Abstract
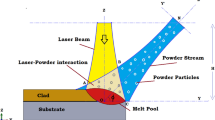
Laser engineered net shaping (LENS) and other similar processes facilitate building of parts with freeform shapes by melting and deposition of metallic powders layer by layer. A-priori estimation of the layerwise variations in peak temperature, build dimension, cooling rate, and mechanical property is requisite for successful application of these processes. We present here an integrated approach to estimate these build attributes. A three-dimensional (3-D) heat transfer analysis based on the finite element method is developed to compute the layerwise variation in thermal cycles and melt pool dimensions in the single-line multilayer wall structure of austenitic stainless steel. The computed values of cooling rates during solidification are used to estimate the layerwise variation in cell spacing of the solidified structure. A Hall–Petch like relation using cell size as the structural parameter is used next to estimate the layerwise hardness distribution. The predicted values of layer widths and build heights have depicted fair agreement with the corresponding measured values in actual deposits. The estimated values of layerwise cell spacing and hardness remain underpredicted and overpredicted, respectively. The slight underprediction of the cell spacing is attributed to the possible overestimation of the cooling rates that may have resulted due to the neglect of convective heat transport within the melt pool. The overprediction of the layerwise hardness is certainly due to the underprediction of corresponding cell spacing. The application of Hall–Petch coefficients, which is strictly valid for wrought and annealed grain structures, to estimate the hardness of as-solidified cellular structures may have also contributed to the overprediction of the layerwise hardness.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Keicher and K.E. Smugeresky: JOM, 1997, vol. 49 (5), pp. 51–54.
M.L. Griffith, M.E. Schlienger, L.D. Harwell, M.S. Oliver, M.D. Baldwin, M.T. Ensz, J.E. Smugeresky, M. Essien, J. Brooks, C.V. Robino, W.H. Hofmeister, M.J. Wert, and D.V. Nelson: Mater. Des., 1999, vol. 20 (2–3), pp. 107–13.
G.K. Lewis and E. Schlienger: Mater. Des., 2000, vol. 21 (4), pp. 417–23.
K.L. Schwender, R. Banerjee, P.C. Collins, C.A. Brice, and H.L. Fraser: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 45 (10), pp. 1123–29.
P.C. Collins, R. Banerjee, and H.L. Fraser: Scripta Mater., 2003, vol. 48 (10), pp. 1445–50.
L. Wang and S. Felicelli: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 129 (6), pp. 1028–34.
L. Costa, R. Vilar, T. Reti, and A. Deus: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53 (14), pp. 3987–99.
J. Choi and Y. Chang: Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf., 2005, vol. 45 (4–5), pp. 597–607.
R.R. Unocic and J.N. DuPont: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 143–52.
A. Vasinonta, J. Beuth, and M.L. Griffith: J. Manufact. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2001, vol. 123 (4), pp. 615–22.
P. Peyre, P. Aubry, R. Fabbro, R. Neveu, and A. Longuet: J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 41 (2), article no. 0254031, pp. 1–10.
W. Hoffmeister, M. Wert, J. Smugeresky, J.A. Philliber, M.L. Griffith, and M. Ensz: JOM, 1999, vol. 51 (7), JOM-e (www.tms.org/pubs/journals/JOM/9907/Hofmeister/Hofmeister-9907.html).
B. Zheng, Y. Zhou, J.E. Smugeresky, J.M. Schoenung, and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2228–36.
S. Ghosh and J. Choi: J. Manufact. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2007, vol. 129 (2), pp. 319–32.
S.M. Kelly and S.L. Kampe: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 1861–67.
B. Zheng, Y. Zhou, J.E. Smugeresky, J.M. Schoenung, and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2237–45.
J.E. Smugeresky, D.M. Keicher, J.A. Romero, M.L. Griffith, and L.D. Howell: DOI:10.2172/554828, Technical Report, Sandia National Laboratories, Livermore, CA, 1997.
Y. Xiong, W.H. Hofmeister, Z. Cheng, J.E. Smugeresky, E.J. Lavernia, and J.M. Schoenung: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57 (18), pp. 5419–29.
Q. Xu, V.V. Gupta, and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 527–39.
J. Allison, M. Lei, C. Wolverton, and X. Su: JOM, 2006, vol. 58 (11), pp. 28–35.
J. Allison, D. BackMann, and L. Christodoulou: JOM, 2006, vol. 58 (11), pp. 25–27.
V. Neela and A. De: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, vol. 45 (9–10), pp. 935–43.
S. Bag and A. De: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2009, vol. 14 (4), pp. 333–45.
W.S. Chang and S.J. Na: J. Mater. Processing Technol., 2002, vol. 120 (1–3), pp. 208–14.
W. Koechner: Solid State Laser Engineering, 3rd ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1992, p. 194.
ABAQUS Reference Manual, ch. 6, Heat Transfer Analysis, Hibbit, Karlson & Sorensen, Pawtucket, RI, 2001.
D. Tabor: Rev. Phys. Technol., 1970, vol. 1 (3), pp. 145–79.
J.R. Cahoon, W.H. Broughton, and A.R. Kutzak: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 1979–83.
B.P. Kashyap and K. Tangri: Acta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 43 (11), pp. 3971–81.
K.K. Singh, S. Sangal, and G.S. Murty: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2002, vol. 18 (2), pp. 165–72.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd ed., McGraw Hill Book Co., Singapore, 1998, p. 330.
F.A. McClintock and A.S. Argon: Mechanical Behaviour of Materials, Addison-Wesley Publ. Co., Reading, MA, 1966, p. 457.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Defense R & D Organisation, India for this study. Processing and characterization support from Dr. Vijay Singh, U. Savitha, and the Structural & Failure Analysis Group of DMRL are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 11, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manvatkar, V.D., Gokhale, A.A., Jagan Reddy, G. et al. Estimation of Melt Pool Dimensions, Thermal Cycle, and Hardness Distribution in the Laser-Engineered Net Shaping Process of Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 4080–4087 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0787-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0787-8