Abstract
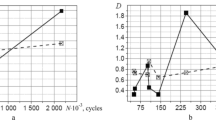
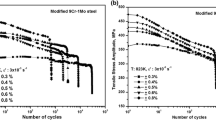
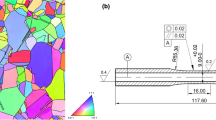
Cumulative fatigue damage under sequential low cycle fatigue (LCF) and high cycle fatigue (HCF) cycling was investigated at 923 K (650 °C) by conducting HCF tests on specimens subjected to prior LCF cycling at various strain amplitudes. Remnant HCF lives were found to decrease drastically with increase in prior fatigue exposure as a result of strong LCF–HCF interactions. The rate of decrease in remnant lives varied as a function of the applied strain amplitude. A threshold damage in terms of prior LCF life-fraction was found, below which no significant LCF–HCF interaction takes place. Similarly, a critical damage during the LCF pre-cycling marking the highest degree of LCF–HCF interaction was identified which was found to depend on the applied strain amplitude. In view of the non-linear damage accumulation behavior, Miner’s linear damage rule proved to be highly non-conservative. Manson’s damage curve approach, suitably modified, was found to be a better alternative for predicting the remnant HCF life. The single constant (β) employed in the model, which reflects the damage accumulation of the material under two/multi-level loading conditions is derived from the regression analysis of the experimental results and validated further.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Chellapandi, A. Biswas, R. Srinivasan, S.C. Chetal and S.B. Bhoje, Trans Indian Inst. Met., 2005, vol. 58 (2), pp. 207-19.
P. Chellapandi, Report No. TWF-FR/144, Beijing, China, 2010.
S.B. Bhoje, P. Chellapandi, Proc. Technical Committee Meeting, IAEA Tech. Doc 933, Manchester, UK, 1997, pp. 97–115.
M.D. Mathew, R. Sandhya, K. Laha, Energy Procedia, 2011, vol. 7, pp. 250-56
P. Chellpandi, S.C. Chetal and Baldev Raj, Nucl. Eng. Des., 2009, vol. 239(12), pp. 2745-65
A. Sarkar, A. Nagesha, R. Sandhya and M.D. Mathew. High Temp. Mater. Proc., 2015, vol. 34(5), pp. 435-439.
T. Topper, B. Sandor and J. Morrow, J. Mater., 1969, vol. 4(1), pp. 189-99
Gary Halford, Int. J. Fatigue, 1997, vol. 19, pp. S253-S260
Y.K. Wong, X.Z. Hu and M.P. Norton, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2002, vol. 25, pp. 201-13
Y.K. Wong. X.Z. Hu and M.P. Norton, J. Test. Eval., 2001, vol. 29(2), pp. 138-45
M.J. O’Neil, ARL/SM-Report-326, Aeronautical Research Laboratories, Melbourne, Australia, 1970
S.R. Velluri, Report No. ARL 182, Aeronautical Research Laboratory, United States Air Force, 1961
S. Zhao-Feng, W. De-Jun and X. Hao, Int. J. Fatigue, 1992, vol. 14(6), pp. 395-98
J. Dubuc, T. Bui-Quoc,, A. Bazergui and A. Biron, WRC Bulletin, 1971, vol. 162, pp. 1-20
M.A. McGrew: Proceedings of an Exposition and Symposium of Structures Technology, Cleveland, OH, USA, 1988, vol. 3, pp. 201–11,
S.S. Manson, G.R. Halford, Int. J. Fracture, 1981, vol. 17, pp. 169-192
S.S. Manson, J.C. Freche and C.R. Ensign: ASTM STP 415, 1967, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 384–412
S.S. Manson and G.R. Halford, Int. J. Fract., 1981, vol. 17, pp. R35-R42
P.T. Bizon, D.J. Thoma and G.R. Halford: NASA CP-2381, Center for Aerospace Information, Linthicum Heights, Maryland, 1985, pp. 129–38
S.S. Manson and S. Hailu: in PVP, vol. 290, S.Y. Zamrick and G.R. Halford, eds., ASME, New York, 1994, pp. 1–9
V.S. Srinivasan, R. Sandhya, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, S.L. Mannan, K.S. Raghavan, Int. J. Fatigue, 13 (1991) pp. 471-78.
G.V. Prasad Reddy, R. Sandhya, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao and S. Sankaran: Proc. Eng., 2010, vol. 2, pp. 2181–88
A.H.Cottrell, In; Dislocations and plastic flow in crystals; 1st Edition, Oxford University, Oxford, 1953.
P. Rodriguez, Bulletin Mater. Sci. 6 (1984) 653-63.
J. Ganesh Kumar, M. Chowdary, V. Ganesan, R.K. Paretkar, K.B.S. Rao, and M.D. Mathew, Nucl. Eng. Des., 2010, vol. 240(6), pp. 1363-70.
S.M. Marco and W.L. Starkey, Trans. ASME, 1953, vol. 53, pp. 627-32
B.F. Langer: Trans. ASME, 1937, vol. 59, p. A-160
T. Nicholas, Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. S21-S31.
A. Plamgren, Zeitschrift des Vereinesdeutscher Ingeneerure, 1924, vol. 68(14) pp. 339-41
M.A. Miner, J. Appl. Mechanics, 1945, vol. 67, pp. A159-A164
G.R. Halford and S.S. Manson: NASA CP-2381, 1985, Center for aerospace information, Linthicium Heights, Maryland, pp. 139–45
S.S. Manson, G.R. Halford, Fatigue and durability of structural materials, ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 2006, pp. 123-56
S.S. Manson, Engg. Fract. Mech., 1986, vol. 25, pp. 539-571
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 17, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, A., Nagesha, A., Parameswaran, P. et al. Investigation of Cumulative Fatigue Damage Through Sequential Low Cycle Fatigue and High Cycle Fatigue Cycling at High Temperature for a Type 316LN Stainless Steel: Life-Prediction Techniques and Associated Mechanisms. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 953–964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3909-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3909-5