Abstract
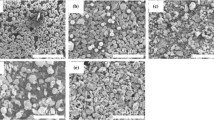
In Part II of this article, the high-strength Al-Si/TiC composite and the elevated-temperature-resistant Al-Fe(-V-Si)/TiC composite, developed on the basis of the in situ Al-TiC composites (Part I of the article),[8] have been evaluated for their room- and elevated-temperature mechanical behavior. The microstructural characteristics of ingot metallurgy (IM) or rapid solidification (RS) Al-Si/TiC and Al-Fe(-V-Si)/TiC composites could be thought of as a combination of the related alloy matrix microstructures and the IM or RS Al/TiC composites. The IM Al/TiC and the Al-Si/TiC composites show superior strength and ductility to the relevant aluminum-based composites. The RS Al/TiC and the Al-Fe-V-Si/TiC exhibit high Young’s moduli and substantial improvements in room- and elevated-temperature tensile properties compared to those of rapidly solidified alloys and conventional composites. The Young’s modulus values of RS Al/TiC and Al-Fe-V-Si/TiC composites are well within Hashin-Shtrikman (H-S) limits, in keeping with the strong interfacial bonding. In the micro-mechanics approach, the principal strengthening mechanisms for the present dispersed, particle-hardened RS in situ Al-TiC composites would include Orowan strengthening, grain-size and substructure strengthening, and solid-solution strengthening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.P. You, M. Dollor, A.W. Thompson, and I.M. Bernstein: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2445–50.
C.C. Perng, J.R. Hwang, and J.L. Doong: Compos. Sci. Technol., 1993, vol. 49, pp. 225–36.
A.K. Kuruvilla, K.S. Prasad, V.V. Bhanuprasad, and Y.R. Mahajan: Scripta Metall., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 873–78.
W. Kai, J.M. Yang, and W.C. Harrigan, Jr.: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1989, vol. 23, pp. 1277–80.
P.K. Rohatgi: Key Eng. Mater., 1995, vols. 104–107, pp. 293–312.
P.C. Maity and S.C. Panigrahi: Key Eng. Mater., 1995, vols. 104–107, pp. 313–28.
A. Chrysanthou: Key Eng. Mater., 1995, vols. 104–107, pp. 381–86.
X.C. Tong and H.S. Fang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 875–91.
Z. Wang and R.J. Zhang: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 1585–93.
F.J. Humphreys, A. Basu, and M.R. Djazeb: in Metal Matrix Composites, N. Hansen, D. Juul Jensen, T. Leffers, H. Lilholt, T. Lorentzen, A.S. Pederson, O.B. Pederson, B. Ralph, eds., RISØ National Laboratory, Roskilde, Denmark, 1991, pp. 51–66.
R. Mitra, M.E. Fine, and J.R. Weertman: J. Mater. Res., 1993, vol. 8, pp. 2370–79.
V.V. Bhanuprasad, M.A. Staley, P. Ramakrishnan, and Y.R. Mahajaw: Key Eng. Mater., 1995, vols. 104–107, pp. 495–506.
D.J. Lloyds: Int. Mater. Rev. 1994, vol. 39, pp. 1–23.
M. Gupta, J. Juarez-Islas, W.E. Frazier, F.A. Mohamed, and E.J. Lavernia: Metall. Trans. B, 1992, vol. 23B, pp. 719–36.
S.K. Das, P.S. Gilman, and D. Raybould: Key Eng. Mater., 1989, vols. 38-39, pp. 367–92.
R. Mitra, M.E. Fine, and J.R. Weertman: J. Mater. Res., 1993, vol. 8, pp. 2380–92.
T. Christman, A. Needleman, and S. Suresh: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 3029–50.
H.G.F. Wilsdorf: in Dispersion Strengthened Al Alloys, Y.W. Kim and W.M. Griffith, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 3–29.
D.J. Bacon, U.F. Kocks, and R.O. Scattergood: Phil. Mag., 1972, vol. 28, pp. 1241–63.
A. Barbacki and W. Frackowiak: Z. Metallkd., 1988, vol. 79, pp. 410–12.
L.C. Davis and J.E. Allison: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 2487–96.
M.K. Premkumar, A. Lawley, and M.J. Koczak: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1994, vol. 174, pp. 127–39.
R.J. McElroy and Z.C. Szkopiak: Int. Met. Rev., 1972, vol. 17, pp. 175–202.
John D. Verhoeven: Fundamentals of Physical Metallurgy, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1975, p. 518.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, X.C., Fang, H.S. Al-TiC composites in situ-processed by ingot metallurgy and rapid solidification technology: Part II. Mechanical behavior. Metall Mater Trans A 29, 893–902 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-0279-7
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-998-0279-7