Abstract
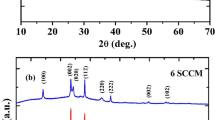
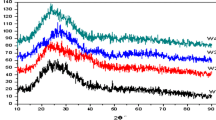
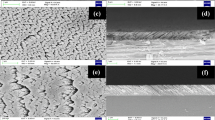
Thin films of pure and molybdenum (Mo)-doped tungsten trioxide (WO3) were deposited on indium tin oxide (ITO)-coated glass and Corning glass substrates by RF magnetron sputtering technique. The effect of Mo doping on the structural, morphological, optical and electrochromic properties of WO3 films was studied systematically. The energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX) revealed that the films consist of molybdenum concentrations from 0 to 2 at.%. X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies indicated that with the increase of Mo concentration the structural phase transformation takes place from polycrystalline to amorphous phase. The crystallite size of the films decreased from 24 to 12 nm with increase of doping concentration of Mo in WO3. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis revealed that Mo dopant led to significant changes in the surface morphology of the films. The electrochemical and electrochromic performance of the pure and Mo-doped WO3 were studied. The WO3 films formed with 1.3 at.% Mo dopant concentration exhibited high optical modulation of 44.3 % and coloration efficiency of 42.5 cm2/C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Granqvist CG (1995) Handbook of inorganic elecrochromic materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Cai GF, Zhou D, Xiong QQ, Zhang JH, Wang XL, Gu CD, Tu JP (2013) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 117:231
Noerochim L, Wang JZ, Wexler D, Chao Z, Liu HK (2013) J Power Sources 228:198
Qin Y, Fan G, Liu K, Hu M (2014) Sensors Actuators B 190:141
Hari Krishna K, Hussain OM, Julien CM (2010) Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 99:921
Madhavi V, Kondaiah P, Subba Rayudu S, Hussain OM, Uthanna S (2013) Mater Express 5:135
Zheng H, Ou JZ, Strano MS, Kaner RB, Mitchell A, Kalantar-zadeh K (2011) Adv Funct Mater 21:2175
Faughnan BW, Crandall RS (1977) Appl Phys Lett 31:834
Bathe SR, Patil PS (2008) Solid State Ionics 179:314
Rougier A, Blyr A, Garcia J, Zhang Q, Impey SA (2002) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 71:343
Penin N, Rougier A, Laffont L, Poizot P, Tarascon JM (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:422
Kondrachova L, Benjamin PH, Vijayaraghavan G, Williams RD, Stevenson KJ (2006) Langmuir 22:10490
Gesheva K, Cziraki A, Ivanova T, Szekeres A (2005) Thin Solid Films 492:322
Rueda de Leon JMO, Acosta DR, Pal U, Castaneda L (2011) Electrochim Acta 56:2599
Kalidindi NR, Manciu FS, Ramana CV (2011) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:863
Kalidindi NR, Bharathi KK, Ramana CV (2011) Appl Phys Lett 97:142107
Lethy KJ, Beena D, Mahadevan Pillai VP, Ganesan V (2008) J Appl Phys 104:033515
Lethy KJ, Beena D, Mahadevan Pillai VP, Ganesan V (2009) J Phys D Appl Phys 42:85407
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addition-Wesley, Reading, MA
Kovendhan M, Joseph DP, Kumar ES, Sendilkumar A, Manimuthu P, Sambasivam S, Venkateswaran C, Mohan R (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:8127
Papadimitropoulos G, Vourdas N, Giannakopoulos K, Vasilopoulou M, Davazoglou D (2011) J Appl Phys 109:103527
Gullapalli SK, Vemuri RS, Ramana CV (2010) Appl Phys Lett 96:171903
Gaury J, Kelder EM, Bychkov E, Biskos G (2013) Thin Solid Films 534:32
Swanepoel R (1983) J Phys E Sci Instrum 16:1214
Patil CE, Jadhav PR, Tarwal NL, Deshmukh HP, Karanjar MM, Patil PS (2011) Mater Chem Phys 126:711
Mahajan SS, Mujawar SH, Shinde PS, Inamder AI, Patil PS (2009) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 93:183
Nicholson RS, Shain I (1964) Anal Chem 36:706
Chen HS, Jan DJ, Chen CH, Huang KT (2013) Electrochem Acta 93:307
Acknowledgments
One of the authors, V. Madhavi, is thankful to the University Grant Commission, India for the award of UGC - RFSMS Junior Research Fellowship to carry out the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhavi, V., Kumar, P.J., Kondaiah, P. et al. Effect of molybdenum doping on the electrochromic properties of tungsten oxide thin films by RF magnetron sputtering. Ionics 20, 1737–1745 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1073-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1073-8