Abstract
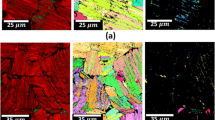
The influence of microstructure on the fracture toughness of Ti-23A1-9Nb-2Mo-1Zr-1.2Si (at. pct) and Ti-23A1-11Nb-0.9Si (at. pct) Ti3Al-based alloys has been investigated. Basket-weave microstructures comprising different volume fractions of α 2 and retained β phases were produced by systematic heat treatments. Besides the volume fraction of the retained β phase, the average size of the β laths has also been used to characterize these microstructures. The toughness of both alloys was examined at room temperature, and the brittle transgranular fracture modes were found to be controlled by microstructure. However, the toughness is not determined solely by the volume fraction of the retained β phase, and a linear relationship has been obtained between the fracture toughness and the average size of the retained β laths. It appears therefore that the toughness of Ti3Al-based alloys at room temperature is controlled primarily by the width of retained β laths rather than by the retained β volume fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.K. Gogia, D. Banerjee, and T.K. Nandy: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 609–25.
A.K. Gogia, T.K. Nandy, and D. Banerjee: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. A159, pp. 73–86.
K.S. Chan: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 2687–99.
D.A. Lukasak and D.A. Koss: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 135–43.
W.O. Soboyejo: Metall. Trans. A. 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1737–50.
S. Kerry: DRA, SMC Farnborough, United Kingdom, private communication 1993.
Methods of Test for Plane Strain Fracture Toughness (K IC ) of Metallic Materials, British Standard Institution BS 5447, British Standard Institution, London, U.K., 1977.
X. Wu: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 1996.
Z. Cheng, F. Simca, and M.T. Cope: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, vol. 8, pp. 729–38.
Z.X. Cheng: University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, private communication 1994.
R.A. Chave: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, 1994.
S. Kerry: The Effect of Minor Alloying Additions on the Mechanical Properties of Titanium Aluminide Alloy, Internal Research Report No. DRA/TR/93061/1.0, Sept. 1993.
P. Bowen, S.G. Druce, and J.F. Knott: Acta Metall., 1987, vol. 35 (7), pp. 1735–46.
P. Bowen, S.G. Druce, and J.F. Knott: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34 (6), pp. 1121–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Bowen, P. Effects of microstructure on the fracture toughness of Ti3Al-based titanium aluminides. Metall Mater Trans A 28, 1357–1365 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0272-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-997-0272-6