Abstract
Purpose
To identify optimal classification methods for computed tomography (CT) radiomics-based preoperative prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) grade.
Materials and methods
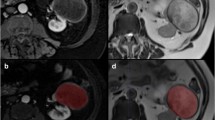
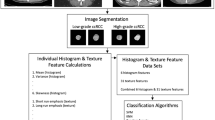
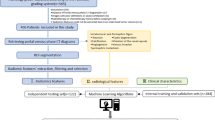
Seventy-one ccRCC patients (31 low grade and 40 high grade) were included in this study. Tumors were manually segmented on CT images followed by the application of three image preprocessing techniques (Laplacian of Gaussian, wavelet filter, and discretization of the intensity values) on delineated tumor volumes. Overall, 2530 radiomics features (tumor shape and size, intensity statistics, and texture) were extracted from each segmented tumor volume. Univariate analysis was performed to assess the association between each feature and the histological condition. Multivariate analysis involved the use of machine learning (ML) algorithms and the following three feature selection algorithms: the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, Student’s t test, and minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance. These selected features were then used to construct three classification models (SVM, random forest, and logistic regression) to discriminate high from low-grade ccRCC at nephrectomy. Lastly, multivariate model performance was evaluated on the bootstrapped validation cohort using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) metric.
Results
The univariate analysis demonstrated that among the different image sets, 128 bin-discretized images have statistically significant different texture parameters with a mean AUC of 0.74 ± 3 (q value < 0.05). The three ML-based classifiers showed proficient discrimination between high and low-grade ccRCC. The AUC was 0.78 for logistic regression, 0.62 for random forest, and 0.83 for the SVM model, respectively.
Conclusion
CT radiomic features can be considered as a useful and promising noninvasive methodology for preoperative evaluation of ccRCC Fuhrman grades.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capitanio U, Montorsi F (2016) Renal cancer. Lancet 387(10021):894–906
Srigley JR, Delahunt B, Eble JN, Egevad L, Epstein JI, Grignon D, Hes O, Moch H, Montironi R, Tickoo SK (2013) The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver classification of renal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1469–1489
Marconi L, Dabestani S, Lam TB, Hofmann F, Stewart F, Norrie J, Bex A, Bensalah K, Canfield SE, Hora M (2016) Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumour biopsy. Eur Urol Oncol 69(4):660–673
Muglia VF, Prando A (2015) Renal cell carcinoma: histological classification and correlation with imaging findings. Radiol Bras 48(3):166–174
Delahunt B, Cheville JC, Martignoni G, Humphrey PA, Magi-Galluzzi C, McKenney J, Egevad L, Algaba F, Moch H, Grignon DJ (2013) The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1490–1504
Lohse CM, Blute ML, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Cheville JC (2002) Comparison of standardized and nonstandardized nuclear grade of renal cell carcinoma to predict outcome among 2,042 patients. Am J Clin Pathol 118(6):877–886
Delahunt B (2009) Advances and controversies in grading and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 22(S2):S24
Tomaszewski JJ, Uzzo RG, Smaldone MC (2014) Heterogeneity and renal mass biopsy: a review of its role and reliability. Cancer Biol Med 11(3):162
Blumenfeld AJ, Guru K, Fuchs GJ, Kim HL (2010) Percutaneous biopsy of renal cell carcinoma underestimates nuclear grade. Urology 76(3):610–613
Kutikov A, Kunkle DA, Uzzo RG (2009) Focal therapy for kidney cancer: a systematic review. Curr Opin Urol 19(2):148–153
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Fernández-Pello S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA (2019) European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol 75(5):799–810
Volpe A, Panzarella T, Rendon RA, Haider MA, Kondylis FI, Jewett MA (2004) The natural history of incidentally detected small renal masses. Cancer 100(4):738–745
Bratslavsky G, Kirkali Z (2010) The changing face of renal-cell carcinoma. J Endourol 24(5):753–757
Kunkle DA, Egleston BL, Uzzo RG (2008) Excise, ablate or observe: the small renal mass dilemma—a meta-analysis and review. J Urol 179(4):1227–1234
Yoshida R, Yoshizako T, Hisatoshi A, Mori H, Tamaki Y, Ishikawa N, Kitagaki H (2017) The additional utility of apparent diffusion coefficient values of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma for predicting metastasis during clinical staging. Acta Radiol Open 6(1):2058460116687174
Ishigami K, Leite LV, Pakalniskis MG, Lee DK, Holanda DG, Kuehn DM (2014) Tumor grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma assessed by contrast-enhanced computed tomography. SpringerPlus 3(1):694
Ding J, Xing Z, Jiang Z, Chen J, Pan L, Qiu J, Xing W (2018) CT-based radiomic model predicts high grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 103:51–56
Lambin P, Leijenaar RT, Deist TM, Peerlings J, De Jong EE, Van Timmeren J, Sanduleanu S, Larue RT, Even AJ, Jochems A (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(12):749
Shiri I, Maleki H, Hajianfar G, Abdollahi H, Ashrafinia S, Hatt M, Oveisi M, Rahmim A (2019) Next generation radiogenomics sequencing for prediction of EGFR and KRAS mutation status in NSCLC patients using multimodal imaging and machine learning approaches. arXiv preprint arXiv:190702121
Hajianfar G, Shiri I, Maleki H, Oveisi N, Haghparast A, Abdollahi H, Oveisi M (2019) Noninvasive O6 Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase status prediction in glioblastoma multiforme cancer using magnetic resonance imaging radiomics features: univariate and multivariate radiogenomics analysis. World Neurosurg 132:140–161
Abdollahi H, Mahdavi SR, Shiri I, Mofid B, Bakhshandeh M, Rahmani K (2019) Magnetic resonance imaging radiomic feature analysis of radiation-induced femoral head changes in prostate cancer radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther 15(8):11
Abdollahi H, Shiri I, Heydari M (2019) Medical imaging technologists in radiomics era: an alice in wonderland problem. Iran J Public Health 48(1):184
Shiri I, Rahmim A, Ghaffarian P, Geramifar P, Abdollahi H, Bitarafan-Rajabi A (2017) The impact of image reconstruction settings on 18F-FDG PET radiomic features: multi-scanner phantom and patient studies. Eur Radiol 27(11):4498–4509
Shiri I, Ghafarian P, Geramifar P, Leung KH-Y, Ghelichoghli M, Oveisi M, Rahmim A, Ay MR (2019) Direct attenuation correction of brain PET images using only emission data via a deep convolutional encoder-decoder (Deep-DAC). Eur Radiol 29(12):6867–6879
Bektas CT, Kocak B, Yardimci AH, Turkcanoglu MH, Yucetas U, Koca SB, Erdim C, Kilickesmez O (2019) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: machine learning-based quantitative computed tomography texture analysis for prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade. Eur Radiol 29(3):1153–1163
Feng Z, Shen Q, Li Y, Hu Z (2019) CT texture analysis: a potential tool for predicting the Fuhrman grade of clear-cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 19(1):6
Shu J, Wen D, Xi Y, Xia Y, Cai Z, Xu W, Meng X, Liu B, Yin H (2020) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: machine learning-based computed tomography radiomics analysis for the prediction of WHO/ISUP grade. Eur J Radiol 121:108738 in press
Akin O, Elnajjar P, Heller M, Jarosz R, Erickson B, Kirk S, Filippini J (2016) Radiology data from the cancer genome atlas kidney renal clear cell: carcinoma [TCGA-KIRC] collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive Website: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/TCGA-KIRC
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin JC, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward S, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1323–1341
Shafiq-ul-Hassan M, Zhang GG, Latifi K, Ullah G, Hunt DC, Balagurunathan Y, Abdalah MA, Schabath MB, Goldgof DG, Mackin D (2017) Intrinsic dependencies of CT radiomic features on voxel size and number of gray levels. Med Phys 44(3):1050–1062
Van Griethuysen JJ, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V, Beets-Tan RG, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pieper S, Aerts HJ (2017) Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res 77(21):e104–e107
Haynes W (2013) Benjamini–hochberg method. Encyclopedia of systems biology, pp 78–78
Kickingereder P, Götz M, Muschelli J, Wick A, Neuberger U, Shinohara RT, Sill M, Nowosielski M, Schlemmer H-P, Radbruch A (2016) Large-scale radiomic profiling of recurrent glioblastoma identifies an imaging predictor for stratifying anti-angiogenic treatment response. Clin Cancer Res 22(23):5765–5771
Guo P, Zeng F, Hu X, Zhang D, Zhu S, Deng Y, Hao Y (2015) Improved variable selection algorithm using a LASSO-type penalty, with an application to assessing hepatitis B infection relevant factors in community residents. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0134151
Tian K, Rubadue CA, Lin DI, Veta M, Pyle ME, Irshad H, Heng YJ (2019) Automated clear cell renal carcinoma grade classification with prognostic significance. PLoS ONE 14(10):e0222641
Ficarra V, Righetti R, Martignoni G, D’Amico A, Pilloni S, Rubilotta E, Malossini G, Mobilio G (2001) Prognostic value of renal cell carcinoma nuclear grading: multivariate analysis of 333 cases. Urol Int 67(2):130–134
Vetterlein MW, Jindal T, Becker A, Regier M, Kluth LA, Tilki D, Chun FK-H (2016) Small renal masses in the elderly: contemporary treatment approaches and comparative oncological outcomes of nonsurgical and surgical strategies. Investig Clin Urol 57(4):231–239
Jewett MA, Mattar K, Basiuk J, Morash CG, Pautler SE, Siemens DR, Tanguay S, Rendon RA, Gleave ME, Drachenberg DE (2011) Active surveillance of small renal masses: progression patterns of early stage kidney cancer. Eur Urol 60(1):39–44
Rosenkrantz AB, Niver BE, Fitzgerald EF, Babb JS, Chandarana H, Melamed J (2010) Utility of the apparent diffusion coefficient for distinguishing clear cell renal cell carcinoma of low and high nuclear grade. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195(5):W344–W351
Maruyama M, Yoshizako T, Uchida K, Araki H, Tamaki Y, Ishikawa N, Shiina H, Kitagaki H (2015) Comparison of utility of tumor size and apparent diffusion coefficient for differentiation of low-and high-grade clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Acta Radiol 56(2):250–256
Zhang J, Mazaheri Tehrani Y, Wang L, Ishill NM, Schwartz LH, Hricak H (2008) Renal masses: characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: a preliminary experience. Radiology 247(2):458–464
Goyal A, Sharma R, Bhalla AS, Gamanagatti S, Seth A, Iyer VK, Das P (2012) Diffusion-weighted MRI in renal cell carcinoma: a surrogate marker for predicting nuclear grade and histological subtype. Acta Radiol 53(3):349–358
Shu J, Tang Y, Cui J, Yang R, Meng X, Cai Z, Zhang J, Xu W, Wen D, Yin H (2018) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: CT-based radiomics features for the prediction of Fuhrman grade. Eur J Radiol 109:8–12
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences under Grant Number 388 and the Swiss National Science Foundation under Grant SNRF 320030_176052.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not needed for this study.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All human subject studies were downloaded from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA), an open-access database of medical images for cancer research. The site is funded by the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Imaging Program, and the contract operated by the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazari, M., Shiri, I., Hajianfar, G. et al. Noninvasive Fuhrman grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma using computed tomography radiomic features and machine learning. Radiol med 125, 754–762 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01169-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01169-z