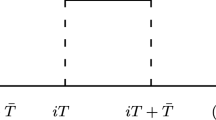
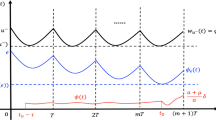
Abstract
In this paper, we formulate discrete-time mathematical models for the interactive wild and sterile mosquitoes. Instead of the Ricker-type of nonlinearity for the survival functions, we assume the Beverton–Holt-type in these models. We consider three different strategies for the releases of sterile mosquitoes and investigate the model dynamics. Threshold values for the releases of sterile mosquitoes are derived for all of the models that determine whether the wild mosquitoes are wiped out or coexist with the sterile mosquitoes. Numerical examples are given to demonstrate the dynamics of the models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allee, W.C.: The Social Life of Animals, 2nd edn. Beacon Press, Boston (1958)
Alphey, L., Benedict, M., Bellini, R., Clark, G.G., Dame, D.A., Service, M.W., Dobson, S.L.: Sterile-insect methods for control of mosquito-borne diseases: an analysis. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 10, 295–311 (2010)
Barclay, H.J.: The sterile insect release method for species with two-stage life cycles. Res. Popul. Ecol. 21, 165–180 (1980)
Barclay, H.J.: Pest population stability under sterile releases. Res. Popul. Ecol. 24, 405–416 (1982)
Barclay, H.J.: Modeling incomplete sterility in a sterile release program: interactions with other factors. Popul. Ecol. 43, 197–206 (2001)
Barclay, H.J.: Mathematical models for the use of sterile insects. In: Dyck, V.A., Hendrichs, J., Robinson, A.S. (eds.) Sterile Insect Technique. Principles and Practice in Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management, pp. 147–174. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Barclay, H.J., Mackuer, M.: The sterile insect release method for pest control: a density dependent model. Environ. Entomol. 9, 810–817 (1980)
Bartlett, A.C., Staten, R.T.: Sterile Insect Release Method and other Genetic Control Strategies. Radcliffe’s IPM World Textbook (1996) http://ipmworld.umn.edu/chapters/bartlett.htm
Beverton, R.J.H., Holt, S.J.: On the Dynamics of Exploited Fish Populations, Volume 19 of Fishery Investigations (Great Britain, Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Food). HM Stationery office, London (1957)
Bohner, M., Warth, H.: The Beverton–Holt dynamic equation. Appl. Anal. 86, 1007–1015 (2007)
Cai, L., Ai, S., Li, J.: Dynamics of mosquitoes populations with different strategies for releasing sterile mosquitoes. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 74, 1786–1809 (2014)
Dennis, B.: Allee effects: population growth, critical density, and the chance of extinction. Nat. Res. Model. 3, 481–538 (1989)
Dumont, Y., Tchuenche, J.M.: Mathematical studies on the sterile insect technique for the Chikungunya disease and Aedes albopictus. J. Math. Biol. 65, 809–854 (2012)
Dye, C.: Intraspecific competition amongst larval Aedes aegypti: food exploitation or chemical interference. Ecol. Entomol. 7, 39–46 (1982)
Elaydi, S.: An Introduction to Difference Equations, 3rd edn. Springer, London (2005)
Elaydi, S.: Discrete Chaos: With Applications in Science and Engineering, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2007)
Esteva, L., Yang, H.M.: Mathematical model to assess the control of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by the sterile insect technique. Math. Biosci. 198, 132–147 (2005)
Fister, K.R., McCarthy, M.L., Oppenheimer, S.F., Collins, C.: Optimal control of insects through sterile insect release and habitat modification. Math. Biosci. 244, 201–212 (2013)
Floresa, J.C.: A mathematical model for wild and sterile species in competition: immigration. Phys. A 328, 214–224 (2003)
Gleiser, R.M., Urrutia, J., Gorla, D.E.: Effects of crowding on populations of Aedes albifasciatus larvae under laboratory conditions. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 95, 135–140 (2000)
Li, J.: Simple mathematical models for interacting wild and transgenic mosquito populations. Math. Biosci. 189, 39–59 (2004)
Li, J.: Simple stage-structured models for wild and transgenic mosquito populations. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 17, 327–347 (2009)
Li, J.: Modeling of mosquitoes with dominant or recessive transgenes and Allee effects. Math. Biosci. Eng. 7, 101–123 (2010)
Li, J.: Simple discrete-time malarial models. J. Differ. Equ. Appl. 19, 649–666 (2013)
Li, J.: New revised simple models for interactive wild and sterile mosquito populations and their dynamics. J. Biol. Dyn. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/17513758.2016.1216613
Li, J., Yuan, Z.: Modeling releases of sterile mosquitoes with different strategies. J. Biol. Dyn. 9, 1–14 (2015)
May, R.M.: Theoretical Ecology: Principles and Applications. Saunders, Philadelphia (1976)
May, R.M., Conway, G.R., Hassell, M.P., Southwood, T.R.E.: Time delays, density-dependence and single-species oscillations. J. Anim. Ecol. 43, 747–770 (1974)
May, R.M., Oster, G.F.: Bifurcations and dynamic complexity in simple ecological models. Am. Nat. 110, 573–599 (1976)
Otero, M., Solari, H.G., Schweigmann, N.: A stochastic population dynamics model for Aedes aegypti: formulation and application to a city with temperate climate. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 1945–1974 (2006)
Schreiber, S.J.: Allee effects, extinctions, and chaotic transients in simple population models. Theor. Popul. Biol. 64, 201–209 (2003)
Thome, R.C.A., Yang, H.M., Esteva, L.: Optimal control of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes by the sterile insect technique and insecticide. Math. Biosci. 223, 12–23 (2010)
Wikipedia, Sterile insect technique (2013) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sterile$_$insect$_$technique
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Nakul Chitnis and an anonymous reviewer for their careful reading and valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article belongs to the Special Issue: Demographic and temporal heterogeneity in infectious disease epidemiology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Li, J. Discrete-time models for releases of sterile mosquitoes with Beverton–Holt-type of survivability. Ricerche mat 67, 141–162 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11587-018-0361-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11587-018-0361-4
Keywords
- Mathematical modeling
- Beverton–Holt survivability
- Discrete-time models
- Sterile mosquitoes
- Vector-borne diseases