Abstract
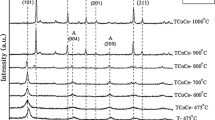
TiO2 nanopowders with different nitrogen (N) dopant concentrations were first synthesized by sol-gel method. XRD, TEM, HRTEM, XPS, UV-vis DRS were used to characterize the effects of N doping on the microstructures and optical properties of TiO2. The results indicated that the prepared TiO2 only contained anatase phase with a slight distortion, and the N doping improved the dispersity of TiO2. The N doping leaded to more defects in TiO2, capturing the charge carriers and inhibiting the combination of electrons and holes. Also, the N-doped TiO2 was composed of Ti, O and N. Further, N was doped into the TiO2 lattice by substituting for O, forming the oxidized nitrogen in the form of Ti–N–O or Ti–O–N bond, and Ti was present in the form of Ti4+ in TiO2. Finally, the absorbance of N-doped TiO2 was obviously improved in both UV and visible light region. Optical absorption edges of N-doped TiO2 samples showed obvious red shift, which expanded spectral absorption range of TiO2 and improved the utilization efficiency of visible light. It is concluded that N element was successfully doped into TiO2 crystal lattice, and the N dopant concentration of 3.0% was designed to modify TiO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Hao YB, Lu HQ. A Systematic Study on Visible–Light N–Doped TiO2 Photocatalyst Obtained from Ethylenediamine by Sol–Gel Method[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 344: 112–118
Chen ML, Oh WC. The Improved Photocatalytic Properties of Methylene Blue for V2O3/CNT/TiO2 Composite under Visible Light[J]. Int. J. Photoenergy, 2010, 4: 424–448
Lv K, Xiang Q, Yu J. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Morphology and Photocatalytic Activity of Anatase TiO2 Nanosheets with Exposed(001) Facets[J]. Appl. Cataly. B, 2011, 104(3): 275–281
Lu HQ, Yao JF. Recent Advances in Liquid–Phase Heterogeneous Photocatalysis for Organic Synthesis by Selective Oxidation[J]. Curr. Org. Chem., 2014, 18(10): 1 365–1 372
Veluru JB, Appukuttan SN, Zhu PN. Synthesis and Characterization of Rice Grains Like Nitrogen–Doped TiO2 Nanostructures by Electrospinning–Photocatalysis[J]. Mater. Lett., 2011, 65(19–20): 3 064–3 068
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Robert D. Modified TiO2 for Environmental Photocatalytic Applications: a Review[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2013, 52(10): 3 581–3 590
Macwan DP, Dave PN, Chaturvedi S. A Review on Nano–TiO2 Sol–Gel Type Syntheses and Its Applications[J]. J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46(1): 3 669–3 686
Cui XL, Li YG, Zhang QH. Silver Orthophosphate Immobilized on Flaky Layered Double Hydroxides As the Visible–Light–Driven Photocatalysts[ J]. Int. J. Photoenergy, 2012, 1110–662X: 1 302–1 312
Wang Y, He Y, Lai Q. Review of the Progress in Preparing Nano TiO2: An Important Environmental Engineering Material[J]. J. Envir. Sci., 2014, 26(11): 2 139–2 177
Pang YL, Lim S, Ong HC. A Critical Review on the Recent Progress of Synthesizing Techniques and Fabrication of TiO2–Based Nanotubes Photocatalysts[J]. Appl. Catal. A–Gen., 2014, 481(25): 127–142
Gu D, Zhu Y, Xu Z. Effects of Ion Doping on the Optical Properties of Dye–Sensitized Solar Cells[J]. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem., 2014, 4(10): 187–193
Banerjee AN. The Design, Fabrication, and Photocatalytic Utility of Nanostructured Semi–Conductors: Focus on TiO2–Based Nanostructures[ J]. Nanotech. Sci. Appl., 2011, 4: 35–65
Silija P, Yaakob Z, Suraja V. An Enthusiastic Glance in to the Visible Responsive Photocatalysts for Energy Production and Pollutant Removal, with Special Emphasis on Titania[J]. Int. J. Photoenergy, 2012, 44(1): 90–99
Mallakpour S, Nikkhoo E. Surface Modification of Nano–TiO2 with Trimellitylimido–Amino Acid–Based Diacids for Preventing Aggregation of Nanoparticles[J]. Adv. Powder Technol., 2014, 25(1): 348–353
Dong H, Zeng G, Tang L. An Overview on Limitations of TiO2–Based Particles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants and the Corresponding Countermeasures[J]. Water Res., 2015, 79: 128–146
Ohno T, Murakami N. Develpoment of Metal Cation Compound–Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts Having a Rutile Phase under Visible Light[J]. Appl. Catal. A–Gen., 2008, 349(1): 70–75
Li FF, Jing YS, Xia MS. Effect of the P/Ti Ratio the Visible–Light Photocatalytic Activity of P–Doped TiO2[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(42):18 134–18 141
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA. TiO2 Photocatalysis and Related Surface Phenomena[J]. Surf. Sci. Rep., 2009, 63(12): 515–582
Gomathi Devi L, Kavitha R. A Review on Nonmetal Ion Doped Titania for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants under UV/Solar Light: Role of Photogenerated Charge Carrier Dynamics in Enhancing the Activity[J]. Appl. Catal. B–Environ., 2013, s140–141(8): 559–587
Mamane H, Horovitz I, Lozzi L. The Role of Physical and Operational Parameters in Photocatalysis by N–Doped TiO2 Sol–Gel Thin Films[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 257(6): 159–169
Yang G, Jiang Z, Shi H. Preparation of Highly Visible–Light Active N–Doped TiO2 Photocatalyst[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(25): 5 301–5 309
Chen X, Mao SS. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications[J]. Chem. Rev., 2007, 38(41): 2 891–2 959
Jiang Z, Kong L, Alenazey FS. Enhanced Visible–Light–Driven Photocatalytic Activity of Mesoporous TiO2–xNx Derived from the Ethylenediamine–Based Complex[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(12): 5 396–5 402
Behnajady MA, Eskandarloo H, Modirshahla N. Investigation of the Effect of Sol–Gel Synthesis Variables on Structural and Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Nanoparticles[J]. Desalination, 2011, 278(1–3): 10–17
Lee HU, Lee SC, Choi S. Efficient Visible–Light Induced Photocatalysis on Nanoporous Nitrogen–Doped Titanium Dioxide Catalysts[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 228(14): 756–764
Todorova N, Vaimakis T, Petrakis D. N and N, S–Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts and Their Activity in NOx Oxidation[J]. Catal. Today, 2013, 209(12): 41–46
Powell MJ, Dunnill CW, Parkin IP. N–Doped TiO2 Visible Light Photocatalyst Films via a Sol–Gel Route Using TMEDA As the Nitrogen Source[J]. J. Photochem. Photob. A: Chem., 2014, 281(5): 27–34
Ramchiary A, Samdarshi SK. Hydrogenation Based Disorder–Engineered Visible Active N–Doped Mixed Phase Titania[J]. Solar Ener. Mater. Solar Cell, 2015, 134: 381–388
Monteiro RAR, Miranda SM, Vilar VJP. N–Modified TiO2 Photocatalytic Activity Towards Diphenhydraminedegradation and Escherichia Coli Inactivation in Aqueous Solutions[J]. Appl. Catal. B–Envir., 2015, 162(6): 66–74
Emeline AV, Sheremetyeva NV, Khomchenko NV. Photoinduced Formation of Defects and Nitrogen Stabilization of Color Centers in N–Doped Titanium Dioxide[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(30): 11 456–11 462
Lee K, Kim D, Roy P. Anodic Formation of Thick Anatase TiO2 Mesosponge Layers for High–Efficiency Photocatalysis[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(5): 1 478–1 489
Pelaez M, Nolan NT, Pillai SC. A Review on the Visible Light Active Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysts for Environmental Applications[J]. Appl. Catal. B–Envir., 2012, 125(33): 331–349
Dong F, Guo S, Wang H. Enhancement of the Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity of C–Doped TiO2 Nanomaterials Prepared by a Green Synthetic Approach[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 115(27): 13 285–13 292
Leong KH, Monash P, Ibrahim S. Solar Photocatalytic Activity of Anatase TiO2 Nanocrystals Synthesized by Non–Hydrolitic Sol–Gel Method[J]. Solar Energy, 2014, 101(1): 321–332
Aziz AA, Puma GL, Ibrahim S. Preparation, Characterisation and Solar Photoactivity of Titania Supported Strontium Ferrite Nanocomposite Photocatalyst[J]. J. Exp. Nanosci., 2013, 8(3): 295–310
Ma W, Wang Q, Qin Z. Green Synthesis of Silver–Modified TiO2 Hollow Spheres and Their Visible Photocatalytic Performance[J]. J. Chen, J. Univer. Jinan, 2016, 30: 167–176
Ou HH, Luo SL, Liao CH. N–Doped TiO2 Prepared from Microwave–Assisted Titanate Nanotubes(NaxH2–xTi3O7): the Effect of Microwave Irradiation during TNT Synthesis on the Visible Light Photoactivity of N–Doped TiO2[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(10): 4 000–4 007
Li H, Li J, Huo Y. Highly Active TiO2 N Photocatalysts Prepared by Treating TiO2 Precursors in NH3/Ethanol Fluid under Supercritical Conditions[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006,110(4): 1 559–1 565
Yang X, Cao C, Erickson L. Photo–Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B on C–, S–, N–, and Fe–Doped TiO2 under Visible Light Irradiation[J]. Appl. Catal. B–Envir., 2009, 91(3–4): 657–662
Emeline AV, Kuznetsov VN, Rybchuk VK. Visible–Light–Active Titania Photocatalysts: the Case of N–Doped TiO2–Properties and Some Fundamental Issues[J]. Int. J. Photoenergy, 2008, 4: 1–19
Chen XB, Burda C. Photoelectron Spectroscopic Investigation of Nitrogen–Doped Titania Nanoparticles[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(40): 15 446–15 449
Zhang J, Fu WJ, Xi J. N–doped Rutile TiO2 Nano–Rods Show Tunable Photocatalytic Selectivity[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 575(20): 40–47
Kuo C, Wu C, Wu J, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of a Phosphorus–Doped TiO2 Immobilized Bed for the Photodegradation of Bisphenol A under UV and Sunlight Irradiation[J]. Reac. Kinet. Mech. Cat., 2015, 114(2): 753–766
Pan H, Zhang YW, Shenoy VB. Effects of H–, N–, and(H, N)–Doping on the Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(24): 12 224–12 231
Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T. Visible–Light Photocatalysis in Nitrogen–Doped Titanium Oxides[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5528): 269–271
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Advanced Analysis & Testing Center of Nanjing Forestry University for the assistance in experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51378264), Open Research Fund of National Engineering Laboratory for Advanced Road Materials (No. NLARMORF- 2018-02) and Provincial Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu, China (No. JNHB-050)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, T., Wang, M. & Wang, T. Effects of N Doping on the Microstructures and Optical Properties of TiO2. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 55–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2014-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2014-1