Abstract
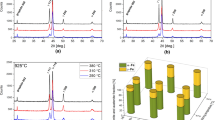
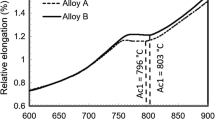
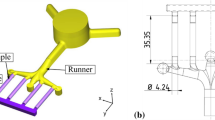
Selecting a suitable manufacturing process is one way of achieving sustainability of a product by diminishing energy consumption during its production cycle and improving material efficiency. The article attempts to explore the new processing technology for direct manufacturing of lightweight austempered ductile iron (ADI) casting in a permanent mold. The new processing technology is based on the innovative integrated approach toward casting and heat-treatment process. In this technology, the ductile iron samples obtained using the permanent mold are first austenized immediately after solidification process followed by austempering heat treatment in the fluidized bed and then air cooled at room temperature to obtain ADI material. The influence of austempering time on the microstructural characteristics, mechanical properties, and strain-hardening behavior of ADI was studied. Optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were performed to correlate the mechanical properties with microstructural characteristics. It was observed that the mechanical properties of resulting ADI samples were influenced by the microstructural transformations and varied retained austenite volume fractions obtained due to different austempering time. The results indicate that the strain-hardening behavior of the ADI material is influenced by the carbon content of retained austenite.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
SIL-O-CEL is a trademark of Johns-Manville Corporation, Denver, CO.
References
L.C. Chang: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 35–38.
F. Klocke, M. Arft, and D. Lung: Prod. Eng., 2010, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 433–41.
J. Achary and D. Venugopalan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 2575–85.
U. Batra, S. Ray, and S.R. Prabhakar: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2003, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 597–601.
Y. Amran, A. Katsman, P. Schaaf, and M. Bamberger: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41B, pp. 1052–58.
A. Trudel and M. Gagne: Can. Metall. Q., 1997, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 289–98.
P.A. Blackmore and R.A. Hardning: J. Heat Treat., 1984, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 310–25.
L. Sidjanin, M. Novovic, and R.E. Smallman: Pract. Metallogr., 1996, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 2–16.
A.A. Nofal and L. Jekova: J. Univ. Chem. Tech. Metall., 2009, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 213–28.
J. Achary: JMEPEG, 2000, vol. 9, pp. 56–61.
J.F. Janowak and R.B. Gundlach: J. Heat Treat., 1985, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 25–31.
J. Yang and S.K. Putatunda: Mater. Des., 2004, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 219–30.
M. Erdogan, V. Kilicli, and B. Demir: J. Mater. Sci., 2009, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 1394–1402.
A. Basso, M. Caldera, M. Chapetti, and J. Sikora: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 302–06.
Ductile Iron Data for Design Engineers, http://www.ductile.org/didata/default.htm.
J.O. Choi, J.Y. Kim, C.O. Choi, J.K. Kim, and P.K. Rohatgi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 383, no. 2, pp. 323–33.
S. Bockus and A. Dobrovolskis: Metalurgica, 2006, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 13–16.
M.H. Jacobs, T.J. Law, D.A. Melford, and M.J. Stowell: Metall. Technol., 1974, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 490–500.
J.R. Davis: ASM Specialty Handbook (Cast Irons), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 131–55.
D.M. Stefanescu: ASM Handbook, vol. 15, Casting, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1998, pp. 441–1500.
A. Meena and M.El Mansori: Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Tech., 2012, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 9–19.
A. Meena and M. El Mansori: Wear, 2011, vol. 271(9–10), pp. 2412–16.
P. Beeley: Foundry Technology, 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, U.K., 2001, pp. 443–622.
S.V. Shepel and S. Paolucci: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2002, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 229–48.
A. Meena, M. El Mansori, and P. Ghidossi: AIP Conf. Proc., 2010, vol. 1315, pp. 1521–26.
A. Meena, M. El Mansori, P. Ghidossi, and A. Mkaddem: AIP Conf. Proc., 2011, vol. 1353, pp. 1800–05.
R.E. Haimbaugh: Practical Induction Heat Treating, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2001, pp. 83–119.
E. Haruman, Y. Sun, A. Triwiyanto, Y.H.P. Manurung, and E.Y. Adesta: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 388–94.
Y. Waseda, E. Matsubara, and K. Shinoda: X-Ray Diffraction Crystallography, Springer, New York, NY, 2011, pp. 107–50.
H.B. Hosseini, B. Karlsson, T. Vouristo, and K. Dalaei: Exp. Mech., 2011, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 59–69.
E.A. Brandes and G.B. Brooks: Smithells Metal Reference Book, 7th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, U.K., 1992, pp. 41–48.
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, SI Metric Edition, McGraw-Hill, Cambridge, U.K., 1988, pp. 103–325.
S. Zhou, K. Zhang, Y. Wang, J.F. Gu, and Y.H. Rong: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43A, pp. 1026–34.
U. Seker and H. Hasirci: J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2006, vol. 173, no. 3, pp. 260–68.
S.K. Putatunda and P.K. Gadicherla: JMEPEG, 2000, vol. 9, pp. 193–203.
B. Bosnjak, B. Radulovic, K. Pop-Tonev, and V. Asanovic: JMEPEG, 2001, vol. 10, pp. 203–11.
S.K Putatunda, S. Kesani, R. Teckett, and G. Lawes: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, vols. 435–436, pp. 112–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 19, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meena, A., El Mansori, M. Material Characterization of Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) Produced by a Sustainable Continuous Casting–Heat Treatment Process. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 4755–4766 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1271-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1271-9