Abstract
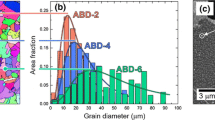
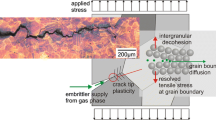
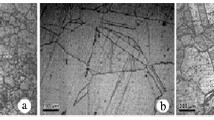
To examine the influence of niobium (Nb) on sustained-load crack growth (SLCG) in oxygen, three powder metallurgy (P/M) nickel-based superalloys, with nominal compositions similar to IN100, but with 0, 2.5, and 5 wt pct of Nb, are used. These alloys are gamma-prime (γ’) strengthened and have comparable volume fractions (53 vol pct) of γ’ precipitates. The SLCG experiments are conducted in high-purity oxygen and argon at 873, 923, and 973 K. The environmental cracking sensitivity (ECS) for the alloys with 2.5 and 5 wt pct of Nb is consistent with that of INCONEL 718 and supports the previously identified role of Nb-rich carbides in enhancing crack growth. The susceptibility of the Nb-free alloy to oxygen, however, is much greater than expected. The apparent activation energy for crack growth in oxygen was found to depend on stress-intensity-factor (K) levels for the Nb-containing alloys and ranged from about 320 to 260 kJ/mol for K levels of 35 to 60 MPa√m. It was nearly independent of K at about 250 kJ/mol for the Nb-free alloy. The results are discussed in terms of the rate-controlling process and of the mechanism for crack-growth enhancement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Floreen and R. Raj: in Flow and Fracture at Elevated Temperature, R. Raj, ed., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1984, pp. 383–405.
E. Andrieu, R. Molins, H. Ghonem, and A. Pineau: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. A134, pp. 21–28.
K.R. Bain and R.M. Pelloux: in Superalloys, M. Gell, C.S. Kortovich, R.H. Bricknell, W.B. Kent, and J.F. Radavich, eds., Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 1741–49.
Ming Gao, D.J. Dwyer, and R.P. Wei: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706 & Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1995, pp. 581–92.
M. Gao and R.P. Wei: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1997, vol. 37 (12), pp. 1843–49.
C. Miller, G.W. Simmons, and R.P. Wei: Scripta Metall. Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 227–32.
K. Sadananda and P. Shahinian: in Corrosion of Nickel-Based Alloys, R.C. Scarberry, ed., 1985, pp. 101–15.
R.P. Wei and R.L. Brazill: in Fatigue Crack Growth Measurement and Data Analysis, ASTM STP 738, ASTM, W. Conshohocken, PA, 1981, pp. 103–09.
J.C. Newman, Jr.: in Fracture Analysis, ASTM, W. Conshohocken, PA, 1974, pp. 105–21.
J.E. Srawley: Int. J. Fracture, 1976, vol. 12, pp. 475–76.
P. Valerio, M. Gao, and R.P. Wei: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 30 (10), pp. 1269–74.
Y. Han and M.C. Chaturvedi: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1987, vol. 89, pp. 25–33.
K. Kusabiraki, E. Amada, and T. Ooka: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1996, vol. 36 (2), pp. 208–14.
R.P. Wei: in Advanced Technologies for Superalloy Affordability, K.-M. Chang, S.R. Srivastava, D.U. Furrer, and K.R. Bain, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 103–12.
R.H. Bricknell and D.A. Woodford: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 30, pp. 257–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Iwashita, C., Chou, I. et al. Environmentally assisted, sustained-load crack growth in powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A 33, 1681–1687 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0177-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0177-3