Summary
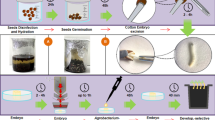
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) resistant plants of transgenic cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) were produced using Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a plasmid carrying the neomycin phosphotransferase II (npt II) and 2,4-D monooxygenase (tfd A) genes. An in vitro assay was performed to determine the sensitivity of seed germination, and the growth of seedlings of transgenic and non-transgenic cotton to various concentrations of kanamycin and 2,4-D. The results indicated that kanamycin caused the cotyledons of non-transgenic plants to turn white, but transgenic plants grew normally. Seed germination and seedling growth of non-transgenic plants were strongly inhibited by 2,4-D, but only slightly for transgenic plants. Transgenic plants and non-transgenic plants can be clearly distinguished by the use of 2 mg l−1 2,4-D in seed germination medium. There was a high correlation between the response of seed germination and the growth of seedlings to kanamycin or 2,4-D, based on the germination ration, albino ratio, dry weight or fresh weight. On this basis, we development a rapid method for identifying transgenic plants that has been verified in the field. These findings will allow identification of cotton transformants at an early stage of plant development, saving time and improving cultivars containing the 2,4-D resistance trait.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley, C.; Trolinder, N. L.; Morgan, M. M.; Quisenberry, J. E.; Ow, D. W. Engineering 2,4-D resistance into cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83:645–649; 1992.
Chen, Z. X.; Liewellyn, D. J.; Fan, Y. L.; Li, S. J.; Guo, S. D.; Jiao, G. L.; Zhao, J. X. 2,4-D resistant transgenic cotton plants produced by Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer. Sci. Agri. Sin: 27(4):31–37; 1994.
Cousins, Y. L.; Lyon, B. B.; Llewellyn, D.J. Transformation of an Australian cotton cultivar: prospects for cotton improvement through genetic engineering. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 18:481–494; 1991.
Gamborg, O.; Miller, R.; Ojima, K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybeant root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 50:151–158; 1968.
International Advisory Committee. Cotton: review of world situation Washington, DC: Monogram by International Advisory Committee; 1996.
Jenkins, J. N.; McCarty, J. C.; Buehler, R. E.; Kiser, J.; Williams C.; Wofford, T. Resistance of cotton with δ-endotoxin genes from Bacillus thringiensis var. kurstaki on selected Lepidopteran insects. Agron. J. 89:768–780; 1997.
John, M. E. Cotton crop improvement through genetic engineering. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 17:185–209; 1997.
Kapaun, J. A.; Cheng, Z. M. Aminoglycoside antibiotics inhibit shoot regeneration from Siberian elm leaf explants. Hortsciences 34:727–729; 1999.
Keller, G.; Spatola, L.; McCabe, D.; Martinell, B.; Swain, W.; John, M. E. Transgenic cotton resistant to herbicide bialaphos. Transgen. Res. 6:385–392; 1997.
Li, Y. E.; Chen, Z. X.; Wu, X.; Li, S. J.; Jiao, G. L.; Wu, J. H.; Fan, X. P.; Meng, J. H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H. L.; Xiao, G. F.; Li, X. H. Obtaining transgenic cotton plants with Cowpea trypsin inhibitor gene. Acta Gossypii Sinica 10:237–243; 1998.
Lyon, B. R.; Cousins, Y. L.; Llewellyn, D. J.; Dennis, E. S. Cotton plants transformed with a bacterial-degradation gene are protected from accidental spray drift damage by the herbicide 2,4-dichorophen-oxyacetic acid. Transgen. Res. 2:162–169; 1993.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–479; 1962.
Ni, W. C.; Zhang, Z. L.; Guo, S. D. Development of transgenic insectresistant cotton plants. Sci. Agri. Sin. 31(2):8–13; 1998.
Perlak, F. J.; Deaton, R. W.; Armstrong, R. L.; Fuchs, R. L.; Sims, S. R.; Greenplate, J. T.; Fischhoff, D. A. Insect resistant cotton plants. Bio/Technology 8:939–943; 1990.
Rajaseharam, K.; Grulam, J. W.; Hudspeth, R. L. Herbicide-resistant Acale and Coker cottons transformation with a native gene encoding mutant forms of acetohydroxyacid synthase. Mol. Breed 2:307–319; 1996.
Thomas, J. C.; Adams, D. G.; Keppenne, V. D.; Wasmann, C. C.; Brown, J. K.; Kanost, M. R.; Bohnert, H. J. Proease inhibitors of Manduce sexta expressed in transgenic cotton. Plant Cell Rep. 14:758–762; 1995.
Umbeck, P.; Johmson, G.; Barton, K. Genetically transformed cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plants. Bio/Technology 5:235–266; 1987.
Wilmink, A.; Dons, J. J. M. Selective agents and marker genes for use in transformation of monocotyledonous plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 11:165–185; 1993.
Xie, D. X.; Fan, Y. L.; Ni, W. C.; Huang, J. Q. Transformed Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene into cotton plants. China Sci. (B) 4:367–373; 1991.
Zhang, B. H.; Feng, R.; Li, X. L.; Li, F. L. Anther culture and plant regeneration of cotton (Gossypium klotzschianum Anderss). Chinese Sci. Bull 41:145–148; 1996b.
Zhang, B. H.; Feng, R.; Liu, F.; Yao, C. B. Direct induction of cotton somatic embryogenesis. Chinese Sei. Bull. 44:766–767; 1999.
Zhang, B. H.; Liu, Z. H.; Wang, H. M.; Yao, C. B. Effects of kanamycin on tissue culture and somatic embryogenesis in cotton. Plant Growth Regul. (in press); 2001.
Zhang, B.H.; Liu, F.; Yao, C. B. Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 89–94; 2000b.
Zhang, B. H.; Liu, F.; Yao, C. B.; Wang, K. B. Recent progress in cotton biotechnology and genetic engineering in China. Curr. Sci. 79:37–44; 2000a.
Zhang, B. H.; Wang, Q. L.; Feng, R.; Li, F. L.; Li, F. G.; Li, X. L. Somatic embryony patterns and plant regeneration in Gossypium hirsutum L. J. Agr. Biotechnol. 4(1):44–50; 1996a.
Zhang, B.H.; Zhao, B. Cotton biotechnology and its application. Beijing: China Agricultural Press; 1997;1–201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, BH., Wang, HM., Liu, F. et al. In vitro assay for 2,4-D resistance in transgenic cotton. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 37, 300–304 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0053-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0053-7