Summary
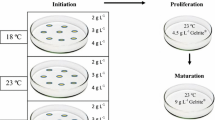
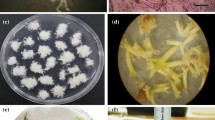
Somatic embryogenesis (SE) initiation in Pinus strobus was optimized by the manipulation of plant growth regulator (PGR) concentrations in the culture medium. Modified Litvay medium (MLV) of Litvay et al. (1985) supplemented with lower than routinely used PGR concentration increased initiation of established embryogenic cultures from approximately 20 to 53%. The original developmental stage of zygotic embryos had a pronounced effect on the SE response. The optimum stage was the pre- to shortly post-cleavage stage. A substantial genetic influence on initiation of SE was indicated by a significant variance component due to families. Genotype X collection date and genotype X media interactions had large effects on initiation of SE. The PGR levels in the culture medium prior to maturation had a significant effect on subsequent production of mature somatic embryos. Embryogenic tissue initiated and proliferated on medium with a low level of PGR consistently produced a high number of somatic embryos, indicating that optimized initiation protocol also enhanced somatic embryo production. Somatic embryos of 93 embryogenic lines (representing five families) that were initiated on media with different PGR concentrations were converted to plants at an overall frequency of 76%, and grown in the greenhouse. With these improved protocols, application of P. strobus SE in commercial clonal forestry is feasible as an alternative to traditional breeding and reforestation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee, S. N.; Radforth, N. W. In vitro studies on the developing embryos of Pinus resinosa, Bot. Mag. Tokyo 82:329–340; 1969.
Becwar, M. R.; Nagmani, R.; Wann, S. R. Initiation of embryogenic cultures and somatic embryo development in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). Can. J. For. Res. 20:810–817; 1990.
Becwar, M. R.; Wann, S. R.; Johnson, M. A.; Verhagen, R. P.; Feirer, R. P.; Nagmani, R. Development and characterization of in vitro embryogenic systems in conifers. In: Ahuja, M. R., ed. Somatic cell genetics of woody plants, Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1988:1–14.
Chalutz, E.; Mattoo, A. K.; Fuchs, Y. Biosynthesis of ethylene: the effect of phosphate. Plant Cell Environ. 3:349–356; 1980.
Cheliak, W. M.; Klimaszewska, K. Genetic variation in somatic embryogenic response in open-pollinated families of black spruce. Theor. Appl. Genet. 82:185–190; 1991.
Dogra, P. D. Morphology, development and nomenclature of conifer embryo. Phytomorphology 28:307–322, 1978.
Filonova, L. H.; Bozhkov, P. V.; von Arnold, S. Developmental pathway of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies as revealed by time-lapse tracking. J. Exp. Bot. 51:249–264; 2000.
Finer, J. J.; Kriebel H. B.; Becwar, M. R. Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). Plant Cell Rep. 8:203–206; 1989.
Garin, E.; Isabel, N.; Plourde, A. Screening of large numbers of seed families of Pinus strobus L. for somatic embryogenesis from immature and mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 18:37–43; 1998.
Gupta, P. K.; Durzan, D. J. Shoot multiplication from mature trees of Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana). Plant Cell Rep. 4:177–179; 1985.
Gyulai, G.; Janovszky, J.; Kiss, E.; Lelik, L.; Csillag, A.; Heszky, L. E. Callus initiation and plant regeneration from inflorescence primordia of the intergeneric hybrid Agropyron repens (L.) Beauv. x Bromus inermis Leyss. cv.nanus on a modified nutritive medium. Plant Cell Rep. 11:266–269; 1992.
Handley, L. W.; Becwar, M. R.; Chesick, E. E.; Coke, J. E.; Godbey, A. P.; Rutter, M. R. Research and development of commercial tissue culture systems in loblolly pine. TAPPI J. 78:169–175; 1995.
Högberg, K. A.; Ekberg, I.; Norell, L.; von Arnold, S. Integration of somatic embryogenesis in a tree breeding programme: a case study with Picea abies. Can. J. For. Res. 28:1536–1545; 1998.
Jensen, W. A. Botanical histochemistry: principles and practice. San Francisco. W.H. Freeman; 1962.
Jones, N. B.; van Staden, J. Plantlet production from somatic embryos of Pinus patula. J. Plant Physiol. 145:519–525; 1995.
Kaul, K. Somatic embryogenesis in eastern white pine (Pinus strobus L.). In: Jain, S.; Gupta, P.; Newton, R., eds., Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 3 Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995:257–268.
Klimaszewska, K.; Bernier-Cardou, M.; Cyr, D. R.; Sutton, B. C. S. Influence of gelling agents on culture medium gel strength, water availability, tissue water potential, and maturation response in embryogenic cultures of Pinus strobus L. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 36:279–286; 2000.
Klimaszewska, K.; Smith, D. R. Maturation of somatic embryos of Pinus strobus is promoted by a high concentration of gellan gum. Physiol. Plant. 100:949–957; 1997.
Lelu, M. A.; Bastien, C.; Drugeault, A.; Gouez, M. L.; Klimaszewska, K. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet development in Pinus sylvestris and Pinus pinaster on medium with and without growth regulators. Physiol. Plant. 105:719–728; 1999.
Li, X. Y.; Huang, F. H.; Gbur E. E., Jr. Effect of basal medium, growth regulators and Phytagel concentration on initiation of embryogenic cultures from immature zygotic embryos of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Plant Cell Rep. 17:298–301; 1998.
Litvay, J. D.; Verma, D. C.; Johnson, M. A. Influence of a loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) culture medium and its components on growth and somatic embryogenesis of the wild carrot (Daucus carota L.). Plant Cell Rep. 4:325–328; 1985.
Miller, L. R.; Murashige, T. Tissue culture propagation of tropical foliage plants. J. Tiss. Cult. Methods 12:797–813; 1976.
Nagmani, R.; Bonga, J. M. Embryogenesis in subcultured callus of Larix decidua. Can. J. For. Res. 15:1088–1091; 1985.
Nagmani, R.; Diner, A. M.; Sharma, G. C. Somatic embryogenesis in longleaf pine (Pinus palustris). Can. J. For. Res. 23:873–876; 1993.
Park, Y. S.; Bonga, J. M.; Cameron, S. I.; Barrett, J. D.; Forbes, K.; DeVerno, L.; Klimaszewska, K. Somatic embryogenesis in jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lamb). In: Jain, M. S.; Gupta, P. K.; Newton, R. J., eds. Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants, vol. 4 Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1999:491–504.
Park, Y. S.; Pond, S. E.; Bonga, J. M. Initiation of somatic embryogenesis in white spruce (Picea glauca): genetic control, culture treatment effects, and implication for tree breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86:427–436; 1993.
Percy, R.; Klimaszewska, K.; Cyr, D. R. Evaluation of somatic embryogenesis for clonal propagation of western white pine. Can. J. For. Res. 30:1867–1876; 2000.
Preece, J. E.; Zhao, J.; Kung, F. H. Callus production and somatic embryogenesis from white ash (Fraxinus americana L.). Hosrt Science 24:377–380; 1989.
Ribnicky, D. M.; Ilic, N.; Cohen, J.; Cooke, T. J. The effects of exogenous auxins on endogenous indole-3-acetic acid metabolism. The implications for carrot somatic embryogemesis. Plant Physiol. 112:549–558; 1996.
Salajova, T.; Salaj, J.; Kormutak, A. Initiation of embryogenic tissues and plantlet regeneration from somatic embryos of Pinus nigra Arn. Plant Sci. 145:33–40; 1999.
Squillace, A. E. Average genetic corelations among offsping from openpollinated forest trees. Silvae Genet. 23:149–156; 1974.
Tuskan, G. A.; Sargent, W. A.; Rensema, T.; Walla, J. A. Influence of plant growth regulators, basal medial and carbohydrate levels on the in vitro development of Pinus ponderosa (Dougl. ex Law.) cotyledon explants. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 20:47–52; 1990.
Verhagen, S. A.; Wann, S. R. Norway spruce somatic embryogenesis: high frequency initiation from light-cultured mature embryos. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 16:103–111; 1989.
von Aderkas, P.; Bonga, J. M.; Klimaszewska, K.; Owens, J. N. Comparison of larch embryogeny in vitro and in vivo. In: Ahuja, M. R., ed. Woody plant biotechnology. New York: Plenum Press; 1991:139–155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klimaszewska, K., Park, YS., Overton, C. et al. Optimized somatic embryogenesis in Pinus strobus L.. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 37, 392–399 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0069-z