Abstract
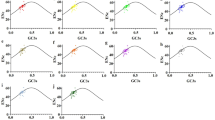
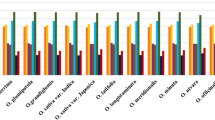
Codon usage in chloroplast genome of six seed plants (Arabidopsis thaliana, Populus alba, Zea mays, Triticum aestivum, Pinus koraiensis and Cycas taitungensis) was analyzed to find general patterns of codon usage in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. The results show that chloroplast genomes of the six seed plants had similar codon usage patterns, with a strong bias towards a high representation of NNA and NNT codons. In chloroplast genomes of the six seed plants, the effective number of codons (ENC) for most genes was similar to that of the expected ENC based on the GC content at the third codon position, but several genes with low ENC values were laying below the expected curve. All of these data indicate that codon usage was dominated by a mutational bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants and that selection appeared to be limited to a subset of genes and to only subtly affect codon usage. Meantime, four, six, eight, nine, ten and 12 codons were defined as the optimal codons in chloroplast genomes of the six seed plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi H. 2001. Gene expression and molecular evolution. Curr. Opin Genet Dev, 11: 660–666
Bernardi G, Bernardi G. 1986. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol, 24: 1–11
Bernardi G. 1993. The vertebrate genome-isochores and evolution. Mol Biol Evol, 10: 186–204
Campell W H, Gowri G. 1990. Codon usage in higher plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol, 92(1): 1–11
Duret L. 2002. Evolution of synonymous codon usage in metazoans. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 12: 640–649
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M. 1980a. Codon frequencies in 119 individual genes confirm consistent choices of degenerate bases according to genome type. Nucleic Acids Res, 8(9): 1893–1912
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M, Mercier R, Pave A, 1980b. Codon catalogue usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res, 8(1): 49–62.
Greenacre M J. 1984. Theory and Applications of Correspondence Analysis. London: Academic Press
Ikemura T. 1985. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol, 2: 13–34
Kawaba A, Miyashita N T. 2003. Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet Syst, 78(5): 343–352
Liu Q, Feng Y, Xue Q. 2004. Analysis of factors shaping codon usage in the mitochondrion genome of Oryza sativa. Mitochondrion, 4: 313–320
Lockhart P J, Penny D, Hendy M D, Howe C J, Beanland T J, Larkum A W D. 1992. Controversy on chloroplast origins. FEBS Lett, 301: 127–131
Morton B R. 1993. Chloroplast DNA codon use: evidence for selection at the psbA locus based on tRNA availability. J Mol Evol, 37: 273–280
Morton B R, Levin J A. 1997. The atypical codon usage of the psbA gene may be the remnant of an ancestral bias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94: 11434–11438
Morton B R. 1998. Selection on the codon bias of chloroplast and cyanelle genes in different plant and algal lineages. J Mol Evol, 46: 449–459
Morton B R. 1999. Strand asymmetry and codon usage bias in the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96: 5123–5128
Morton B R, So B G. 2000. Codon usage in plastid genes is correlated with context, position within the gene, and amino acid content. J Mol Evol, 50: 184–193
Nussinov R. 1984. Strong doublet preferences in nucleotide sequences and DNA geometry. J Mol Evol, 20: 111–119
Peden J F. 1999. Analysis of codon usage. Ph. D. Thesis. Nottingham: University of Nottingham
Perriere G, Thioulouse J, 2002. Use and misuse of correspondence analysis in codon usgae studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 30:4548–4555
Sharp P M, Tuohy T M F, Mosurski K R. 1986. Codon usage in yeast cluster-analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res, 14: 5125–5143
Sharp P M, Cowe E, Higgins D G, Shields D C, Wolfe K H, Wright F. 1988. Codon usage in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens: a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res, 16: 8207–8711
Sharp P M, Devine K M. 1989. Codon usage and gene-expression level in Dictyostelium discoideum-highly expressed genes do prefer optimal codons. Nucleic Acids Res, 17: 5029–5039
Shields D C, Sharp P M. 1987. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res, 15: 8023–8040
Stenico M, Lloyd A T, Sharp P M. 1994. Codon usage in Caenorhabditis elegans: delineation of translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res, 22(13):2437–2446
Sueoka N. 1999. Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the case of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position. Gene, 238: 53–58
Sueoka N. 1988. Directional mutational pressure and neutral pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 85: 2653–2657
Sueoka N. 1962. On the genetic basis of variation and heterogeneity of DNA base composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 48: 582–592
Wolfe K H, Sharp P M. 1988. Identification of functional open reading frames in chloroplast genomes. Gene, 66: 215–222
Wolfe K H, Sharp P M, Li W H. 1989. Mutation-rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature, 337:283–285
Wolfe K H, Morden C W, Ems S C, Palmer J D. 1992. Rapid evolution of the plastid translational apparatus in a nonphotosynthetic plant: loss or accelerated sequence evolution of tRNA and ribosomal protein genes. J Mol Evol, 35: 304–317
Wright F. 1990. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene, 87(1): 23–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Long, W. & Li, X. Patterns of synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. For. Stud. China 10, 235–242 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0047-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0047-1