Abstract
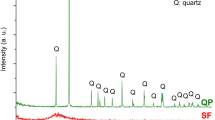
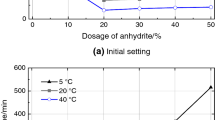
By analyzing the mechanical properties, composition of hydrates, content of Ca(OH)2 and microstructure of the complex binder of silica fume-Portland cement, which cured at constant low temperatures(+5-−10 °C), the effect of different low temperatures on hydration performance of the complex binder at the age of 3, 7 days and 14 days was researched. Experimental results show that hydration processes of the complex binder can be restricted by low temperature. Reducing the curing temperature could cause compressive strength and flexural strength of the complex binder to decrease significantly. The gradient difference between strength diminishes, content of Ca(OH)2 in hydrates reduces, and compactness of the microstructure weakens. Therefore mixing with silica fume can modify various performance indicators of the complex blinder, but reducing the curing temperature restricts the pozzolanic activity of silicon fume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DANG Yudong. Influence of Shrinkage Reducing Admixture and Internal Curing on Volume Stability of Cement Based Material[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012
NIU Ditao, XIAO Qianhui, ZHU Wenping. Concrete Damage and Neutralization under Coupling Effect of Carbonation and Freeze-Thaw Cycles[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2012 (2):353–357
Wang Baomin. Study on Performance and Mechanism of High Performance Concrete with Nano-SiO 2 [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2009
Y Wan. An Advanced Construction Technology for Cable-stayed Bailey Arch[C]. Proceedings of ARCH’ 10-the 6th International Conference on Arch Bridges, Shanghai, 2010
DENG Shouchang. State of Theoretical Study of Cooling Calculation for Concrete Heat-Saving [J]. Journal of Huizhou University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 33 (6):6–20
Ke-fei LI, Qiang ZENG. Influence of Freezing Rate on Cryo-Damage of Cementitious Material[J]. Science A: An International Applied Physics & Engineering Journal, 2009 (1): 17–21
SHENG Zhongyi, HU Yufeng, XUE Jianming, et al. SO2 Poisoning and Regeneration of Mn-Ce/TiO2 Catalyst for Low Temperature NOx Reduction with NH3[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2012 (7):676–682
MIAO Miao. Influence of Binder Material Composition and Temperature on the Deformation of Shrinkage-Compensating Concrete[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Foundation of China (No. 51072122)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Li, Y., Yang, Y. et al. Effect of low temperature on hydration performance of the complex binder of silica fume-portland cement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 29, 75–81 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-014-0870-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-014-0870-2