Abstract
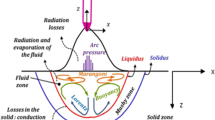
Fluid flow and heat transfer during gas-metal-arc welding (GMAW) of HSLA-100 steel were studied using a transient, three-dimensional, turbulent heat transfer and fluid flow model. The temperature and velocity fields, cooling rates, and shape and size of the fusion and heat-affected zones (HAZs) were calculated. A continuous-cooling-transformation (CCT) diagram was computed to aid in the understanding of the observed weld metal microstructure. The computed results demonstrate that the dissipation of heat and momentum in the weld pool is significantly aided by turbulence, thus suggesting that previous modeling results based on laminar flow need to be re-examined. A comparison of the calculated fusion and HAZ geometries with their corresponding measured values showed good agreement. Furthermore, “finger” penetration, a unique geometric characteristic of gas-metal-arc weld pools, could be satisfactorily predicted from the model. The ability to predict these geometric variables and the agreement between the calculated and the measured cooling rates indicate the appropriateness of using a turbulence model for accurate calculations. The microstructure of the weld metal consisted mainly of acicular ferrite with small amounts of bainite. At high heat inputs, small amounts of allotriomorphic and Widmanstätten ferrite were also observed. The observed microstructures are consistent with those expected from the computed CCT diagram and the cooling rates. The results presented here demonstrate significant promise for understanding both macro-and microstructures of steel welds from the combination of the fundamental principles from both transport phenomena and phase transformation theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M.B. Losz and K.D. Challenger: Recent Trends in Welding Science and Technology, S.A. David and J.M. Vitek, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1990, pp. 229–35.
D.G. Howden, L. Zhang, R.S. Green, K. Smapath, J.H. Devletian, and D. Singh: International Trends in Welding Science and Technology, S.A. David and J.M. Vitek, eds, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, pp. 359–64.
R.P. Martukanitz, P.R. Howell, and W.A. Pratt: International Trends in Welding Science and Technology, S.A. David and J.M. Vitek, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, pp. 271–79.
R.W. Fonda, G. Spanos, and R.A. Vandermeer: in Trends in Welding Research, H.B. Smartt, J.A. Johnson, and S.A. David, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 277–82.
H. Davis: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, September, 1995.
W. Pitscheneder, T. DebRoy, K. Mundra, and R. Ebner: Weld. J., 1996, vol. 75 (3), pp. 71s-80s.
K. Mundra, T. DebRoy, and K. Kelkar: Numerical Heat Transfer, 1996, vol. 29, pp. 115–29.
R.T.C. Choo, J. Szekely, and S.A. David: Metall. Trans. B, 1992, vol. 23B, pp. 371–84.
S. Kou and Y.H. Wang: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 2265–70.
C. Chan, J. Mazumder, and M.M. Chen: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 2175–84.
T. DebRoy and S.A. David: Rev. Modern Phys., 1995, vol. 67 (1), pp. 85–112.
T. Zacharia, S.A. David, J.M. Vilek, and T. DebRoy: Weld. J., 1989, vol. 68 (12), pp. 499s-509s.
K. Mundra, T. DebRoy, T. Zacharia, and S.A. David: Weld. J., 1992, vol. 71 (9), pp. 313s-320s.
K. Mundra, J.M. Blackburn, and T. DebRoy: Sci. Technol. Welding Joining, 1997, vol. 2 (4), pp. 174–84.
A. Block-Bolten and T.W. Eager: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 461–69.
P.A.A. Khan and T. DebRoy: Metall. Trans. B, 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 641–44.
K. Mundra and T. DebRoy: Weld. J., 1993, vol. 72 (1), pp. 1s-9s.
K. Mundra, T. DebRoy, S.S. Babu, and S.A. David: Weld. J., 1997, vol. 76 (4), pp. 163s-171s.
Z. Yang and T. DebRoy: Sci. Technol. Welding Joining, 1997, vol. 2 (2), pp. 53–58.
T. Hong, W. Pitscheneder, and T. DebRoy: Sci. Technol. Welding Joining, 1998, vol. 3 (1), pp. 33–41.
M. Malinowski-Brodnicka, G. denOuden, and W.J.P. Vink: Weld. J., 1990, vol. 69, pp. 52s-59s.
R.T.C. Choo and J. Szekely: Weld. J., 1994, vol. 73 (2), pp. 25s-31s.
K. Hong, D.C. Weckman, and A.B. Strong: in Trends in Welding Research, H.B. Smartt, J.A. Johnson, and S.A. David, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1996, pp. 399–404.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: in Mathematical Modeling of Weld Phenomena, H. Cerjak and K.E. Easterling, eds., Institute of Materials, London, 1993, pp. 109–80.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Metal Science, 1982, vol. 16(3), pp. 159–65.
S.V. Patankar: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, New York, NY, 1980.
B.E. Launder and B.D. Spalding: Mathematical Models of Turbulence, Academic Press, New York, NY, 1972.
W.M. Pun and D.B. Spalding: Heat Transfer Section Report No. HTS/76/2, Imperial College, London, 1976.
ILLUSTRATIVE ADAPTATIONS of COMPACT-3D Version 3.1, a general-purpose computer program for three-dimensional fluid flow and heat transfer, Innovative Research Inc., Minneapolis, MN, 1993, p. 14–2.
D.N. Shackleton and W. Lucas: Weld. J., 1974, vol. 53 (12), pp. 537s-547s.
W.G. Essers and R. Walter: Weld. J., 1981, vol. 60 (2), pp. 37s-42s.
J.F. Lancaster: The Physics of Welding, Pergamon Press, New York, NY, 1984.
S. Kumar and S.C. Bhaduri: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 435–41.
L.A. Jones, T.W. Eagar, and J.H. Lang: Weld. J., 1998, vol. 77 (4), pp. 135s-141s.
G.W. Tichellar, G. Jelmorini, and G.J.P.M. vander Henvel: Droplet Temperature Measurement in Arc Welding, IIW Document 212-411-77, International Institute of Welding, France, 1977.
L.-E. Svensson, B. Gretoft, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Scand. J. Metall., 1986, vol. 15, pp. 97–103.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, L.E. Svensson, and B. Gretoft: Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 1271–83.
M. Takahashi and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Trans., 1991, vol. 32 (8), pp. 689–96.
A.D. Wilson, E.G. Hamburg, D.J. Colvin, S.W. Thompson, and Y. Krauss: Proc. Microalloying 88, World Materials Congress, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1988, pp. 259–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Debroy, T. Modeling macro-and microstructures of Gas-Metal-Arc Welded HSLA-100 steel. Metall Mater Trans B 30, 483–493 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-999-0082-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-999-0082-x