Abstract
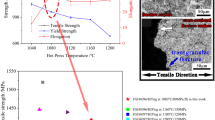
Ti-6Al-4V powders have been hot-isostatically-pressed (“HIPped”) using a range of hot-isostatic-pressing (“HIPping”) conditions, and the effects on microstructure and mechanical properties have been assessed. The properties were measured on test samples machined from HIPped powder billets and on samples that contained the as-HIPped surface. The fatigue limit of samples that contained the as-HIPped surface was improved by using a new HIPping procedure. The machined samples that had been HIPped at 1203 K (930 °C) exhibited a better balance of properties than those HIPped at 1153 K (880 °C) or 1293 K (1020 °C). The fine microstructure, formed from the martensitic structure of the atomized powder, coarsens with the increase of temperature or time during HIPping. These changes have been correlated with the corresponding changes in properties and with the fracture surfaces. The significance of these observations, especially the fatigue properties of samples that contain the as-HIPped surface, is discussed in terms of the properties of net-shape HIPped components.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
PHILIPS is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
References
W.B. Li, M.F. Ashby, and K.E. Easterling: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35 (12), pp. 2831–42.
D. Seliverstov, V. Samarov, V. Goloveshkin, S. Alexandrov, and P. Elkstrom: Proc. Conf. on “Hot Isostatic Pressing,” L. Delaey and H. Tas, eds., Elsevier Science BV., Amsterdam, 1994, pp. 555–60.
C. Dellis, P.L. Gallo, R. Baccino, and F. Morret: Proc. Int. Conf. on “Hot Isostatic Pressing,” ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 75–79.
G. Raisson: Hot Isostatic Pressing Int. Conf. 1999, International Academic Publishing, Beijing, 1999, pp. 390–93.
R. Baccino, F. Morret, F. Fellerin, D. Guichard, and G. Raisson: Mater. Design, 2000, vol. 21, pp. 345–50.
E. Arzt, M.F. Ashby, and K.E. Easterling: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 211–21
W.X. Yuan, J. Mei, V. Samarov, D. Seliverstov, and X. Wu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, vol. 182, pp. 39–49.
F.H. Froes and J. Hebeisen: Hot Isostatic Pressing Int. Conf. 1999, International Academic Publishing, Beijing, 1999, pp. 1–24.
Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1994, pp. 483–84.
R.R. Boyer: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1996, vol. A213, pp. 103–14.
G. Lütjering and J.C. Willians: Engineering Materials and Processes: Titanium, Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2003.
I.J. Polmear: Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 3rd ed., Edward Arnold, London, 1995.
J.C. Williams: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1999, vol. A263, pp. 107–11.
A. Davidson, K. Zhang, W. Yuan, J. Mei, M.R. Bache, M.H. Loretto, W. Voice, and X. Wu: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 22 (5), pp. 553–60.
British Standard, “Fracture Mechanics Toughness Tests—Part 1: Method for Determination of K Ic , Critical CTOD, and Critical J Values of Metallic Materials,” BSI BS7448-1, 1991.
D.P. DeLo and H.R. Piehler: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47 (9), pp. 2841–52.
D.P. DeLo, R.E. Dutton, S.L. Semiatin, and H.R. Piehler: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47 (11), pp. 3159–67.
J.H. Kim, S.L. Semiatin, and C.S. Lee: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 5613–26.
S.L. Semiatin and T.R. Bieler: Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 3565–73.
M.R. Bache: Int. J. Fatigue, 2003, vol. 25, pp. 1079–87.
S. Mironov, M. Murzinova, S. Zherebtsov, G.A. Salishchev, and S.L. Semiatin: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 2470–81.
M.R. Bache: Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. 105–11.
C. Kelto: in Powder Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys, F. Froes and J. Smugeresky, eds., AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1980, pp. 5–9.
D. Novovic: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 2004.
C. Arvieu, J.P. Manaud, and J.M. Quenisset: J. Alloys Compd., 2003, vol. 368, pp. 116–22.
X. Wu: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 1996.
Materials Properties Handbook, Titanium Alloys, R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1994, p. 64.
J. Mei: University of Birmingham (IRC), Birmingham, United Kingdom, unpublished research, 2007.
D.B. Lanning, T. Nicholas, and G.K. Haritos: Mech. Mater., 2002, vol. 34, pp. 127–34.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of this work by ORS and Rolls-Royce plc. Tremendous thanks are due to Professor M.H. Loretto for many stimulating discussions and thoughtful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 20, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Mei, J., Wain, N. et al. Effect of Hot-Isostatic-Pressing Parameters on the Microstructure and Properties of Powder Ti-6Al-4V Hot-Isostatically-Pressed Samples. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 1033–1045 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0149-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0149-y