Abstract
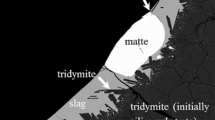
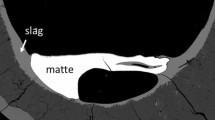
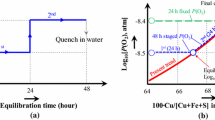
The majority of primary pyrometallurgical copper making processes involve the formation of two immiscible liquid phases, i.e., matte product and the slag phase. There are significant gaps and discrepancies in the phase equilibria data of the slag and the matte systems due to issues and difficulties in performing the experiments and phase analysis. The present study aims to develop an improved experimental methodology for accurate characterisation of gas/slag/matte/tridymite equilibria in the Cu-Fe-O-S-Si system under controlled atmospheres. The experiments involve high-temperature equilibration of synthetic mixtures on silica substrates in CO/CO2/SO2/Ar atmospheres, rapid quenching of samples into water, and direct composition measurement of the equilibrium phases using Electron Probe X-ray Microanalysis (EPMA). A four-point-test procedure was applied to ensure the achievement of equilibrium, which included the following: (i) investigation of equilibration as a function of time, (ii) assessment of phase homogeneity, (iii) confirmation of equilibrium by approaching from different starting conditions, and (iv) systematic analysis of the reactions specific to the system. An iterative improved experimental methodology was developed using this four-point-test approach to characterize the complex multi-component, multi-phase equilibria with high accuracy and precision. The present study is a part of a broader overall research program on the characterisation of the multi-component (Cu-Fe-O-S-Si-Al-Ca-Mg), multi-phase (gas/slag/matte/metal/solids) systems with minor elements (Pb, Zn, As, Bi, Sn, Sb, Ag, and Au).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.G.I. Davenport, M. King, M. Schlesinger, and A.K. Biswas: Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 4th ed., Pergamon, 2002.
Y. Takeda: Oxygen potential measurement of iron silicate slag-copper-matte system. in Proc. Int. Conf. Molten Slags, Fluxes Salts, 5th., Iron and Steel Society Warrendale, PA, 1997.
U. Kuxmann and F.Y. Bor, Erzmetall., 1965. 18: pp. 441–450.
N. Korakas: Etude thermodynamic de l’équilibre entre scories ferro-siliceuses et mattes de cuivre. Application aux problèmes posés par la formation de magnetite lors du traitement des minerais sulfurés de cuivre. Univirsité de Liège, 1964.
F.J. Tavera and W.G. Davenport, Metall. Trans. B, 1979. 10B(2): pp. 237-241.
J.M. Font, G. Roghani, M. Hino, and K. Itagaki, Metall. Rev. MMIJ, 1998. 15(1): pp. 75-86.
H.M. Henao, L.A. Ushkov, and E. Jak: Thermodynamic Predictions and Experimental Investigation of Slag Liquidus and Minor Element Partitioning Between Slag and Matte in Support of the Copper Isasmelt Smelting Process Commissioning and Optimisation at Kazzinc, 2012.
H. Li and W.J. Rankin, Metall. Trans. B, 1994. 25B(1): pp. 79-89.
Z. Sun, T. Hidayat, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak: iquidus Temperatures, Major and Minor Elements Equilibrium Partitioning in Copper Smelting Slag/Matte/Gas Systems. in 8th International Copper Conference, Chile, 2013.
F.J. Tavera and E. Bedolla, Int. J. Miner. Process., 1990. 29(3-4): pp. 289-309.
A. Geveci and T. Rosenqvist, Trans. Inst. Min. Metall., 1973. 82: pp. C193-C201.
R. Shimpo, S. Goto, O. Ogawa, and I. Asakura, Can. Metall. Q., 1986. 25(2): pp. 113-121.
M. Nagamori, Metall. Trans. B, 1974. 5B(3): pp. 531-538.
A. Yazawa, S. Nakazawa, and Y. Takeda: Distribution Behavior of Various Elements in Copper Smelting Systems. in Proceed. of International Sulfide Smelting Symposium, San Francisco, USA: Metall. Soc. AIME, 1983.
G.H. Kaiura, K. Watanabe, and A. Yazawa, Can. Metall. Q., 1980. 19(2): pp. 191-200.
H. Jalkanen, Scand. J. Metall., 1981. 10(4): pp. 177-184.
E. Jak: Integrated Experimental and Thermodynamic Modelling Research Methodology for Metallurgical Slags with Examples in the Copper Production Field. in Intl. Conf. on Molten Slags and Fluxes, Beijing, China, 2012.
S.A. Decterov and A.D. Pelton, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999. 30B(4): pp. 661-669.
S.A. Decterov and A.D. Pelton, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999. 30B(6): pp. 1033-1044.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Australian Research Council Linkage program, Altonorte Glencore, Atlantic Copper, Aurubis, Olympic Dam Operation BHP Billiton, Kazzinc Glencore, PASAR Glencore, Outotec Oy (Espoo), Anglo American Platinum, Umicore, and Kennecott Rio Tinto for the financial and technical support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 21, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallah-Mehrjardi, A., Hidayat, T., Hayes, P.C. et al. Experimental Investigation of Gas/Slag/Matte/Tridymite Equilibria in the Cu-Fe-O-S-Si System in Controlled Atmospheres: Development of Technique. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 3002–3016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1073-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1073-y