Abstract
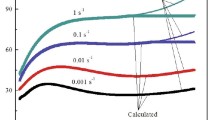
The evolution mechanisms of dislocation microstructures and new grains at high strains of above 4 were studied by means of multiple compression of a polycrystalline copper (99.99 pct). Deformation was carried out by multipass compression with changing of the loading direction in 90 deg in each pass at temperatures of 473 K to 573 K (0.35 to 0.42 T m ) under a strain rate of 10−3 s−1. The flow stresses increase to a peak followed by a work softening accompanied mainly by dynamic recrystallization (DRX) at 523 K to 573 K. In contrast, the steady-state-like flow appears at 473K accompanied with the development of fine grains at strains as high as 4.2. The relationship of flow stress to the new grain size evolved can be expressed by a power law function with a grain size exponent of about −0.35, which is different from −0.75 for high-temperature DRX at above 0.5 T m . At 473 K, misorientations of deformation-induced dislocation subboundaries increase with increasing strain, finally leading to the evolution of new grains. It is concluded that the dynamic grain formation at 473 K cannot result from DRX, but from the evolution of deformation-induced dislocation subboundaries with high misorientations and, concurrently, the operation of dynamic recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.J. McQueen and J.J. Jonas: in Treatise on Materials Science and Technology, R.J. Arsenault, ed., Academic Press, New York, NY, 1975, pp. 393–493.
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 189–209.
A.K. Ghosh and C. Gandhi: in Strength of Metals and Alloys (ICSMA7), H.J. McQueen, J.-P. Bailon, J.I. Dickson, J.J. Jonas, and M.G. Akben, eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1985, pp. 2065–72.
S.J. Hales, T.R. McNelley, and H.J. McQueen: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 1037–47.
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1996, pp. 363–92.
N.A. Smirnova, V.I. Levit, V.I. Pilyugin, R.I. Kuznetsov, L.S. Davydova, and V.A. Sazonova: Phys. Met. Metallogr., 1986, vol. 61, pp. 127–34.
V.Y. Gertsman, R. Birringer, R.Z. Valiev, and H. Gleiter: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 30, pp. 229–34.
M. Furukawa, Z. Horita, M. Nemoto, R.Z. Valiev, and T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4619–29.
R.Z. Valiev, Yu. V. Ivanisenko, E.F. Rauch, and B. Baudelet: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4705–12.
G.A. Salishchev, R.G. Zaripova, A.A. Zakirova, and H.J. McQueen: in Hot Workability of Steels and Light Alloys-Composites, H.J. McQueen, E.V. Konopleva, and N.D. Ryan, eds., TMS-CIM, Montreal, 1996, pp. 217–26.
A. Belyakov, R. Kaibyshev, and T. Sakai: Metall. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 161–67.
N. Hansen: Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 2167–90.
D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf and N. Hansen: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1991, vol. 25, pp. 1557–62.
D.A. Hughes, Q. Liu, D.C. Chrzan, and N. Hansen: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 105–12.
V.V. Rybin: Large Plastic Deformation and Destructure of Metals, Metallurgy, Moscow, 1986, pp. 61–89.
R. Kaibyshev and O. Sitdikov: Z. Metallkd., 1994, vol. 85, pp. 738–43.
A. Belyakov, H. Miura, and T. Sakai: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 595–601.
G. Tomas and M.J. Goringe: Transmission Electron Microscopy of Materials, Wiley, New York, NY, 1979, pp. 112–24.
T. Sakai: J. Mater. Processing Technol., 1995, vol. 53, pp. 349–61.
T. Sakai and H. Miura: in Hot Workability of Steels and Light Alloys-Composites, H.J. McQueen, E.V. Konopleva, and N.D. Ryan, eds., TMS-CIM, Montreal, 1996, pp. 161–72.
J.E. Bailey and P.B. Hirsh: Proc. R. Soc. London, 1962, vol. A267, pp. 11–30.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby: Deformation-Mechanism Maps, Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1982, pp. 1–5.
K. Tsuzaki, Huang Xiaoxu, and T. Maki: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 4491–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belyakov, A., Gao, W., Miura, H. et al. Strain-induced grain evolution in polycrystalline copper during warm deformation. Metall Mater Trans A 29, 2957–2965 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-0203-1
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-0203-1