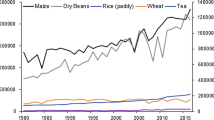
Abstract
Agriculture, especially the irrigated sector, is the mainstay of Sudan’s economy as it accounts for 40 % of gross domestic product (GDP) and employs 70 % of the workforce. The economic viability of irrigated schemes is dependent on three factors: crop yield, water management and cropped area. The research question of this study was whether or not the current status of these factors can be sustained in order to maintain the economic viability of irrigation systems? To answer this question, a new (to the best of the author’s knowledge) approach was developed based on time series analysis, and on the Theil–Sen estimator of slope. The study defined sustainability conceptually as “the ability of an irrigation system to sustain crop yields using the optimum cropped area and water consumption to realize the economic viability of the irrigation system without a decline in soil quality and environment”. Time series datasets of crop yields, cropped area and irrigation water consumption are collected routinely by statistical departments. Any abrupt years in the development of trends were detected and related to their driving forces/causes, of which climatic conditions and marketing policies were found to be the most important. The simple approach developed proved its suitability for quantifying the progress of irrigated schemes’ towards sustainability development as tested under the conditions of Gezira irrigated scheme in Sudan—the largest singly managed irrigation scheme in the world. The scheme was found to be sustainable under the condition that the crop yield is considered as the top priority; otherwise, the sustainability of the scheme is jeopardized.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhadi A, Adam S, Hassan A, Hata T (2004) Participatory management: would it be a turning point in the history of the Gezira scheme. Irrig Drain 53:429–436
Adam H (2005) Agroclimatology, crop water requirement and water management. University of Gezira Press, Wadmedani
Ahmed I, Stigter C, Adam H, Adeeb A (2002) Water-use efficiency of sorghum and groundnut under traditional and current irrigation in the Gezira scheme, Sudan. Irrig Sci 21:115–125
Basistha A, Arya D, Goel N (2009) Analysis of historical changes in rainfall in the Indian Himalayas. Int J Climatol 29:555–572
Bassi N, Kumar D (2011) Can sector reforms improve efficiency? Insight from irrigation management transfer in central India. Int J Water Resour Dev 27:709–721
Böhringer C, Jochem P (2007) Measuring the immeasurable—a survey of sustainability indices. Ecol Econ 63:1–8
Bos G, Burton A, Molden J (2005) Irrigation and drainage performance assessment; practical guidelines. CABI, Wallingford
Burn D, Hag Elnur M (2002) Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J Hydrol 255:107–122
Cai X, McKinney D, Rosegrant M (2003) Sustainability analysis for irrigation water management in the Aral Sea region. Agric Syst 76:1043–1066
Challinor A, Wheeler T, Garforth C, Craufurd P, Kassam A (2007) Assessing the vulnerability of food crop systems in Africa to climate change. Clim Chang 83:381–399
De Fraiture C, Wichelns D (2010) Satisfying future water demands for agriculture. Agric Water Manag 97:502–511
Doorenbos J (1976) Agro-meteorological field stations. FAO Irrigation and Drainage paper (27). Rome, Italy
Essiet E (2001) Agricultural sustainability under small-holder farming in Kano, northern Nigeria. J Arid Environ 48:1–7
Faki H (1981) Effect of irrigation–water management on the farmers’ income in the Gezira, Sudan. Q J Int Agric 20:345–359
Faki H, Yousif G, Mohamed I (1995) Potentials of the Sudan’s irrigated sector in cereals grain production: analysis of various policy options. Agric Syst 48:457–483
Fan P, Qi J (2010) Assessing the sustainability of major cities in China. Sustain Sci 5:51–68
Farah S, Salih A, Taha A, Ali Z, Ali A (1997) Grain sorghum response to supplementary irrigations under post-rainy season conditions. Agric Water Manag 33:31–41
Gerstengarbe F, Werner P (1999) Estimation of the beginning and end of recurrent events within a climate regime. Clim Res 11:97–107
Grenier P, Bramel P, Dahlberg J, El-Ahmadi A, Mahmoud M, Peterson G, Rosennows D, Ejeta G (2004) Sorghums of the Sudan: analysis of regional diversity and distribution. Genet Resour Crop Evol 51:489–500
Guvele C (2001) Gains from crop diversification in the Sudan Gezira scheme. Agric Syst 70:319–333
Hansen J (1996) Is agricultural sustainability is a useful concept? Agric Syst 50(1):I7–I143
Hansen J, Jones J (1996) A systems framework for characterizing farm sustainability. Agric Syst 51:185–201
Hay J, Mimura N (2006) Supporting climate change vulnerability and adaptation assessments in the Asia-Pacific region: an example of sustainability science. Sustainability Science 1:23–35
Hsiao T, Steduto P, Fereres E (2007) A systematic and quantitative approach to improve water use efficiency in agriculture. Irrig Sci 25:209–231
Hulme M (1987) Rainfall in central Sudan: an asset or a liability? Geoforum 18(3):321–331
Ibrahim A (1984) Concept of design and practice for irrigation distribution systems in Sudan. In: Fadl O, Baily C (eds) Conference of water distribution in Sudanese irrigated agriculture. Gezira University, Wadmedani, pp 105–116
IPCC (2007) Climate change, synthesis report. The 4th assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Valencia, Spain
Karatas B, Akkuzu E, Unal H, Asik S, Avci M (2009) Using satellite remote sensing to assess irrigation performance in Water User Associations in the Lower Gediz Basin, Turkey. Agric Water Manag 96:982–990
Knott D, Hewitt R (1996) Future water development planning in the Sudan. In: Howell P, Allan J (eds) The Nile sharing a scarce resource: an historical and technical review of water management and of economical and legal issues. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 205–216
Komatsu Y, Tsunekawa A, Ju H (2005) Evaluation of agricultural sustainability based on human carrying capacity in drylands: a case study in rural villages in Inner Mongolia, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 108:29–43
Lee Y, Huang C (2007) Sustainability index for Taipei. Environ Impact Assess Rev 27:505–521
Moeller C, Sauerborn J, Voil P, Manschadi A, Pala M, Meinke H (2013) Assessing the sustainability of wheat-based cropping systems using simulation modelling: sustainability = 42? Sustain Sci. doi:10.1007/s11625-013-0228-2
Morid S, Shahkarami N, Jamnani M (2007) Optimization of cropped area, based on forecast streamflows (a case study: Soofichay irrigation systems). In: Reducing the Vulnerability of Societies to Water Related Risks at the Basin Scale. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Integrated Water Resources Management, Bochum, Germany, September. IAHS 317:235–240
Nasri M, Modarres R (2009) Dry spell analysis of Isfahan province, Iran. Int J Climatol 29:1430–1438
Omer A (2005) Agriculture and irrigation water management in the Sudanese national irrigated schemes. Ph. D. thesis Water Management and Irrigation Institute, University of Gezira, Wadmedani
Perry C, Steduto P, Allen GR, Burt CM (2009) Increasing productivity in irrigated agriculture: agronomic constraints and hydrological realities. Agric Water Manage 96:1517–1524
Plusquellec H (1990) The Gezira irrigated scheme in Sudan: objectives, design and performance. World Bank Technical Paper No. 120
Pretty J, Morison J, Hine R (2003) Reducing food poverty by increasing agricultural sustainability in developing countries. Agric Ecosyst Environ 95:217–234
Rigby D, Caceres D (2001) Organic farming and the sustainability of agricultural systems. Agric Syst 68:21–40
Samad M, Vermillion D (1999) An assessment of the impact of participatory irrigation management in Sri Lanka. Int J Water Resour Dev 15(1–2):219–240
Shamseddin A (2012) Impacts of climate change on rainfed agriculture in a Semi Arid Zone—a case study from Sudan. In: Bogardi J et al (eds), River Basin and Changes GWSP and UNESCO-IHE, pp 8–13
Shamseddin A, Lars R (2011) Analysis of water footprints of rainfed and irrigated crops in Sudan. J Nat Resour Dev 3:01–09
Stoneham G, Eigenraam M, Ridley A, Barr N (2003) The application of sustainability concepts to Australian agriculture: an overview. Aust J Exp Agric 43:195–203
Sulser T, Duryea M, Frolich L, Cuaspud G (2001) A field practical approach for assessing biophysical sustainability of alternative agricultural systems. Agric Syst 68:113–135
Sydorovych O, Wossink A (2008) The meaning of agricultural sustainability: evidence from a conjoint choice survey. Agric Syst 98:10–20
UN (1987) Our common future. The report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, transmitted to the General Assembly as an Annex to document A/42/427—Development and International Cooperation: Environment
UN (2007) Indicators of sustainable development: Guidelines and methodologies, 3rd edn. United Nations, New York
UNEP (2007) Sudan Post-conflict environmental assessment. United Nation Environment Programme
World Bank (2000) Options for the sustainable development of the Gezira scheme. Report No. 20398-Su
Yildirim Y, Cakmak B (2004) Participatory irrigation management in Turkey. Int J Water Resour Dev 20(2):219–228
Yue S, Wang C (2004) The Mann–Kendall test modified by effective sample size to detect trend in serially correlated hydrological series. Water Resour Manag 18:201–218
Yue S, Pilon P, Cavadias G (2002) Power of Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271
Zwart S, Leclert L (2010) A remote sensing-based irrigation performance assessment: a case study of the Office du Niger in Mali. Irrig Sci 28:371–385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handled by Shiqiu Zhang, Peking University, College of Environmental Science and Engineering, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S.M. Assessment of irrigation system sustainability using the Theil–Sen estimator of slope of time series. Sustain Sci 9, 293–302 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-013-0237-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-013-0237-1