Abstract
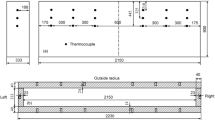
In order to quantify the cooling conditions undergone by an ingot during direct-chill (DC) casting, thermocouples were immersed in the liquid pool and consequently entrapped in the solid, thus monitoring the temperature of the metal during its descent. Assuming steady-state thermal conditions, the time-dependent temperatures measured by these thermocouples were then converted into spacedependent temperature profiles. These values were the input of a Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) inverse method described by Rappaz et al.,[1] which has been adapted in this case to steady-state thermal conditions. This MAP method permits the deduction of the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity of the alloy, initially, and then of the highly nonuniform heat-flux distribution along the ingot rolling faces, in a second step. The obtained values are in good agreement with literature and clearly reflect the widely different boundary conditions associated with primary cooling (contact with the mold) and secondary cooling (water jet).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Rappaz, J.-L. Desbiolles, J.-M. Drezet, C.-A. Gandin, A. Jacot, and P. Thévoz: in Modeling of Casting, Welding and Advanced Solidification Processes, M. Cross and J. Campbell, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 449–57.
J.-M. Drezet: Ph.D. Thesis No. 1509, EPF-Lausanne, Lausanne, 1996.
J.-M. Drezet, M. Rappaz, B. Carrupt, and M. Plata: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1995, vol. 26B, pp. 821–30.
A. Mo, T. Rusten, H.J. Thevik, B.R. Henriksen, and E.K. Jensen: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 667–74.
J.-M. Drezet and M. Rappaz: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 3214–25.
H. Yu: Light Metals 1980, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1980, pp. 613–28.
F.P. Incropera and D.P. de Witt: Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1985, p. 461.
D.C. Weckman and P. Niessen: Metall. Trans. B, 1982, vol. 13B, pp. 593–602.
J.F. Grandfield, A. Hoadley, and S. Instone: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 691–99.
J.F. Grandfield, K. Goodall, P. Misic, and X. Zhang: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 1081–90.
J.A. Bakken and T. Bergstrøm: Light Metals 1986, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 883–89.
E.K. Jensen, S. Johansen, T. Bergstrøm, and J.A. Bakken: Light Metals 1986, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1986, pp. 891–96.
L. Maenner, B. Magnin, and Y. Caratini: in Light Metals 1997, R. Huglen, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 701–07.
I. Opstelten and J. Rabenberg: in Light Metals 1999, C. Eckert, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 729–35.
J.V. Beck, B. Blackwell, and C.R. St Clair, Jr.: Inverse Heat Conduction—Ill-Posed Problems, Wiley, New York, NY, 1985.
J.V. Beck and K.J. Arnold: Parameter Estimation in Engineering and Science, Wiley, New York, NY, 1977.
G. Milano and F. Scarpa: Universita di Genova, Italia, private communication, 1994.
P. Thévoz, M. Rappaz, and J.L. Desbiolles: in Light Metals 1990, C.M. Bickert, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1990, pp. 975–84.
A.L. Dons, E.K. Jensen, Y. Langsrud, E. Trømborg, and S. Brusethaug: in Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 2135–46.
D.C. Prasso, J.W. Evans, and I.J. Wilson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1995, vol. 26B, pp. 1281–87.
J.A. Dantzig: Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1985, vol. 56 (5), pp. 723–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drezet, J.M., Rappaz, M., Grün, G.U. et al. Determination of thermophysical properties and boundary conditions of direct chill-cast aluminum alloys using inverse methods. Metall Mater Trans A 31, 1627–1634 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0172-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0172-5