon resonance in polymeric optical fibers for chemical and biochemical applications. Adv Photonics:6–8
Verma RK, Sharma AK, Gupta BD (2008) Surface plasmon resonance based tapered fiber optic sensor with different taper profiles. Opt Commun 281:1486–1491. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2007.11.007
Sla R, Homola J, Brynda E (2002) A miniature fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor for fast detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biosens Bioelectron 17:591–595
Lin H, Tsai W, Tsao Y, Sheu B (2007) Side-polished multimode fiber biosensor based on surface plasmon resonance with halogen light. Appl Opt 46:800–806
Lye PG, Boerkamp M, Ernest A, Lamb DW (2005) Investigating the sensitivity of PMMA optical fibres for use as an evanescent field absorption sensor in aqueous solutions. J Phys Conf Ser 15:262–269. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/15/1/044
Cheng S, Chau L (2003) Colloidal gold-modified optical fiber for chemical. Anal Chem 75:16–21
Cao J, Sun T, Grattan KTV (2014) Gold nanorod-based localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors: a review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 195:332–351. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.056
Pesavento M, Cennamo N, Donà A, et al. (2014) A new approach for selective optical fiber sensors based on localized surface plasmon resonance of gold nanostars in molecularly imprinted polymer. In: Recent Adv. Biomed. Chem. Eng. Mater. Sci. Venice, Italy, March 15‐17, 2014. pp 71–75
He Y, Fu J, Zhao Y (2014) Oblique angle deposition and its applications in plasmonics. Front Phys 9(1):47–59. doi:10.1007/s11467-013-0357-1
Siegel J, Kvítek O, Kolská Z, Slepička P, Švorčík V (2012) Gold nanostructures prepared on solid surface. Metall - Adv Mater Process:44–70. doi:10.5772/51617
Leosson K, Ingason AS, Agnarsson B et al (2013) Ultra-thin gold films on transparent polymers. Nanophotonics 2:3–11. doi:10.1515/nanoph-2012-0030
Gowri A, Sai VVRVR (2016) Development of LSPR based U-bent plastic optical fiber sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 230:536–543. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.02.074
Vasanthakumari P, Khosravi Z, Sai VVR, Klages C-P (2016) PMMA surface functionalization using atmospheric pressure plasma for development of plasmonically active polymer optical fiber probes. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 36:1067–1083. doi:10.1007/s11090-016-9717-2
Cennamo N, D’Agostino G, Galatus R et al (2013) Sensors based on surface plasmon resonance in a plastic optical fiber for the detection of trinitrotoluene. Sensors Actuators B Chem 188:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2013.07.005
Freund LB, Suresh S (2004) Modes of film growth by vapor deposition. In: Thin film materials: stress, defect formation and surface evolution Cambridge University Press, New York. pp 15–29
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (1998) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New York. doi:10.1002/9783527618156.ch1
Siegel J, Lyutakov O, Rybka V et al (2011) Properties of gold nanostructures sputtered on glass. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:96. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-6-96
Egitto FD, Matienzo LJ (1994) Plasma modification of polymer surfaces for adhesion improvement. IBM J Res Dev 38:423–439. doi:10.1147/rd.384.0423
Satyam PV, Kamila J, Mohapatra S et al (2003) Crater formation in gold nanoislands due to MeV self-ion irradiation. J Appl Phys 93:6399. doi:10.1063/1.1569026
Papal RM (1999) Cratering in PMMA induced by gold ions: dependence on the projectile velocity. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res B 148:126–131
Lippert T, Dickinson JT (2003) Chemical and spectroscopic aspects of polymer ablation: special features and novel directions. Chem Rev 103:453–485. doi:10.1021/cr010460q
Ben-Yakar A, Harkin A, Ashmore J et al (2007) Thermal and fluid processes of a thin melt zone during femtosecond laser ablation of glass: the formation of rims by single laser pulses. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:1447–1459. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/40/5/021
Yip J, Chan K, Moon K, Shui K (2006) Formation of periodic structures by surface treatments of polyamide fiber part II. Low temperature plasma treatment 253:2493–2497. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.05.004
Brito PCA, Souza TXR, Gomes RF et al (2011) Au/Ag nanostructures on PMMA surface. Sci Plena 7:2–6
Cole RM, Baumberg JJ, Abajo FJG De, et al. (2007) Understanding plasmons in nanoscale voids. Nano letters 7(7):2094–2100
Iga M, Seki A, Watanabe K (2005) Gold thickness dependence of SPR-based hetero-core structured optical fiber sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 106:363–368. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2004.08.017
Cennamo N, Zeni L (2014) Bio and chemical sensors based on surface plasmon resonance in a plastic optical fiber. In: Opt. Sensors - New Dev. Pract. Appl. Intech. Rijeka, Intech. pp 119–140
Jun S, Leong C, Gyu H et al (2013) Optical fiber sensor for refractive index measurement based on localized surface Plasmon resonance. Conf Lasers Electro-Optics Pacific Rim WPF-20:2–3
Tu H, Sun T, Grattan KT (2013) SPR-based optical fiber sensors using gold–silver alloy particles as the active sensing material. IEEE Sensors J 13:2192–2199
Cao J, Tu MH, Sun T, Grattan KTV (2013) Wavelength-based localized surface plasmon resonance optical fiber biosensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 181:611–619. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2013.02.052
Hlubina P, Ciprian D (2014) Reflection-based fibre-optic refractive index sensor using surface plasmon resonance. J Eur Opt Soc 14033:14033
Wieduwilt T, Kirsch K, Dellith J (2013) Optical fiber micro-taper with circular symmetric gold coating for sensor applications based on surface plasmon resonance. Plasmonics 8:545–554. doi:10.1007/s11468-012-9432-7
Cao J, Galbraith EK, Sun T, Grattan KT V (2012) Cross-comparison of surface plasmon with different coating structures 12:2355–2361.
Schulz U, Kaiser N (2006) Vacuum coating of plastic optics. Prog Surf Sci 81:387–401. doi:10.1016/j.progsurf.2006.07.001
Christopher CGC, Vasanthakumari P, Annasamy G, et al. (2016) SERS based sandwich immunosensing with plasmonically active plastic optical fiber sensor probes. In: Adv. Photonics 2016 (IPR, NOMA, Sensors, Networks, SPPCom, SOF). Optical Society of America, p SeW3E.7
Acknowledgements
We thank Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd., Japan, for providing POF samples. We acknowledge the SEM facility in the Department of Chemical Engineering, IIT Madras for EDX spectra; SEM facility in Department of Mechanical Engineering, York University, Toronto, for SEM images; and INUP, IIT Bombay, for profilometer measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 0.98 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christopher, C., Subrahmanyam, A. & Sai, V.V.R. Gold Sputtered U-Bent Plastic Optical Fiber Probes as SPR- and LSPR-Based Compact Plasmonic Sensors. Plasmonics 13, 493–502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0535-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0535-z