Abstract
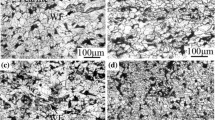
Four Nb-Ti microalloyed steels were refined and rolled to study the composition optimization of Nb-Ti microalloyed steels. The effects of Nb and Ti on the microstructures, precipitates and properties of Nb-Ti microalloyed steel were investigated. The results showed that an increase in Ti content resulted in the appearance of many fine precipitates leading to a strong precipitation strengthening effect. Hence, the yield strength increased. Besides, the increased strength by the combined increase of Nb and Ti was similar to that observed for the increase in Ti content alone. This increase in strength was attributed widely to the increase in the Ti content alone rather than Nb. Moreover, the increase in Nb content beyond 0.036 wt% exerted no significant effect on the strength of Ti-Nb microalloyed steels, in which more Ti could be added to further improve the strength of steels.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Liu D L, Fu J, Kang Y L. Oxide and Sulfide Dispersive Precipitation and Effects on Microstructure and Properties of Low Carbon Steels[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2002, l8: 7–9
Mao X.P. Microalloying Technology on Thin Slab Casting and Direct Rolling Process[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008: 5–10
Peng Z W, Li L J, Gao J X, et al. Precipitation Strengthening of Titanium Microalloyed High-Strength Steel Plates with Isothermal Treatment[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 657: 413–421
He K J, Baker T N. The Effects of Small Titanium Additions on the Mechanical Properties and the Microstructures of Controlled Rolled Niobium-Bearing HSLA Plate Steels[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, 169: 53–65
Moon J, Kim S, Lee J, et al. Limiting Austenite Grain Size of TiN-Containing Steel Considering the Critical Particle Size[J]. Scripta Mater., 2007, 56: 1083–1086
Jia Z, Misra R D K, O’Malley R, et al. Fine-Scale Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of Thin Slab Processed Titanium–Niobium Bearing High Strength Steels[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528: 7077–7083
Misra R D K, Nathani H, Hartmann J E, et al. Microstructural Evolution in A New 770 MPa Hot Rolled Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 394: 339–352
Charleux M, Poole W J, Militzer M, et al. Precipitation Behavior and Its Effect on Strengthening of an HSLA-Nb/Ti Steel[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32: 1635–1647
Hu Z W, Xu G, Yang H L, et al. The Effects of Cooling Mode on Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of A Ti-Nb Microalloyed Steel[J]. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23: 4216–4222
Kostryzhev A G, Al Shahrani A, Zhu C, et al. Effect of Deformation Temperature on Niobium Clustering, Precipitation and Austenite Recrystallisation in A Nb–Ti Microalloyed Steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 581: 16–25
Xu G, Gan X L, Ma G J, et al. The Development of Ti-Alloyed High Strength Microalloy Steel[J]. Mater. Design, 2010, 31: 2891–2896
Li Y, Wilson J A, Crowther D N, et al. The Effects of Vanadium, (Nb, Ti) on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thin Slab Cast Steels[C]. International Symposium 2002 on Thin Slab Casting and Direct Rolling. Guangzhou: The Chinese Society for Metals, 2002, 59–64
Wang R Z, Carcia C I, Hua M, et al. Microstructure and Precipitation Behavior of Nb, Ti Complex Microalloyed Steel Produced by Compact Strip Processing[J]. ISIJ Int., 2006, 46: 1345–1353
Deardo A J. Niobium in Modern Steels[J]. Int. Mater. Rev., 2003, 48: 371–402
Misra R D K, Weatherly G C, Hartmann J E, et al. Ultrahigh Strength Hot Rolled Microalloyed Steels: Microstructural Aspects of Development[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, 17: 1119
Hong S G, Kang K B, Park C G. Strain-Induced Precipitation of NbC in Nb and Nb-Ti Microalloyed HSLA Steels[J]. Scripta Mater., 2002, 46: 163–168
Pickering F B. Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels[M]. London: Applied Science Publishing Ltd., 1978
Yen H W, Chen P Y, Huang C Y, et al. Interphase Precipitation of Nanometer-Sized Carbides in A Titanium-Molybdenum-Bearing Low-Carbon Steel[J]. Acta Mater., 2011, 59: 6264–6274
Gladman T. Precipitation Hardening in Metals [J]. Mater Sci Technol., 1999, 15: 30–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Major Projects of Technology Innovation of Hubei Province (No.2017AAA116), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 51274154, 51704217) and Hebei Joint Research Fund for Iron and Steel (No.E2018318013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, X., Xu, G., Zhao, G. et al. Composition Optimization of Nb-Ti Microalloyed High Strength Steel. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 33, 1193–1197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-018-1952-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-018-1952-3