Abstract
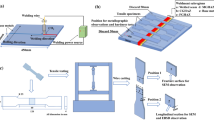
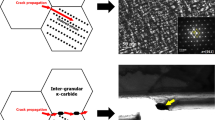
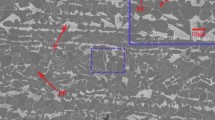
The effect of Mg content on the microstructure and toughness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) of steel plates after high heat input welding was investigated by means of welding thermal simulation test and in situ observation through high-temperature laser scanning confocal microscopy. It was found that with the increase of Mg content in the steel, the former austenite grain sizes were greatly decreased and the mainly microstructural constituents in HAZ were changed from the brittle constituents of Widmanstätten ferrite, ferrite side plate and upper bainite to the ductile constituents of intragranular acicular ferrite and polygonal ferrite. The proportion of grain boundary ferrite was decreased greatly with the further addition of Mg from 27 to 99 ppm. As a result, the HAZ toughness after welding with heat input of 400 kJ cm−1 is increased with increasing Mg content in the steel plate.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kojima, A. Kiyose, R. Uemori, M. Minagawa, M. Hoshino, T. Nakashima, K. Ishida and H. Yasui: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2004, pp. 2–6.
T. Koseki and G. Thewlis: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 21, pp. 867-879.
D. Phelan, N. Stanford and R. Dippenaar: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 407, pp. 127-134.
D. S. Sarma, A. V. Karasev and P. G. Jönsson: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 1063-1074.
D. Zhang, H. Terasaki and Y. I. Komizo: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 1369-1378.
J. Yang, K. Zhu, R. Z. Wang, Y. Zhang and J. G. Shen: Baosteel Tech. Res., 2010, vol. 4, pp. 32-36.
J. Yang, Z. G. Ma, K. Zhu, R. Z. Wang and Q. Zheng: Baosteel Tech. Res., 2012, vol. 9, pp. 41-46.
8. D. Zhang, Y. Shintaku, S. Suzuki and Y. I. Komizo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43, pp. 447-458.
S. Ogibayashi: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 1994, pp. 70–76.
Z. Zhang and R. A. Farrar: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1996, vol. 12, pp. 237-260.
G. Thewlis: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 22, pp. 153-166.
C. H. Chang, I. H. Jung, S. C. Park, H. S. Kim and H. G. Lee: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2005, vol. 32, pp. 251-257.
H. S. Kim, C. H. Chang and H. G. Lee: Scripta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 1253-1258.
14. F. Chai, C. F. Yang, H. Su, Y. Q. Zhang and Z. Xu: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2009, vol. 16, pp. 69-74.
A. V. Karasev and H. Suito: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1507-1516.
B. Wen and B. Song: J. Manuf. Sci. Prod., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 61-72.
K. Zhu, J. Yang, R. Z. Wang and Z. G. Yang: J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 18, pp. 60-64.
Y. I. Komizo: Trans. JWRI, 2011, vol. 40, pp. 7-20.
X. L. Wan, K. M. Wu, L. Cheng and R. Wei: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 679-685.
T. L. Zhang, Z. X. Li, S. Kou, H. Y. Jing, G. D. Li, H. Li and H. J. Kim: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 628, pp. 332-339.
J. Yang, L. Y. Xu, K. Zhu, R. Z. Wang, L. J. Zhou and W. L. Wang: Steel Res. Int., 2015, vol. 85, pp. 619-625.
X. S. Jiang and H. Zhao: Steel Fracture Microstructure Handbook, China Machine Press, Beijing, 2010, p. 9.
23. J. Yang, K. Zhu and G. D. Wang: Baosteel Tech. Res., 2008, vol. 2, pp. 9-16.
H. K. Sung, S. S. Sohn, S. Y. Shin, K. S. Oh and S. Lee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 3036-3050.
M. H. Shi, P. Y. Zhang and F. X. Zhu: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 188-192.
Y. TERADA, H. TAMEHIRO and R. CHIJIIWA: Tetsu- to- Hagane, 2004, vol. 90, pp. 812-818.
Yang Jian, Zhu Kai, Wang Ruizhi and Shen Jianguo: Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 82, pp. 552-556.
Acknowledgment
The financial support from Baosteel Group Corporation is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 21, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, LY., Yang, J., Wang, RZ. et al. Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Toughness of Heat-Affected Zone of Steel Plate after High Heat Input Welding. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 3354–3364 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3535-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3535-2