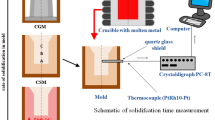
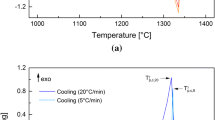
Cooling rate is an important and controllable variable in casting processing. The effect of cooling rate on the microsegregation and Laves phase in INCONEL718 superalloy castings was studied by high-temperature–laser confocal scanning microscopy and quantitative metallography in this study. The transformation rate of solid phase with a feature of Gaussian distribution in the solidifications at the cooling rates of 0.10 to 14 K/s is acquired. The solidification time and secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) as a function of cooling rate are analyzed. The amount of Laves phase presents a maximum value at a threshold cooling rate of 3 K/s owing to the opposite effects of cooling rate on the solidification time and SDAS. A modified dimensionless microsegregation index criterion was used for the scaling of solute segregation and Laves phase depending on cooling rates. The prediction of maximal microsegregation and the amount of Laves phase by MSI and experiments provide a guide for cooling rate control in the casting applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
INCONEL718 is a trademark of Special Metals Corporation, Huntington, WV.
References
http://www.specialmetals.com/documents/Inconel%20alloy%20718.pdf.
D. Furrer and H. Fecht: JOM, 1999, vol. 51, pp. 14–17.
T.M. Pollock and S. Tin: J. Propul. Power, 2006, vol. 22, pp. 361–74.
M.D. Kang, H.Y. Gao, J. Wang, L.S.B. Ling, and B.D. Sun: Materials, 2013, vol. 6, pp. 1789–1802.
B. Seiser, R. Drautz, and D.G. Pettifor: Acta Mater., 2011, vol. 59, pp. 749–63.
N. Zhou, D.C. Lv, H.L. Zhang, D. McAllister, F. Zhang, M.J. Mills, and Y. Wang: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 65, pp. 270–86.
G.A. Knorovsky, M.J. Cieslak, and T.J. Headley: Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 2149–58.
L. Nastac: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 4253–62.
J.N. DuPont, C.V. Robino, and A.R. Marder: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 4781–90.
L. Wang, Y. Yao, J. Dong, and Z. Maicang: Chem. Eng. Commun., 2010, vol. 197, pp. 1571–85.
T.F. Bower, H.D. Brody, and M.C. Flemings: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 624–33.
M.C. Flemings: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 2121–34.
T. Antonsson and H. Fredriksson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, vol. 36B, pp. 85–96.
L. Nastac and D.M. Stefanescu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 1582–87.
L. Nastac and D.M. Stefanescu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 4061–74.
L. Nastac and D.M. Stefanescu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 4075–83.
H. Yin and T. Emi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34B, pp. 483–93.
D. Phelan, M. Reid, and R. Dippenaar: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 985–94.
P.T. Jones, D. Desmet, M. Guo, D. Durinck, F. Verhaeghe, J.V. Dyck, J. Liu, B. Blanpain, and P. Wollants: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 3497–3507.
M.M. Attallah, H. Terasaki, R.J. Moat, S.E. Bray, Y. Komizo, and M. Preuss: Mater. Characterization, 2011, vol. 62, pp. 760–67.
T.Z. Kattamis, J.C. Coughlin, and M.C. Flemings: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239.
M.C. Flemings: Mater. Trans., 2005, vol. 46, 895–900.
V.R. Voller and C. Beckermann: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 3016–19.
V.R. Voller: Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2000, vol. 43, pp. 2047–52.
J.L. Fife and P.W. Voorhees: Acta Mater., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 2418–28.
Q. Du, D.G. Eskin, A. Jacot, and L. Katgerman: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 1523–32.
M. Paliwal and I.H. Jung: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 4848–60.
Acknowledgments
This work is sponsored by the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (Grant No. 13QA1401800), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (Grant No. 20120073110007), and the Program for Science and Technology Development of Shanghai (Grant No. 11521100703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted June 23, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, L., Han, Y., Zhou, W. et al. Study of Microsegregation and Laves Phase in INCONEL718 Superalloy Regarding Cooling Rate During Solidification. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 354–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2614-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2614-5