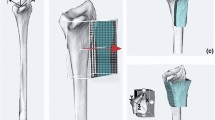
Abstract
Purpose
This article presents the results of a multiuser, randomized laboratory trial comparing the accuracy and precision of image-based navigation against individualized guides for distal radius osteotomy (DRO).
Methods
Six surgeons each performed four DROs using image-based navigation and four DROs using individualized guides in a laboratory setting with plastic phantom replicas of radii from patients who had received DRO as treatment for radial deformity. Time required and correction errors of ulnar variance, radial inclination, and volar tilt were measured.
Results
There were no statistically significant differences in the average correction errors. There was a statistically significant difference in the standard deviation of ulnar variance error (2.0 mm for navigation vs. 0.6 mm for guides). There was a statistically significant difference in the standard deviation of radial inclination error (\(6.1^{\circ }\) for navigation vs. \(1.4^{\circ }\) for guides). There were statistically significant differences in the times required (705 s for navigation vs. 214 s for guides) and their standard deviations (144 s for navigation vs. 98 s for guides).
Conclusions
Compared to navigated DRO, individualized guides were easier to use, faster, and produced more precise correction of ulnar variance and radial inclination. The combination of true three-dimensional planning, ease of use, and accurate and precise corrective guidance makes the individualized guide technique a promising approach for performing corrective osteotomy of the distal radius.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athwal GS, Ellis RE, Small CF, Pichora DR (2003) Computer-assisted distal radius osteotomy. J Hand Surg 28A(6):951–958
Nana AD, Joshi A, Lichtman DM (2005) Plating of the distal radius. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 13(3):159–171
McGrory BJ, Amadio PC (1998) Malunion of the distal radius. In: Cooney WP, Linscheid RL, Dobyns JH (eds) The wrist: diagnosis and operative treatment. Mosby, St. Louis, MO, pp 356–384
Bushnell BD, Bynum DK (2007) Malunion of the distal radius. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15(1):27–40
Croitoru H, Ellis RE, Prihar R, Small CF, Pichora DR (2001) Fixation-based surgery: a new technique for distal radius osteotomy. Comput Aided Surg 6(3):160–169
Jupiter JB, Ruder J, Roth DA (1992) Computer-generated bone models in the planning of osteotomy of multidirectional distal radius malunions. J Hand Surg Am 17(3):406–415
Dobbe JGG, Strackee SD, Schreurs AW, Jonges R, Carelsen B, Vroemen JC, Grimbergen CA, Streekstra GJ (2011) Computer-assisted planning and navigation for corrective distal radius osteotomy, based on pre- and intraoperative imaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):182–190
Oka K, Murase T, Moritomo H, Goto A, Nakao R, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H (2011) Accuracy of corrective osteotomy using a custom-designed device based on a novel computer simulation system. J Orthop Sci 16(1):85–92
Miyake J, Murase T, Moritomo H, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H (2011) Distal radius osteotomy with volar locking plates based on computer simulation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(6):1766–1773
Dobbe JG, Vroemen JC, Strackee SD, Streekstra GJ (2013) Corrective distal radius osteotomy: including bilateral differences in 3-D planning. Med Biol Eng Comput 51(7):791–797
Dobbe JG, Vroemen JC, Strackee SD, Streekstra GJ (2013) Patient-tailored plate for bone fixation and accurate 3D positioning in corrective osteotomy. Med Biol Eng Comput 51(1–2):19–27
Radermacher K, Portheine F, Anton M, Zimolong A, Kaspers G, Rau G, Staudte HW (1998) Computer assisted orthopaedic surgery with image based individual templates. Clin Orthop Relat Res 354:28–38
Dobbe JG, Pré KJ, Kloen P, Blankevoort L, Streekstra GJ (2011) Computer-assisted and patient-specific 3-D planning and evaluation of a single-cut rotational osteotomy for complex long-bone deformities. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(12):1363–1370
Oka K, Moritomo H, Goto A, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H, Murase T (2008) Corrective osteotomy for malunited intra-articular fracture of the distal radius using a custom-made surgical guide based on three-dimensional computer simulation: Case report. J Hand Surg Am 33(6):835–840
Murase T, Oka K, Moritomo H, Goto A, Yoshikawa H, Sugamoto K (2008) Three-dimensional corrective osteotomy of malunited fractures of the upper extremity with use of a computer simulation system. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(11):2375–2389
Ma B, Kunz M, Ling M, Rudan JR, Ellis RE, Abolmaesumi P, Pichora DR (2008) Laboratory and pilot study of customized jigs for distal radius osteotomy. In: Computer assisted orthopaedic surgery: 8th annual meeting of CAOS-international
Sherouse GW, Novins K, Chaney EL (1990) Computation of digitally reconstructed radiographs for use in radiotherapy treatment design. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 18(3):651–658
Langlotz F (2004) Potential pitfalls of computer aided orthopedic surgery. Injury 35(Suppl 1):S-A17–S-A23
Ma B, Ellis RE (2003) Robust registration for computer-integrated orthopedic surgery: laboratory validation and clinical experience. Med Image Anal 7(3):237–250
Graham TJ (1997) Surgical correction of malunited fractures of the distal radius. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 5(5):270–281
Aro HT, Koivunen T (1991) Minor axial shortening of the radius affects outcome of Colles’ fracture treatment. J Hand Surg Am 16(3):392–398
Fernandez DL, Capo JT, Gonzalez E (2001) Corrective osteotomy for symptomatic increased ulnar tilt of the distal end of the radius. J Hand Surg Am 26(4):722–732
Robertson C, Ellis RE, Goetz T, Gofton W, Fenton PV, Small CF, Pichora DR (2002) The sensitivity of carpal bone indices to rotational malpositioning. J Hand Surg Am 27(3):435–442
Park MJ, Cooney WP 3rd, Hahn ME, Looi KP, An KN (2002) The effects of dorsally angulated distal radius fractures on carpal kinematics. J Hand Surg Am 27(2):223–232
Vroemen JC, Dobbe JG, Strackee SD, Streekstra GJ (2013) Positioning evaluation of corrective osteotomy for the malunited radius: 3-D CT versus 2-D radiographs. Orthopedics 36(2):193–199
Bilić R, Zdravković V, Boljević Z (1994) Osteotomy for deformity of the radius: computer-assisted three-dimensional modelling. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76(1):150–154
Schweizer A, Fürnstahl P, Harders M, Székely G, Nagy L (2010) Complex radius shaft malunion: osteotomy with computer-assisted planning. Hand 5(2):171–178
Eufinger H, Wehmöller M, Machtens E (1997) Individual prostheses and resection templates for mandibular resection and reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35(6):413–418
Brown GA, Firoozbakhsh K, DeCoster TA, Reyna JR Jr, Moneim M (2003) Rapid prototyping: the future of trauma surgery? J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A(Suppl 4):49–55
Hafez MA, Chelule KL, Seedhom BB, Sherman KP (2006) Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty using patient-specific templating. Clin Orthop Relat Res 444:184–192
Kunz M, Rudan JF, Xenoyannis GL, Ellis RE (2010) Computer-assisted hip resurfacing using individualized drill templates. J Arthroplasty 25(4):600–606
Rengier F, Mehndiratta A, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Zechmann CM, Unterhinninghofen R, Kauczor H-U, Giesel FL (2010) 3D printing based on imaging data: review of medical applications. Int J CARS 5:335–341
Conflict of interest
Burton Ma, Manuela Kunz, Braden Gammon, Randy E. Ellis, and David R. Pichora declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, B., Kunz, M., Gammon, B. et al. A laboratory comparison of computer navigation and individualized guides for distal radius osteotomy. Int J CARS 9, 713–724 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0966-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0966-8