Abstract
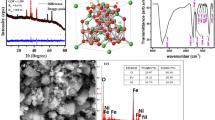
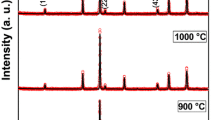
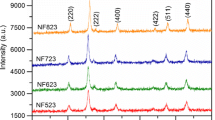
The heat treatment of nanoparticles can have a direct effect on their particle sizes, which, in turn, can influence many of their structural and magnetic properties. Here, we report the effect of sintering temperature on the chemically synthesized high-quality NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. The structural studies show the formation of pure NiFe2O4 nanoparticles with the space group \( Fd{\bar{\text{3}}}m \). The inverse spinel structure was also confirmed from the lattice vibrations analyzed from Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra. The presence of strong exchange interactions was detected from the temperature-dependent magnetization study. Moreover, at higher sintering temperatures, the grain growth due to fusion of several smaller particles by coalescing their surfaces enhances the crystallinity and its magnetocrystalline anisotropy. Coercivity and saturation magnetization were found to depend significantly on the sintering temperature, which was understood in the realm of the formation of single-domain-like structure and change in magnetocrystalline anisotropy at higher sintering temperatures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.S. Mathew and R.S. Juang: Chem. Eng. J., 2007, vol. 129, pp. 51–56.
B. Aslibeiki, P. Kameli, H. Salamati, M. Eshraghi, and T. Tahmasebi: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2010, vol. 322, pp. 2929–34.
D.H. Han, H.L. Luo, and Z. Yang: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1996, vol. 161, pp. 376–78.
C.H. Cunningham, T. Arai, P.C. Yang, M.V. McConnell, J.M. Pauly, and S.M. Connolly: Magn. Reson. Med., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 999–1005.
A.K. Giri, K. Pellerin, W. Pongsaksawad, M. Sorescu, and S.A. Majetich: IEEE Trans. Magn., 2000, vol. 36, pp. 3029–31.
R. Valenzuela: Phys. Res. Int., 2012, vol. 2012, p. 591839.
Y.T. Jong, K.J. Sung, K.B. Geol, K. Nam, C.M. Haing, and L.J. Kyu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, vol. 44, pp. 1068–95.
B.D. Cullity and S. Graham: Introduction to Magnetic Materials, Wiley, New York, NY, 2009.
A. Godman: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1995, vol. 4, pp. 395–400.
J. Zhang, J. Shi, and M. Gong: J. Solid State Chem., 2008, vol. 182, pp. 2135–40.
X.M. Liu, S.Y. Fu, and C.J. Huang: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2004, vol. 281, pp. 234–39.
M.S. Niasari, F. Davar, and T. Mahmoudi: Polyhedron, 2009, vol. 28, pp. 1455–58.
M.A.F. Ramalho, L. Gama, S.G. Antonio, C.O. Paiva-Santos, E.J. Miola, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, and A.C.F.M. Costa: J. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 42, pp. 3603–06.
W.Z. Wang, C.K. Xu, G.H. Wang, K.L. Liu, and C.L. Zheng: Adv. Mater., 2002, vol. 14, pp. 837–40.
K. Maaz, A. Mumtaz, S.K. Hasanain, and A. Ceylan: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, vol. 308, pp. 289–95.
M.K. Roy, B. Halder, and H.C. Verma: Nanotechnology, 2006, vol. 17, pp. 232–37.
M.G. Naseri, E.B. Saion, H.A. Ahangar, M. Hashim, and A.H. Shaari: Powder Technol., 2011, vol. 212, pp. 80–88.
W.B. White and B.A. DeAngelis: Spectrochim. Acta, 1967, vol. 23A, pp. 985–95.
Z.H. Zhou, J.M. Xue, J. Wang, H.S.O. Chan, T. Yu, and Z.X. Shen: J. Appl. Phys., 2002, vol. 91, pp. 6015–20.
J. Kreisel, G. Lucazeau, and H. Vincent: J. Solid State Chem., 1998, vol. 137, pp. 127–37.
Y. Shi, J. Ding, Z.X. Shen, W.X. Sun, and L. Wang: Solid State Commun., 2000, vol. 115, pp. 237–41.
A.A. Kamnev and M. Ristic: J. Mol. Struct., 1997, vols. 408–409, pp. 301–04.
S. Yan, J. Geng, J. Chen, L. Yin, Y. Zhou, and E. Zhou: J. Cryst. Growth, 2004, vol. 262, pp. 415–19.
K.S.K. Varadwaj, M.K. Panigrahi, and J. Ghose: J. Solid State Chem., 2004, vol. 177, pp. 4286–92.
T. Shimada, T. Tachibana, T. Nakagawa, and T.A. Yamamoto: J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 379, pp. 122–26.
Z.M. Tian, S.L. Yuan, S.Y. Yin, L. Liu, J.H. He, H.N. Duan, P. Li, and C.H. Wang: Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, vol. 93, pp. 222505-1–222505-3.
S.S. Starchikov, I.S. Lyubutin, C.R. Lin, Y.T. Tseng, K.O. Funtov, Y.L. Ogarkova, T.V. Dmitrieva, and A.G. Ivanova: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, vol. 17, pp. 15829–15836.
V. Sepelak, K. Tkacova, V.V. Boldyrev, S. Wibmann, and K.D. Becker: Physica B, 1997, vols. 234–236, pp. 617–19.
S. Chikazumi: Physics of Magnetism, John Wiley, New York, NY, 1959.
M. George, A.M. John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, and M.R. Anantharaman: J. Magn. Magn. Mater., vol. 302, 2006, pp. 190–95.
M.A. Gabal, Y.M.A. Angari, and M.W. Kadi: Polyhedron, 2011, vol. 30, pp. 1185–90.
Y. Cheng, Y. Zheng, Y. Wang, F. Bao, and Y. Qin: J. Solid State Chem., 2005, vol. 178, pp. 2394–97.
S. Rana, R.S.M. Srivastava, M. Sorensson, and R.D.K. Misra: Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2005, vol. 119, pp. 144–51.
R.D.K. Misra, S. Gubbala, A. Kale, and W.F. Egelhoff, Jr.: Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2004, vol. 111, pp. 164–70.
A.H. Morrish and K.H. Haneda: J. Appl. Phys., 1981, vol. 52, pp. 2496–98.
J.M.D. Coey: Phys. Rev. Lett., 1971, vol. 27, pp. 1140–42.
A.E. Berkowitz, J.A. Lahut, I.S. Jacobs, L.M. Levinson, and D.W. Forester: Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, vol. 34, pp. 594–97.
A.E. Berkowitz, J.A. Lahut, and C.E. VanBuren: IEEE Trans. Magn. Mag., 1980, vol. 16, pp. 184–90.
J. Jacob and M.A. Khadar: J. Appl. Phys., 2010, vol. 107, pp. 114310-1-114310-10.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. Alok Banerjee, Scientist, UGC-DAE (Indore, India), for providing the SQUID facility and discussing the ZFC–FC results. The authors are also thankful to Mr. Debraj Gangopadhyay for helping with the Raman measurement and for discussing the Raman results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 1, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Patel, P.C., Gangopadhyay, D. et al. Structural and Magnetic Studies of Thermally Treated NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 6135–6141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4344-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4344-y